在數據交換與系統集成中,JSON 與 Excel 是兩種極為常見的數據格式。JSON 適用於系統間傳輸,結構靈活;而 Excel 更適合可視化展示與手動編輯。本文將介紹如何使用 Python 實現 將 JSON 轉換為格式化的 Excel 文件、從 Excel 生成 JSON 文件,並 處理嵌套 JSON 的扁平化問題,幫助你在多數據源場景下高效完成數據轉換。
- 將 JSON 導入為格式化 Excel
- 將 Excel 導出為結構化 JSON
- 處理嵌套 JSON:扁平化技巧與示例
本文使用的方法需要用到 Free Spire.XLS for Python,可通過pip安裝:pip install spire.xls.free。
將 JSON 導入為格式化 Excel
將結構化 JSON 文件導入為 Excel 表格時,可以通過 Spire.XLS 自動寫入列頭與數據,同時設置單元格樣式,使內容更清晰易讀。
操作説明:
- 讀取 JSON 文件,提取鍵名作為表頭;
- 寫入數據並設置表頭樣式(加粗、背景色);
- 自動調整列寬,提升可讀性;
- 保存為
.xlsx文件。
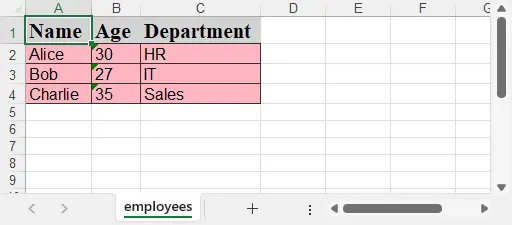
示例 JSON:employees.json
[
{"Name": "Alice", "Age": 30, "Department": "HR"},
{"Name": "Bob", "Age": 27, "Department": "IT"},
{"Name": "Charlie", "Age": 35, "Department": "Sales"}
]代碼示例:
from spire.xls import Workbook, FileFormat, Color
import json
# 加載 JSON 數據
with open("employees.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.load(f)
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.Worksheets.Clear()
sheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("employees")
# 寫入表頭並設置樣式
headers = list(data[0].keys())
for col, header in enumerate(headers):
cell = sheet.Range[1, col + 1]
cell.Text = header
cell.Style.Font.FontName = "Times New Roman"
cell.Style.Font.IsBold = True
cell.Style.Font.Size = 16.0
cell.Style.Color = Color.get_LightGray()
# 寫入數據並設置樣式
for row_idx, row in enumerate(data, start=2):
for col_idx, key in enumerate(headers):
sheet.Range[row_idx, col_idx + 1].Text = str(row.get(key, ""))
dataRange = sheet.Range[2, 1, sheet.LastRow, sheet.LastColumn]
dataRange.Style.Color = Color.get_LightPink()
dataRange.Style.Font.FontName = "Arial"
dataRange.Style.Font.Size = 12.0
dataRange.BorderInside()
dataRange.BorderAround()
# 自動調整列寬
for i in range(1, len(headers) + 1):
sheet.AutoFitColumn(i)
# 保存 Excel 文件
workbook.SaveToFile("output/employees.xlsx", FileFormat.Version2016)
workbook.Dispose()生成的 Excel 文件截圖:
將 Excel 導出為結構化 JSON
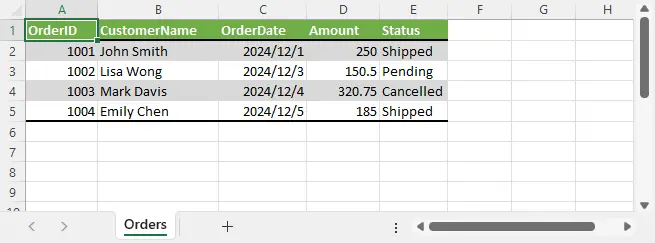
將 Excel 表格導出為 JSON 時,可以自動讀取第一行作為鍵名,並逐行構造字典列表,最終保存為 .json 文件。
操作説明:
- 獲取最後一行和最後一列;
- 讀取第一行作為 headers;
- 逐行讀取數據並轉換為字典結構;
- 使用
json.dump輸出到文件。
代碼示例:
import json
# 獲取最大行列
rows = sheet.LastRow
cols = sheet.LastColumn
# 提取表頭
headers = [sheet.Range[1, i + 1].Text for i in range(cols)]
data = []
# 構造 JSON 數據
for r in range(2, rows + 1):
row_data = {}
for c in range(cols):
row_data[headers[c]] = sheet.Range[r, c + 1].Text
data.append(row_data)
# 輸出 JSON 文件
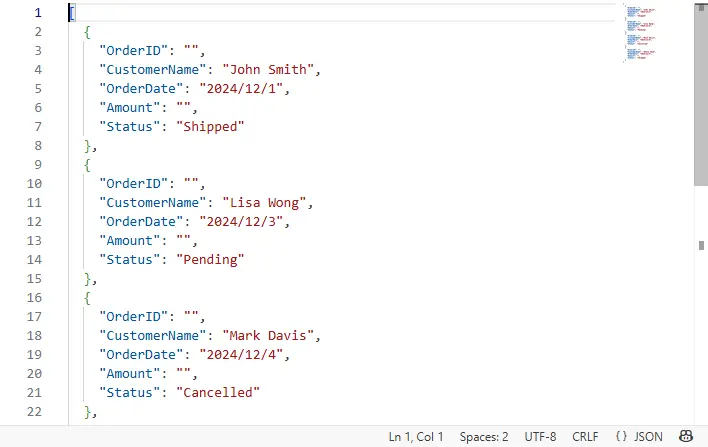
with open("output/products_out.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(data, f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)Excel文件數據:
生成的 JSON 文件片段:
處理嵌套 JSON:扁平化轉換
在實際開發中,JSON 數據經常包含嵌套對象。若直接導入 Excel,結構會混亂或不完整。可使用扁平化(flatten)技術,將嵌套結構展平為扁平鍵名形式(如 address.city)。
示例嵌套 JSON:
[
{
"name": "John",
"email": "john@example.com",
"address": {
"city": "New York",
"zip": "10001"
}
}
]Python 扁平化函數示例:
def flatten_json(obj, prefix=""):
flat = {}
for key, value in obj.items():
full_key = f"{prefix}{key}" if prefix == "" else f"{prefix}.{key}"
if isinstance(value, dict):
flat.update(flatten_json(value, full_key))
else:
flat[full_key] = value
return flat
# 使用扁平化函數
with open("nested.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
nested_data = json.load(f)
flat_data = [flatten_json(item) for item in nested_data]扁平化後的結構:
[
{
"name": "John",
"email": "john@example.com",
"address.city": "New York",
"address.zip": "10001"
}
]總結
藉助 Spire.XLS for Python,我們可以在 Python 項目中輕鬆實現 JSON 與 Excel 之間的相互轉換,滿足數據展示、系統交互等多種場景需求。對於結構複雜的 JSON 數據,也可通過自定義方法進行處理,從而實現高效的數據導入導出。
更多Excel處理教程請參考:Spire.XLS for Python 教程中心