1. 從 Corrective RAG 到多模態檢索
在第三章,我們學習了 Corrective RAG(CRAG),通過文檔評分和託底機制來提升 RAG 系統的可靠性。CRAG 主要解決檢索結果的質量驗證問題,但在檢索環節本身,傳統 RAG 系統還存在一個根本性的問題:單一檢索方式的盲區。
本章將解決這個問題:如何通過混合檢索(Hybrid Search)結合多種檢索方式,提升檢索的召回率和精確度。
2. 為什麼需要混合檢索?
2.1 什麼是混合檢索?
混合檢索(Hybrid Search)是一種結合向量檢索、稀疏檢索、全文檢索三種模態,通過加權分數融合來提升檢索效果的技術。它通過讓不同檢索方式互補,克服單一檢索方式的盲區,從而提高召回率和精確度。
2.2 單一檢索方式的問題
我們先來看看單靠一種檢索方式會遇到什麼問題。
向量檢索的盲區:
向量檢索擅長理解語義和概念,但它會遺漏精確的關鍵詞。比如你搜索 “GAAP” 或 “Q3 2023” 這樣的專有名詞,向量檢索可能會返回一些概念相似但實際不相關的結果。還有一個問題是過度泛化——它可能返回概念上相似,但實際上答非所問的文檔。
關鍵詞檢索的盲區:
關鍵詞檢索擅長匹配精確的術語,但它不理解語義。比如你搜索 “machine learning”,它找不到包含 “AI” 的文檔;你搜索 “revenue”,它找不到包含 “earnings” 或 “income” 的內容。這就是語義盲區的問題。
問題的本質在於:向量檢索會遺漏關鍵詞,關鍵詞檢索會遺漏語義——每種方法都有自己的盲區。
2.3 混合檢索:融合三種模態
混合檢索的思路是:既然單一方法都有盲區,那就把它們組合起來。具體來説,混合檢索結合了三種互補的檢索方式:
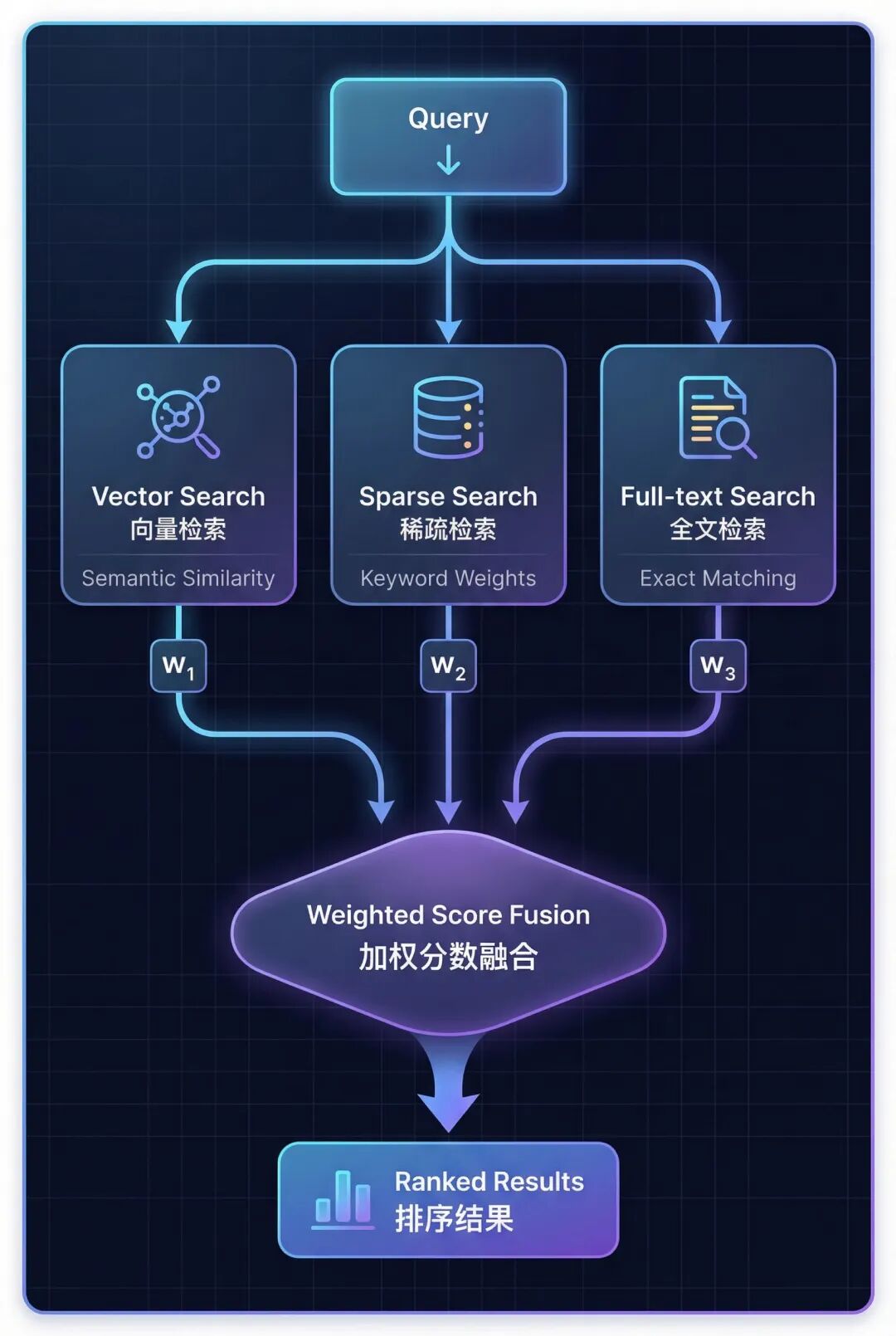
三種檢索方式各有側重:
- Vector Search(向量檢索) → 理解語義相似度
- Sparse Search (稀疏檢索) → 匹配關鍵詞和同義詞
- Full-text Search (全文檢索) → 精確短語匹配
2.4 Hybrid RAG vs Corrective RAG
混合檢索和糾錯機制解決的是不同階段的問題:
| 對比維度 | Hybrid RAG (本章) | Corrective RAG (第三章) |
|---|---|---|
| 核心目標 | Better Retrieval (更好的檢索) | Better Validation (更好的驗證) |
| 實現方式 | 結合 3 種檢索模態 | 文檔相關性評分 |
| 關鍵機制 | 加權分數融合 | 查詢重寫 + 託底機制 |
| 作用階段 | 檢索階段 | 檢索後驗證階段 |
| Agent 作用 | 選擇檢索策略 | 評估質量 + 觸發託底 |
這兩種技術可以完美配合:用混合檢索提升檢索質量,再用 Corrective RAG 進行質量驗證。
3. 三種檢索模態詳解
理解了混合檢索的必要性後,我們來深入瞭解構成混合檢索的三種核心模態。
3.1 向量檢索(Vector Search)
向量檢索通過將文本轉換為稠密向量(Dense Embeddings,通常 768-1536 維),然後使用餘弦相似度測量向量之間的角度,返回語義上最相似的文檔。
它的優勢在於理解概念和語義關係,能夠處理釋義和同義表達。但它無法精確匹配特定術語,比如 “GAAP” 或 “SKU-12345” 這樣的專有名詞。
適用場景:概念性查詢,比如 “What causes inflation?”
3.2 稀疏檢索(Sparse Search)
稀疏檢索使用 TF-IDF(詞頻-逆文檔頻率)提取關鍵詞,可以在詞彙表內擴展同義詞,基於關鍵詞權重進行匹配(不是精確字符串匹配)。
TF-IDF 的原理是:Term Frequency × Inverse Document Frequency——在整個文檔集中越罕見的詞獲得越高的權重。
稀疏檢索的優勢是能夠匹配相關術語,比如 revenue、earnings、income 這些同義詞,而且不需要嵌入模型。但它受詞彙表維度限制,難以處理稀有專有名詞。
典型應用場景:工具選擇(Tool Selection)
稀疏檢索在混合檢索中發揮關鍵詞匹配作用,特別在工具選擇、術語敏感查詢(如專有名詞、技術縮寫)中表現優異。
3.3 全文檢索(Full-text Search)
全文檢索通過構建帶分詞的倒排索引(Inverted Index),應用 BM25 評分算法(改進的 TF-IDF,加入了文檔長度歸一化),返回精確短語匹配的結果。
BM25 是 TF-IDF 的改進版本,它加入了文檔長度歸一化,避免長文檔獲得不公平的高分。
全文檢索的優勢是能夠精確匹配短語(如 “Item 1A Risk Factors”),處理稀有專有名詞,支持精確章節定位。但它無法處理拼寫錯誤或變體,也不理解語義關係。
適用場景:精確章節查找,比如 “查找第 10-K 報告的風險因素章節”
3.4 三種模態的選擇
沒有單一模態是最好的,關鍵是根據查詢模式組合使用:
| 檢索模態 | 最適合的查詢類型 | 示例查詢 | 核心優勢 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 向量檢索 | 概念性查詢,需要語義理解 | “What are Nike’s financial risks?” | 語義理解 |
| 稀疏檢索 | 同義詞感知的關鍵詞匹配 | “Nike earnings 2023” | 關鍵詞泛化 |
| 全文檢索 | 精確短語查詢,章節名稱 | “Item 1A Risk Factors” | 精確匹配 |
4. seekdb:AI 原生的搜索數據庫
4.1 seekdb 是什麼?
seekdb 是 OceanBase 推出的 AI 原生搜索數據庫,它將向量存儲、關係數據、全文搜索整合到一個統一的平台中。傳統方案需要使用專門的向量數據庫,會帶來額外的運維成本和系統複雜度,seekdb 通過統一的多模型引擎解決了這個問題。
4.2 seekdb 的核心優勢

4.3 為什麼選擇 seekdb 實現混合檢索?
- 單次查詢就能調用 3 種模態,無需調用外部服務
- 原生加權融合,內置 RRF 和線性組合算法
- 自動索引同步,向量、稀疏、BM25 索引自動維護
- MySQL 協議,兼容現有工具和驅動
- 可以無縫遷移到 OceanBase 集羣
5. 實戰:實現混合檢索
5.1 準備環境:
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv("../.env")
# Verify configuration
print("✅ Configuration loaded:")
print(f"📍 OceanBase: {os.getenv('OCEANBASE_HOST')}:{os.getenv('OCEANBASE_PORT')}")
print(f"📍 Database: {os.getenv('OCEANBASE_DB')}")
print(f"📍 Embedding Model: {os.getenv('SILICONFLOW_EMBEDDING_MODEL', 'BAAI/bge-m3')}")
加載 embedding 模型
from langchain_dev_utils.embeddings import register_embeddings_provider, load_embeddings
# Register SiliconFlow embeddings provider
SILICONFLOW_BASE_URL = os.getenv("SILICONFLOW_BASE_URL", "https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1")
register_embeddings_provider(
provider_name="siliconflow",
embeddings_model="openai-compatible",
base_url=SILICONFLOW_BASE_URL,
)
# Load embedding model
EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME = os.getenv("SILICONFLOW_EMBEDDING_MODEL", "BAAI/bge-m3")
embeddings = load_embeddings(f"siliconflow:{EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME}")
print(f"✅ Loaded embedding model: {EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME}")
配置 OceanBase 連接
# OceanBase connection parameters
connection_args = {
"host": os.getenv("OCEANBASE_HOST", "127.0.0.1"),
"port": int(os.getenv("OCEANBASE_PORT", "2881")),
"user": os.getenv("OCEANBASE_USER", "root@test"),
"password": os.getenv("OCEANBASE_PASSWORD", ""),
"db_name": os.getenv("OCEANBASE_DB", "test"),
}
print("✅ OceanBase connection configured")
5.2 加載文檔
首先加載源文檔演示混合搜索。
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
# Load Nike 10-K PDF
pdf_path = "./data/nke-10k-2023.pdf"
loader = PyPDFLoader(pdf_path)
documents = loader.load()
# Split into chunks
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000,
chunk_overlap=100,
separators=["
", "
", ". ", " ", ""],
)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
print(f"✅ Loaded {len(documents)} pages and split into {len(splits)} chunks")
# Select a subset for demonstration (first 200 chunks)
demo_docs = splits[:200]
print(f"📄 Using {len(demo_docs)} chunks for hybrid search demo")
5.3 初始化混合存儲
啓用三種搜索模式:
- 密集向量:通過嵌入實現語義相似性
- 稀疏向量:通過 TF-IDF 加權計算關鍵詞重要性
- 全文檢索:精確短語和關鍵詞匹配
from langchain_oceanbase.vectorstores import OceanbaseVectorStore
# Get embedding dimension
embedding_dim = len(embeddings.embed_query("test"))
# Create hybrid search vector store with ALL three modalities enabled
hybrid_store = OceanbaseVectorStore(
embedding_function=embeddings,
table_name="hybrid_search_demo",
connection_args=connection_args,
vidx_metric_type="l2",
include_sparse=True, # Enable sparse vector search (keyword matching)
include_fulltext=True, # Enable full-text search (exact phrase matching)
drop_old=True,
embedding_dim=embedding_dim,
)
print("✅ Hybrid search vector store initialized!")
print(f"📐 Vector dimension: {embedding_dim}")
print(f"🔍 Dense vector: Enabled (L2 distance)")
print(f"🔍 Sparse vector: Enabled (keyword matching)")
print(f"🔍 Full-text search: Enabled (phrase matching)")
5.4 生成稀疏向量
稀疏向量使用 TF-IDF(詞頻-逆文檔頻率)來表示關鍵詞的重要性。
詞頻(TF):一個詞在文檔中出現的頻率逆文檔頻率(IDF):一個詞在語料庫中出現的稀有度或重要性
基於詞彙:直接將詞映射到索引(無哈希衝突)
我們將構建一個自定義的 TF-IDF 編碼器,使其能夠在 OceanBase 的 50 萬維度限制內工作。
import re
import math
from collections import Counter
# Stopwords to filter out common words
STOPWORDS = {
'the', 'and', 'for', 'with', 'that', 'this', 'are', 'was', 'were', 'been',
'has', 'have', 'had', 'its', 'our', 'their', 'from', 'which', 'may', 'can',
'will', 'would', 'could', 'should', 'any', 'such', 'than', 'other', 'more',
'also', 'including', 'related', 'into', 'these', 'those', 'each', 'all',
'some', 'them', 'they', 'being', 'about', 'after', 'before', 'between',
'through', 'during', 'under', 'over', 'above', 'below', 'both', 'same',
'but', 'not', 'only', 'own', 'just', 'now', 'then', 'here', 'there', 'when',
'where', 'why', 'how', 'what', 'who', 'whom', 'his', 'her', 'him', 'she',
'you', 'your', 'yours', 'out', 'off', 'down', 'again', 'further', 'once',
}
classTFIDFEncoder:
"""Simple TF-IDF encoder with vocabulary-based indexing."""
def__init__(self, max_vocab_size=100000):
self.max_vocab_size = max_vocab_size
self.vocab = {} # term -> index
self.idf = {} # term -> idf score
self.doc_count = 0
deftokenize(self, text):
"""Tokenize and clean text."""
words = re.findall(r'\b[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9]*\b', text.lower())
return [w for w in words if w notin STOPWORDS andlen(w) >= 2]
deffit(self, documents):
"""Build vocabulary and compute IDF scores."""
self.doc_count = len(documents)
doc_freq = Counter() # term -> number of docs containing term
# Count document frequencies
for doc in documents:
terms = set(self.tokenize(doc))
for term in terms:
doc_freq[term] += 1
# Select top terms by document frequency (most common across docs)
top_terms = doc_freq.most_common(self.max_vocab_size)
# Build vocabulary and compute IDF
for idx, (term, df) inenumerate(top_terms):
self.vocab[term] = idx
# IDF = log(N / df) + 1 (smoothed)
self.idf[term] = math.log(self.doc_count / df) + 1
print(f" Vocabulary size: {len(self.vocab)}")
print(f" Sample high-IDF terms: {[(t, f'{self.idf[t]:.2f}') for t inlist(self.vocab.keys())[:: len(self.vocab)//5][:5]]}")
defencode(self, text):
"""Encode text to sparse TF-IDF vector."""
terms = self.tokenize(text)
term_freq = Counter(terms)
sparse_vec = {}
for term, tf in term_freq.items():
if term inself.vocab:
idx = self.vocab[term]
# TF-IDF = tf * idf (normalized by max tf)
max_tf = max(term_freq.values()) if term_freq else1
tfidf = (tf / max_tf) * self.idf[term]
sparse_vec[idx] = tfidf
return sparse_vec
# Initialize and fit TF-IDF encoder
print("⏳ Building TF-IDF vocabulary from document corpus...")
tfidf_encoder = TFIDFEncoder(max_vocab_size=100000)
tfidf_encoder.fit([doc.page_content for doc in demo_docs])
print(f"✅ TF-IDF encoder fitted on {len(demo_docs)} documents")
# Generate sparse vectors for all documents
sparse_embeddings = [tfidf_encoder.encode(doc.page_content) for doc in demo_docs]
print(f"✅ Generated {len(sparse_embeddings)} TF-IDF sparse vectors")
print(f"
📊 Sample sparse vector (doc 0):")
print(f" Non-zero terms: {len(sparse_embeddings[0])}")
print(f" Sample entries: {list(sparse_embeddings[0].items())[:5]}...")
5.5 準備全文內容
全文搜索需要獨立的索引內容。我們將通過元數據增強頁面內容
# Create enhanced full-text content
fulltext_content = []
for doc in demo_docs:
# Combine page content with searchable metadata
metadata_text = f"Page {doc.metadata.get('page', 'N/A')} "
metadata_text += f"Title: {doc.metadata.get('title', '')} "
# Full searchable text
full_text = f"{metadata_text}{doc.page_content}"
fulltext_content.append(full_text)
print(f"✅ Prepared {len(fulltext_content)} full-text entries")
print(f"
📝 Sample full-text content (doc 0):")
print(f" {fulltext_content[0][:200]}...")
5.6 添加包含三種模態的文檔
將文檔存儲到向量數據庫,並建立三種索引。
print("⏳ Adding documents with hybrid search capabilities...")
print()
# Step 1: Add documents with dense vectors + full-text content
ids = hybrid_store.add_documents_with_fulltext(
documents=demo_docs,
fulltext_content=fulltext_content,
)
# Step 2: Add sparse embeddings to the same documents
hybrid_store.add_sparse_documents(
documents=demo_docs,
sparse_embeddings=sparse_embeddings,
)
print(f"✅ Added {len(ids)} documents with:")
print(f" • Dense vector embeddings (1024-dim BGE-M3)")
print(f" • Sparse vector embeddings (keyword weights)")
print(f" • Full-text searchable content")
print()
print("="*80)
print("🎉 Hybrid search store populated!")
print("="*80)
print(f"📊 Total documents: {len(demo_docs)}")
print(f" Each document can be searched by:")
print(f" ✓ Semantic similarity (dense vector embeddings)")
print(f" ✓ Keyword matching (sparse vectors)")
print(f" ✓ Exact keywords and phrases (full-text index)")
5.7 測試各個模態
分別測試三種檢索方式,對比搜索結果。
每種模態返回不同的結果——向量檢索找到語義相關的內容,稀疏檢索找到關鍵詞匹配,全文檢索找到精確短語。
5.7.1 向量搜索
query = "What were Nike's total revenues and financial performance?"
# Pure vector search (semantic similarity only)
vector_results = hybrid_store.similarity_search(query, k=3)
print(f"🔍 Query: '{query}'")
print(f"
📊 Vector Search Results (Semantic Similarity Only):
")
for i, doc inenumerate(vector_results, 1):
print(f"Result {i}:")
print(f" Content: {doc.page_content[:150].replace(chr(10), ' ')}...")
print(f" Page: {doc.metadata.get('page', 'N/A')}")
print()
5.7.2 稀疏向量搜索(關鍵詞匹配)
# Generate TF-IDF sparse query vector for keyword matching
query_text = "Nike total revenues fiscal 2023"
sparse_query = tfidf_encoder.encode(query_text)
# Sparse vector search on the hybrid store
sparse_results = hybrid_store.similarity_search_with_sparse_vector(
sparse_query=sparse_query,
k=3
)
print(f"🔍 Query: '{query_text}'")
print(f"🔢 TF-IDF sparse query: {len(sparse_query)} non-zero terms")
print(f" Matched terms: {[t for t in tfidf_encoder.tokenize(query_text) if t in tfidf_encoder.vocab]}")
print(f"
📊 Sparse Vector Search Results (TF-IDF Keyword Matching):
")
for i, doc inenumerate(sparse_results, 1):
print(f"Result {i}:")
print(f" Content: {doc.page_content[:150].replace(chr(10), ' ')}...")
print(f" Page: {doc.metadata.get('page', 'N/A')}")
print()
print("="*70)
print("💡 Note: Sparse search may not find the exact revenue tables.")
print(" Compare with Vector Search (6.1) which found pages 31, 34.")
print(" This demonstrates why Hybrid Search (Step 7) is valuable!")
print("="*70)
5.7.3 全文檢索(精確匹配)
# Full-text search with exact phrase matching
fulltext_results = hybrid_store.similarity_search_with_fulltext(
query="revenue financial performance",
fulltext_query="revenues billion fiscal 2023", # Exact keywords
k=3
)
print(f"🔍 Vector query: 'revenue financial performance'")
print(f"🔍 Full-text query: 'revenues billion fiscal 2023'")
print(f"
📊 Full-Text Search Results (Exact Matching):
")
for i, doc inenumerate(fulltext_results, 1):
print(f"Result {i}:")
print(f" Content: {doc.page_content[:150].replace(chr(10), ' ')}...")
print(f" Page: {doc.metadata.get('page', 'N/A')}")
print()
6. 高級混合檢索
在前面的步驟中,我們已經啓用了三種檢索模態並分別測試了它們的效果。現在的問題是:如何將這三種檢索方式有效地組合起來?
這就是高級混合檢索要解決的核心問題:通過加權分數融合,自動組合多種檢索模態,獲得比單一模態更好的檢索效果。
6.1 內置分數融合機制
OceanBase 提供了 advanced_hybrid_search() 方法,可以自動組合三種模態的檢索結果。
工作原理:
- 並行執行三種檢索 - 同時運行向量檢索、稀疏檢索、全文檢索
- 分數歸一化 - 將每種模態的分數標準化到 0-1 範圍
- 加權融合 - 應用權重公式:
final_score = w₁×vector + w₂×sparse + w₃×fulltext - 排序返回 - 按融合後的分數排序,返回 Top-K 結果
所有的分數歸一化和融合邏輯都在 seekdb 內部自動完成,開發者只需要關注權重配置即可。搜索模式預設
6.1.1 搜索模式預設
不同類型的查詢需要不同的權重配置。我們可以定義幾種常用的搜索模式:
Balanced(平衡模式)
適合通用查詢,比如 “Nike business in 2023”。權重配置:Vector 40%、Sparse 30%、Fulltext 30%。
Semantic(語義模式)
適合概念理解,比如 “What is Nike‘s strategy?”。權重配置:Vector 70%、Sparse 20%、Fulltext 10%。
Keyword(關鍵詞模式)
適合特定術語、數字查詢,比如 “Nike earnings2023”。權重配置:Vector 20%、Sparse 60%、Fulltext 20%。
Exact(精確模式)
適合法律文本、章節查找,比如 “Item 1A Risk Factors”。權重配置:Vector 10%、Sparse 20%、Fulltext 70%。
| 預設 | V/S/F | 使用場景 | 示例查詢 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Balanced | 40/30/30 | 未知或混合類型查詢 | “Nike business in 2023” |
| Semantic | 70/20/10 | 研究、探索性問題 | “What is Nike’s strategy?” |
| Keyword | 20/60/20 | 特定術語、數字查詢 | “Nike earnings 2023” |
| Exact | 10/20/70 | 法律文本、章節查找 | “Item 1A Risk Factors” |
6.2 權重調優建議
- 從平衡模式開始 - 在不確定時使用 40/30/30 作為基準
- 根據業務場景調整 - 分析實際查詢日誌,找出主要查詢類型
- A/B 測試驗證 - 對比不同權重配置的檢索效果
- 允許動態調整 - 不同查詢可以使用不同的權重配置
6.3 融合算法選擇
除了線性加權組合,seekdb 還支持其他融合算法:
- 線性組合(Linear Combination) - 加權平均,適合大多數場景
- RRF(Reciprocal Rank Fusion) - 基於排名融合,對分數尺度不敏感
- 最大值融合 - 取各模態的最高分,適合“或”邏輯
推薦做法:先使用線性組合,如果效果不理想再嘗試 RRF。
💡_ 擴展知識:本節提到的 RRF 和最大值融合是常見的融合算法,seekdb 支持多種融合策略。具體 API 請參考官方文檔。_
7. Agentic Hybrid RAG:讓 Agent 選擇最優策略
7.1 為什麼結合 Agentic + Hybrid Search?
將智能決策和多模態檢索結合,可以獲得兩者的最佳效果。
僅混合檢索的特點:多模態(V+S+F)、更好的召回,但權重固定、總是執行檢索。
Agentic + 混合檢索的特點:動態搜索模式、多步推理、在不需要時跳過檢索、多次搜索結果綜合。
核心價值在於:Agentic RAG + Hybrid Search = 智能決策 + 多模態檢索。
7.2 定義帶動態搜索模式的工具
創建一個讓 Agent 選擇最佳搜索策略的工具。
from langchain.tools import tool
from typing importLiteral
@tool
defhybrid_search_knowledge_base(
query: str,
top_k: int = 3,
search_mode: Literal[
“balanced”, # 40/30/30
“semantic”, # 70/20/10
“keyword”, # 20/60/20
“exact” # 10/20/70
] = “balanced”
) -> str:
“”“Search Nike‘s 10-K with hybrid search.
Args:
query: What to search for
search_mode: Strategy based on query type
”“”
# 權重預設
weight_presets = {
“balanced”: {“vector”: 0.4, “sparse”: 0.3, “fulltext”: 0.3},
“semantic”: {“vector”: 0.7, “sparse”: 0.2, “fulltext”: 0.1},
“keyword”: {“vector”: 0.2, “sparse”: 0.6, “fulltext”: 0.2},
“exact”: {“vector”: 0.1, “sparse”: 0.2, “fulltext”: 0.7},
}
weights = weight_presets[search_mode]
# 生成稀疏向量
sparse_vec = tfidf_encoder.encode(query)
# 執行混合檢索
results = hybrid_store.advanced_hybrid_search(
vector_query=query,
sparse_query=sparse_vec,
fulltext_query=query,
modality_weights=weights,
k=top_k
)
return results
可用的搜索模式:
- balanced(通用場景 40/30/30)
- semantic(概念和語義 70/20/10)
- keyword(關鍵詞查詢 20/60/20)
- exact(精確短語 10/20/70)
Agent 會分析查詢並自動選擇最佳模式。
7.3 使用 LangChain 創建 Agent
構建一個能夠動態使用混合檢索的智能 Agent。
from langchain.agents import create_agent
agent = create_agent(
model=chat_model,
tools=[hybrid_search_knowledge_base],
system_prompt=“”“You are a helpful AI with access to Nike‘s 10-K report.
Choose search_mode based on query type:
- ”semantic“: concepts, strategy, high-level understanding
- ”keyword“: specific terms, numbers, technical abbreviations
- ”exact“: legal text, section names, precise phrases
- ”balanced“: unknown or mixed query types
For complex questions, search multiple times with different modes.”“”
)
# 調用 Agent
result = agent.invoke({
“messages”: [{“role”: “user”, “content”: “Nike 的財務風險是什麼?”}]
})
Agent 能力:在搜索前分析查詢類型、選擇最優搜索模式、對複雜問題進行多步搜索、將結果綜合為連貫的答案。系統提示詞指導 Agent 何時使用每種搜索模式。
進階提示:讓 Agent 輸出自定義權重(如 0.5/0.3/0.2),而不是預設名稱,以獲得更精細的控制。
7.4 Agent 實戰示例
觀察 Agent 如何動態選擇搜索策略。
財務數據查詢:
用户:“Nike revenue fiscal 2023?” → Agent 分析 → search_mode=“keyword”,理由:使用關鍵詞模式查找特定數字。
戰略問題:
用户:“What is Nike‘s innovation approach?” → Agent 分析 → search_mode=“semantic”,理由:使用語義模式理解概念。
章節查找:
用户:“Find Item 1A Risk Factors” → Agent 分析 → search_mode=“exact”,理由:使用精確模式進行精準匹配。
關鍵優勢:Agent 根據查詢分析智能選擇搜索策略——無需手動調優。
8. 核心要點總結
8.1 三種模態
- Vector(向量檢索)→ 語義理解
- Sparse(稀疏檢索)→ 關鍵詞 + 同義詞擴展
- Fulltext(全文檢索)→ 精確短語
8.2 加權融合
- 四種預設模式:balanced / semantic / keyword / exact
- 支持自定義權重組合模態
- 根據你的領域調優權重
8.3 Agentic 方法
- 讓 Agent 選擇搜索策略
- 每個查詢的動態模式選擇
- 複雜問答的多步搜索
8.4 seekdb by OceanBase
- 原生混合檢索支持
- 單次查詢 → 3 種模態
- 輕鬆遷移到 OceanBase 集羣
8.5 實踐建議
- 從平衡模式開始:在不確定查詢類型時使用 40/30/30 權重
- 讓 Agent 做決策:通過系統提示詞指導 Agent 選擇搜索模式
- 迭代調優:根據實際查詢日誌調整權重預設
- 組合使用技術:混合檢索 + Corrective RAG = 更強大的系統
9. 下一步行動
在本章中,我們深入理解了混合檢索(Hybrid Search)的多模態融合機制,學習瞭如何結合向量檢索、稀疏檢索和全文檢索三種模態,並使用 seekdb 構建了完整的 Agentic Hybrid RAG 系統。
歡迎關注公眾號“老紀的技術嘮嗑局”持續關注本系列課程! 讓我們一起探索 Agentic RAG 和混合檢索的更多可能性!🎯
歡迎大家結合我們的 B 站視頻學習【🦜🌊 Agentic RAG 實戰 4️⃣ 基於 seekdb 的混合檢索】:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV139qQBZEok/?share_source=copy_web&vd_source=5092954e66e001740c42dd47abc833d5

