一、Mako是什麼
Mako是一個新的Web打包工具,適用於Web應用、庫和框架。它被設計得快速、可靠且易於使用。Mako已被數百個生產項目中使用。如果你正在尋找一個現代的Web打包工具,Mako是正確的選擇。
二、特點
- 零配置
從一個JS/TS文件開始,Mako將處理其餘部分。開箱即支持TypeScript、Less、CSS、CSS Modules、React、圖像、字體、WASM、Node Polyfill等。不需要配置加載器、插件或其他任何東西。 - 生產級
Mako是可靠的。它被數百個項目使用,如Web應用、混合應用、小程序(部分)、低代碼、Serverless、庫開發、Ant Design等。還在數千箇舊項目和數千個npm包以及不同版本中測試了Mako,以確保兼容性。 - 快如閃電
Mako被設計得快如閃電。在核心打包邏輯中使用Rust,並在Node.js中使用piscina來並行編譯文件。在基準測試中,Mako比其他 Rust打包工具和Webpack更快。 - 熱模塊替換
當文件更改時,Mako將自動更新瀏覽器中的代碼。無需手動刷新頁面。Mako已集成React快速刷新,當你更改React組件時,它只會更新組件,而不是整個頁面。 - 代碼拆分
Mako內置代碼拆分支持。你可以使用動態導入將代碼拆分為單獨的包,從而減小初始包大小並加快加載時間。Mako具有可配置的選項,你可以用來自定義代碼拆分行為。 - Module Concatenation
Module Concatenation是一種優化功能,旨在減少包大小和運行時開銷。Mako實現了與Webpack優化文檔中的實現相當的Module Concatenation。
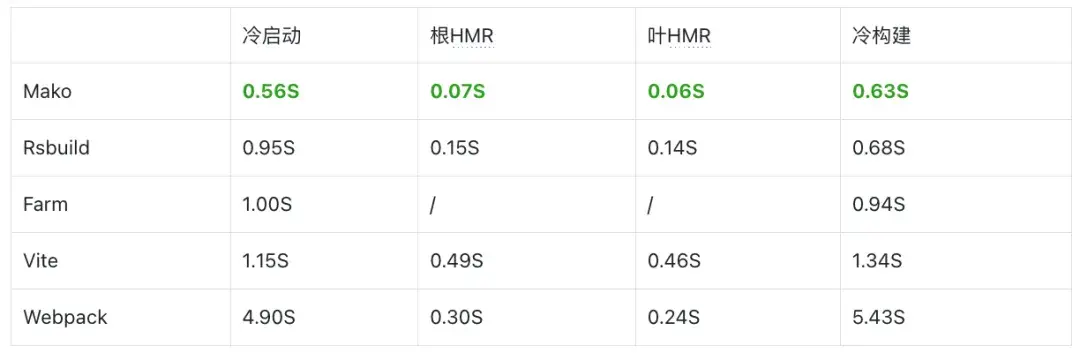
三、性能測試
通過冷啓動、根HMR、葉HMR、冷構建等多個基準測試可以看到,Mako相較於其他構建工具,有着更好的性能。
benchmark基準測試 https://github.com/umijs/benchmark
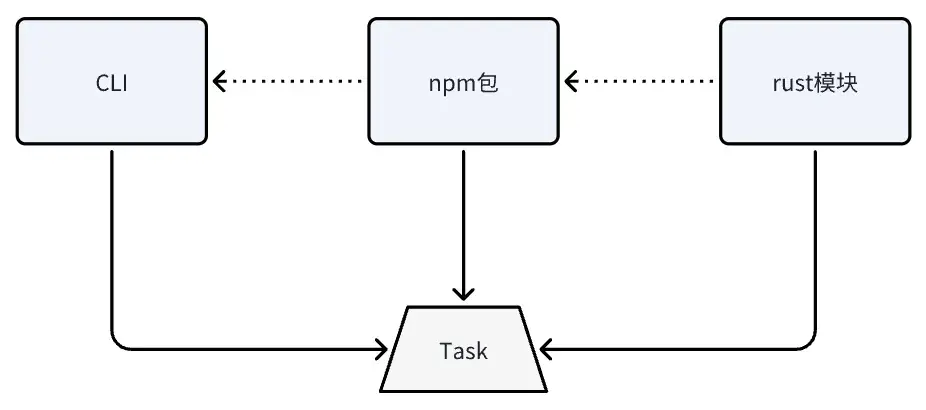
四、項目架構
entry
現階段,可以有三種途徑來使用Mako構建,分別是:
- 通過引用Mako的Rust crate來發起,其核心模塊均已導出(不過好像未發佈到crates.io);
- 通過引用 Mako的npm包來在nodejs中發起;
- 通過Mako的cli來發起。
其中,這三種又都是遞進關係
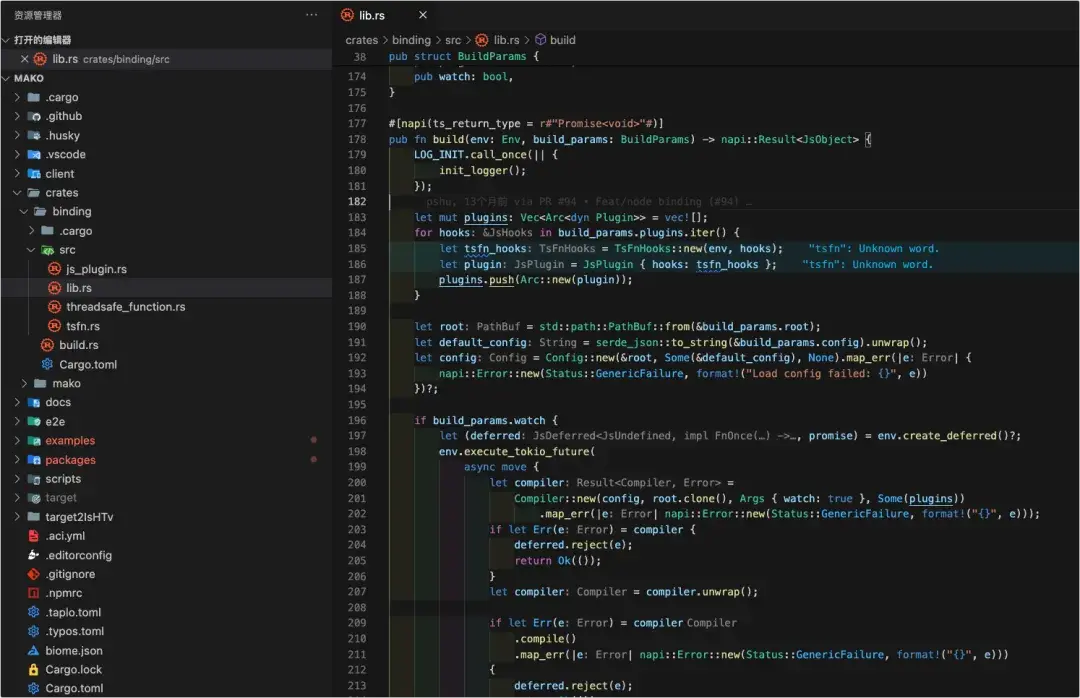
- Rust實現Mako編譯的核心邏輯並進行導出。
Mako crate中核心模塊導出
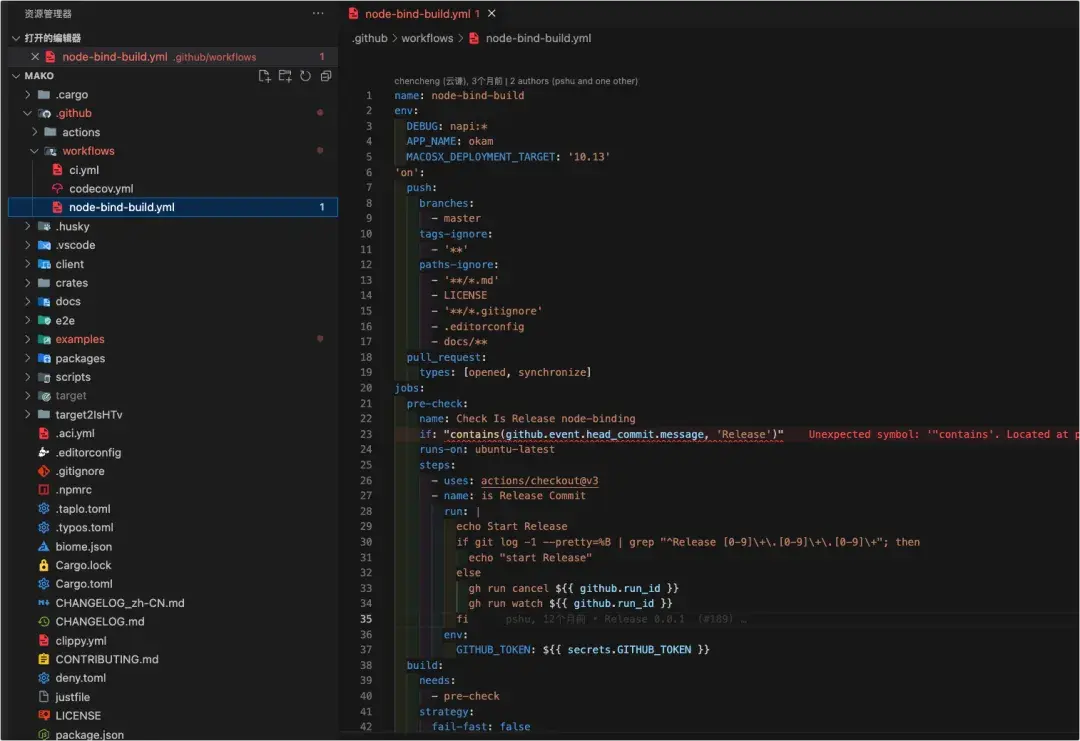
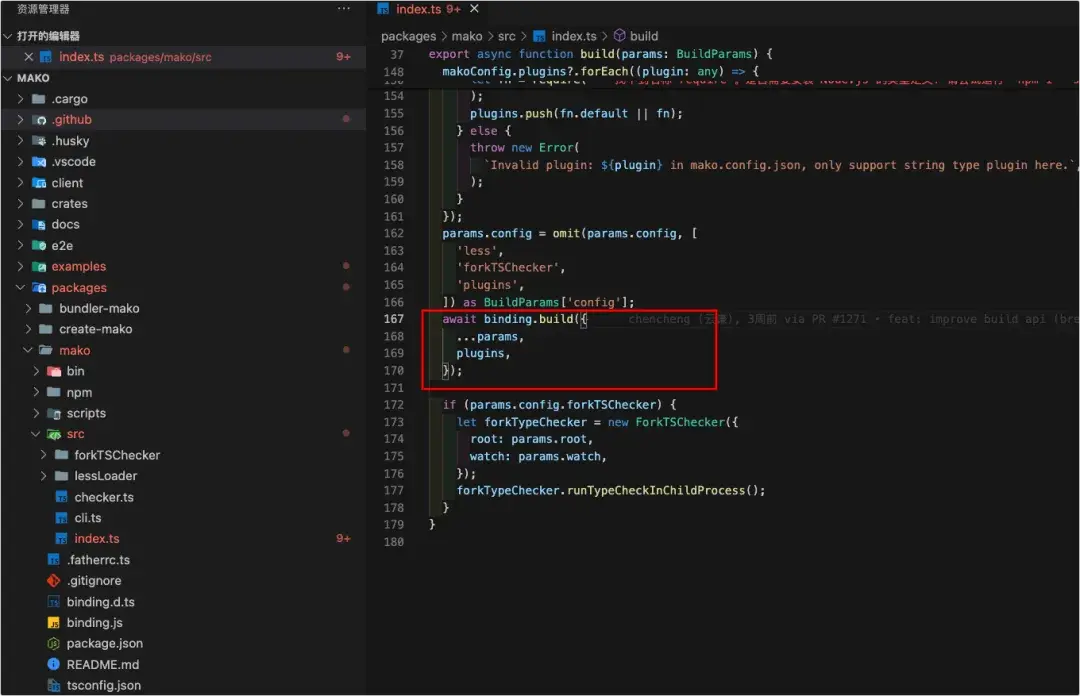
- 通過napi將Mako核心邏輯的Rust代碼,經過膠水層,在github workflows中進行交叉編譯,編譯出多平台的native模塊,然後在npm模塊中進行引用,再次進行一層封裝供用户使用。
使用napi進行編譯的膠水層代碼
此代碼經過編譯後,可在nodejs中進行引用,有關napi的具體細節請參考https://napi.rs/cn
交叉編譯任務的workflows
js層引用編譯好的native模塊,封裝後暴露給外部使用
經過js層的參數融合後,最終使用native模塊進行構建
- 在前兩步已經將功能、暴露均完成的情況,封裝一層cli,根據命令,執行構建。
Mako cli中,匹配到build命令,執行封裝好的build函數
Compiler
在經過cli端、js端、Rust端的配置融合之後,會得到最終的配置。
基於這些配置,Mako會生成一個Compiler,來執行整個編譯流程。
Compiler中存在各種插件來執行任務,插件都擁有如下的生命週期,會在編譯過程的各個階段進行調用。
pub trait Plugin: Any + Send + Sync {
fn name(&self) -> &str;
fn modify_config(&self, _config: &mut Config, _root: &Path, _args: &Args) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn load(&self, _param: &PluginLoadParam, _context: &Arc<Context>) -> Result<Option<Content>> {
Ok(None)
}
fn next_build(&self, _next_build_param: &NextBuildParam) -> bool {
true
}
fn parse(
&self,
_param: &PluginParseParam,
_context: &Arc<Context>,
) -> Result<Option<ModuleAst>> {
Ok(None)
}
fn transform_js(
&self,
_param: &PluginTransformJsParam,
_ast: &mut Module,
_context: &Arc<Context>,
) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn after_generate_transform_js(
&self,
_param: &PluginTransformJsParam,
_ast: &mut Module,
_context: &Arc<Context>,
) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn before_resolve(&self, _deps: &mut Vec<Dependency>, _context: &Arc<Context>) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn after_build(&self, _context: &Arc<Context>, _compiler: &Compiler) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn generate(&self, _context: &Arc<Context>) -> Result<Option<()>> {
Ok(None)
}
fn after_generate_chunk_files(
&self,
_chunk_files: &[ChunkFile],
_context: &Arc<Context>,
) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn build_success(&self, _stats: &StatsJsonMap, _context: &Arc<Context>) -> Result<Option<()>> {
Ok(None)
}
fn build_start(&self, _context: &Arc<Context>) -> Result<Option<()>> {
Ok(None)
}
fn generate_beg(&self, _context: &Arc<Context>) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn generate_end(
&self,
_params: &PluginGenerateEndParams,
_context: &Arc<Context>,
) -> Result<Option<()>> {
Ok(None)
}
fn runtime_plugins(&self, _context: &Arc<Context>) -> Result<Vec<String>> {
Ok(Vec::new())
}
fn optimize_module_graph(
&self,
_module_graph: &mut ModuleGraph,
_context: &Arc<Context>,
) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn before_optimize_chunk(&self, _context: &Arc<Context>) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn optimize_chunk(
&self,
_chunk_graph: &mut ChunkGraph,
_module_graph: &mut ModuleGraph,
_context: &Arc<Context>,
) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
fn before_write_fs(&self, _path: &Path, _content: &[u8]) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
}所有的插件又分為如下幾類:
- 內置的分為兩類的插件11種;
- 外部js編寫的插件(Less的編譯就是使用這種);
- 其他條件型插件。
使用各種插件
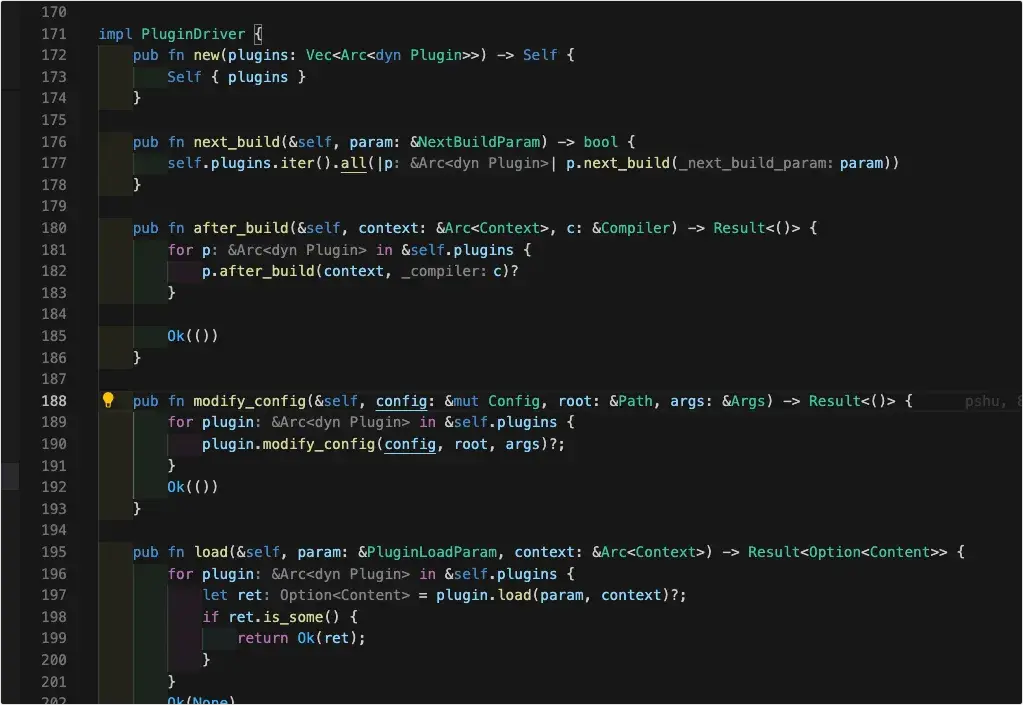
在確定好本次編譯要使用的插件後,會生成一個PluginDriver,來進行整體生命週期的調度,並執行modify_config生命週期,確定最終的config。
根據plugins創建PluginDriver調度所有插件的生命週期
PluginDriver的內部邏輯,即將執行所有插件對應的生命週期一一執行
下一步就是執行整個編譯流程:
build
編譯流程的實現,代碼簡化如下:
impl Compiler {
pub fn build(&self, files: Vec<File>) -> Result<HashSet<ModuleId>> {
let (rs, rr) = channel::<Result<Module>>();
let build_with_pool = |file: File, parent_resource: Option<ResolverResource>| {
let rs = rs.clone();
let context = self.context.clone();
thread_pool::spawn(move || {
let result = Self::build_module(&file, parent_resource, context.clone());
let result = Self::handle_build_result(result, &file, context);
rs.send(result).unwrap();
});
};
let mut count = 0;
for file in files {
count += 1;
build_with_pool(file, None);
}
let mut errors = vec![];
let mut module_ids = HashSet::new();
for build_result in rr {
count -= 1;
// handle build_module error
if build_result.is_err() {
errors.push(build_result.err().unwrap());
if count == 0 {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
let module = build_result.unwrap();
let module_id = module.id.clone();
// xxx
}
drop(rs);
if !errors.is_empty() {
return Err(anyhow::anyhow!(BuildError::BuildTasksError { errors }));
}
Ok(module_ids)
}
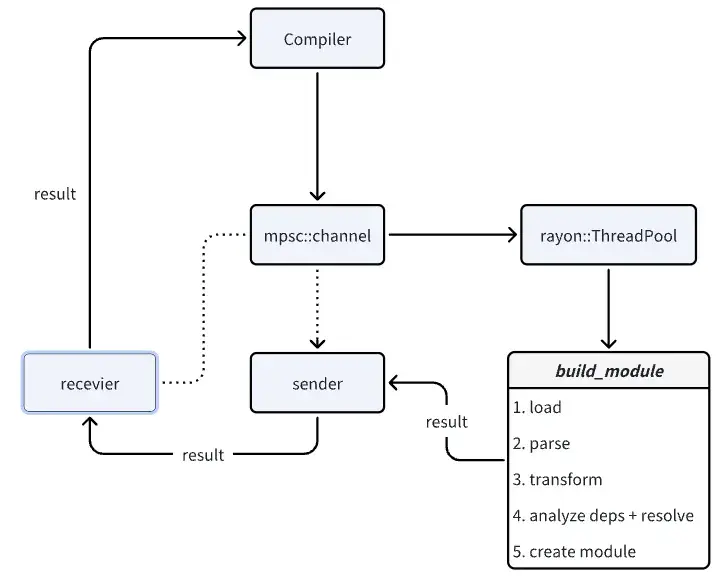
}Compiler會創建管道,然後使用rayon的線程池進行構建任務的執行,執行完成後將結果通過管道送回,再執行後續操作。
build_module實現如下:
pub fn build_module(
file: &File,
parent_resource: Option<ResolverResource>,
context: Arc<Context>,
) -> Result<Module> {
// 1. load
let mut file = file.clone();
let content = load::Load::load(&file, context.clone())?;
file.set_content(content);
// 2. parse
let mut ast = parse::Parse::parse(&file, context.clone())?;
// 3. transform
transform::Transform::transform(&mut ast, &file, context.clone())?;
// 4. analyze deps + resolve
let deps = analyze_deps::AnalyzeDeps::analyze_deps(&ast, &file, context.clone())?;
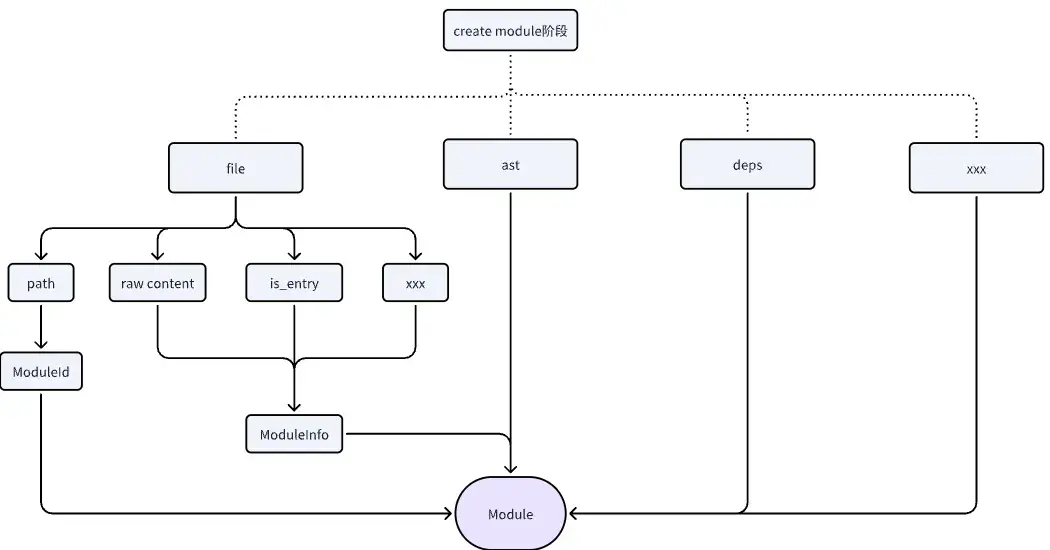
// 5. create module
let path = file.path.to_string_lossy().to_string();
let module_id = ModuleId::new(path.clone());
let raw = file.get_content_raw();
let is_entry = file.is_entry;
let source_map_chain = file.get_source_map_chain(context.clone());
let top_level_await = match &ast {
ModuleAst::Script(ast) => ast.contains_top_level_await,
_ => false,
};
let is_async_module = file.extname == "wasm";
let is_async = is_async_module || top_level_await;
// raw_hash is only used in watch mode
// so we don't need to calculate when watch is off
let raw_hash = if context.args.watch {
file.get_raw_hash()
.wrapping_add(hash_hashmap(&deps.missing_deps))
} else {
0
};
let info = ModuleInfo {
file,
deps,
ast,
resolved_resource: parent_resource,
source_map_chain,
top_level_await,
is_async,
raw_hash,
raw,
..Default::default()
};
let module = Module::new(module_id, is_entry, Some(info));
Ok(module)
}build_module執行階段解析:
Load
根據路徑加載文件,目前內置如下類型(支持通過插件的Load生命週期配置自定義文件)
- virtual:inline_css:runtime
- ?raw
- js
- css
- md & mdx
- svg
- toml
- wasm
- xml
- yaml
- json
- assets
impl Load {
pub fn load(file: &File, context: Arc<Context>) -> Result<Content> {
crate::mako_profile_function!(file.path.to_string_lossy());
debug!("load: {:?}", file);
// plugin first
let content: Option<Content> = context
.plugin_driver
.load(&PluginLoadParam { file }, &context)?;
if let Some(content) = content {
return Ok(content);
}
// virtual:inline_css:runtime
if file.path.to_str().unwrap() == "virtual:inline_css:runtime" {
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: r#"
export function moduleToDom(css) {
var styleElement = document.createElement("style");
styleElement.type = "text/css";
styleElement.appendChild(document.createTextNode(css))
document.head.appendChild(styleElement);
}
"#
.to_string(),
..Default::default()
}));
}
// file exists check must after virtual modules handling
if !file.pathname.exists() || !file.pathname.is_file() {
return Err(anyhow!(LoadError::FileNotFound {
path: file.path.to_string_lossy().to_string(),
}));
}
// unsupported
if UNSUPPORTED_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
return Err(anyhow!(LoadError::UnsupportedExtName {
ext_name: file.extname.clone(),
path: file.path.to_string_lossy().to_string(),
}));
}
// ?raw
if file.has_param("raw") {
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
let content = serde_json::to_string(&content)?;
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: format!("module.exports = {}", content),
..Default::default()
}));
}
// js
if JS_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
// entry with ?hmr
let is_jsx = file.extname.as_str() == "jsx" || file.extname.as_str() == "tsx";
if file.is_entry && file.has_param("hmr") {
let content = format!(
"{}\nmodule.exports = require(\"{}\");\n",
include_str!("../runtime/runtime_hmr_entry.js"),
file.pathname.to_string_lossy(),
);
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent { content, is_jsx }));
}
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent { content, is_jsx }));
}
// css
if CSS_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
return Ok(Content::Css(content));
}
// md & mdx
if MD_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
let options = MdxOptions {
development: matches!(context.config.mode, Mode::Development),
..Default::default()
};
let content = match compile(&content, &options) {
Ok(js_string) => js_string,
Err(reason) => {
return Err(anyhow!(LoadError::CompileMdError {
path: file.path.to_string_lossy().to_string(),
reason,
}));
}
};
let is_jsx = file.extname.as_str() == "mdx";
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent { content, is_jsx }));
}
// svg
// TODO: Not all svg files need to be converted to React Component, unnecessary performance consumption here
if SVG_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
let svgr_transformed = svgr_rs::transform(
content,
svgr_rs::Config {
named_export: SVGR_NAMED_EXPORT.to_string(),
export_type: Some(svgr_rs::ExportType::Named),
..Default::default()
},
svgr_rs::State {
..Default::default()
},
)
.map_err(|err| LoadError::ToSvgrError {
path: file.path.to_string_lossy().to_string(),
reason: err.to_string(),
})?;
let asset_path = Self::handle_asset(file, true, true, context.clone())?;
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: format!("{}\nexport default {};", svgr_transformed, asset_path),
is_jsx: true,
}));
}
// toml
if TOML_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
let content = from_toml_str::<TomlValue>(&content)?;
let content = serde_json::to_string(&content)?;
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: format!("module.exports = {}", content),
..Default::default()
}));
}
// wasm
if WASM_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
let final_file_name = format!(
"{}.{}.{}",
file.get_file_stem(),
file.get_content_hash()?,
file.extname
);
context.emit_assets(
file.pathname.to_string_lossy().to_string(),
final_file_name.clone(),
);
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: format!(
"module.exports = require._interopreRequireWasm(exports, \"{}\")",
final_file_name
),
..Default::default()
}));
}
// xml
if XML_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
let content = from_xml_str::<serde_json::Value>(&content)?;
let content = serde_json::to_string(&content)?;
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: format!("module.exports = {}", content),
..Default::default()
}));
}
// yaml
if YAML_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
let content = from_yaml_str::<YamlValue>(&content)?;
let content = serde_json::to_string(&content)?;
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: format!("module.exports = {}", content),
..Default::default()
}));
}
// json
if JSON_EXTENSIONS.contains(&file.extname.as_str()) {
let content = FileSystem::read_file(&file.pathname)?;
return Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: format!("module.exports = {}", content),
..Default::default()
}));
}
// assets
let asset_path = Self::handle_asset(file, true, true, context.clone())?;
Ok(Content::Js(JsContent {
content: format!("module.exports = {};", asset_path),
..Default::default()
}))
}
}Parse
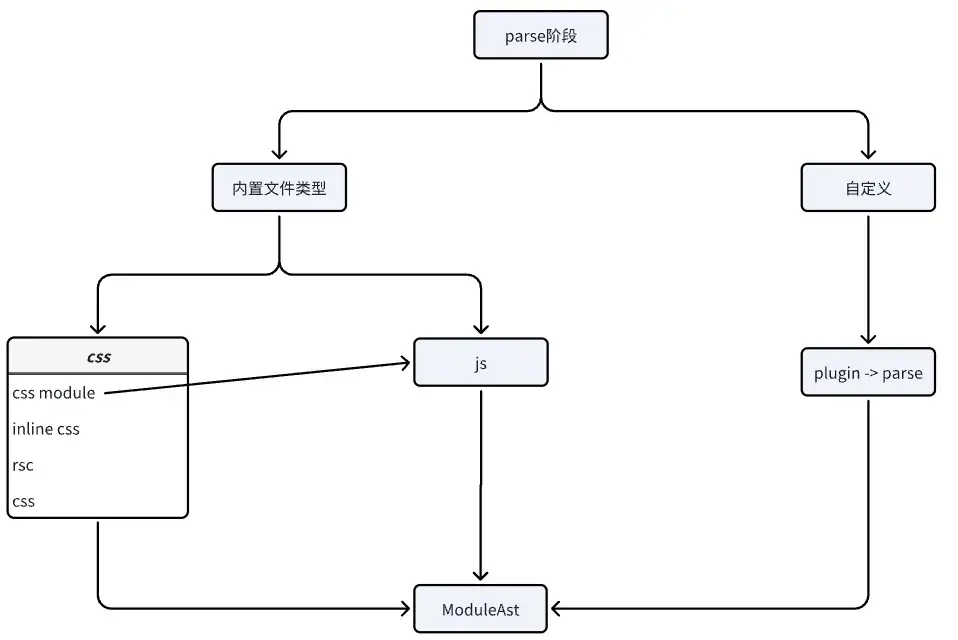
將源文件解析為ModuleAst類型,現階段內置了Script和Css兩種swc ast的封裝,在這個階段會執行plugins中的parse生命週期,可以在這個生命週期中進行自定義語法的ast解析。
比如想支持鴻蒙的ets,編寫插件的話就需要在這個階段進行ast解析
impl Parse {
pub fn parse(file: &File, context: Arc<Context>) -> Result<ModuleAst> {
// plugin first
let ast = context
.plugin_driver
.parse(&PluginParseParam { file }, &context)?;
if let Some(ast) = ast {
return Ok(ast);
}
// js
if let Some(Content::Js(_)) = &file.content {
debug!("parse js: {:?}", file.path);
let ast = JsAst::new(file, context.clone())?;
if let Some(ast) = Rsc::parse_js(file, &ast, context.clone())? {
return Ok(ast);
}
return Ok(ModuleAst::Script(ast));
}
// css
if let Some(Content::Css(_)) = &file.content {
// xxx
}
}
}transform
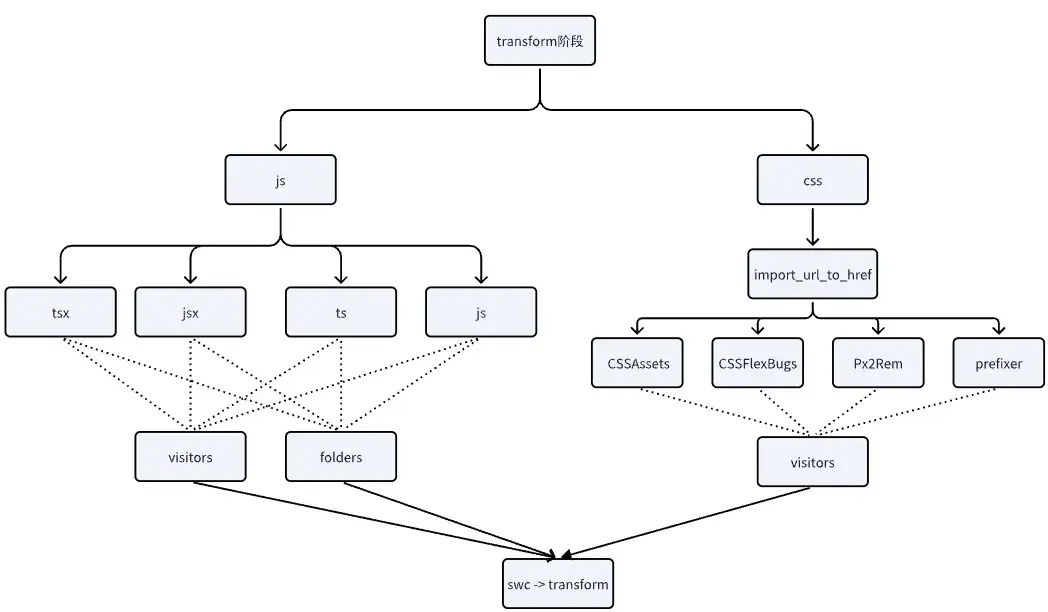
使用swc,通過各種visitor進行ast的轉換操作,生成最終的ast。
impl Transform {
pub fn transform(ast: &mut ModuleAst, file: &File, context: Arc<Context>) -> Result<()> {
crate::mako_profile_function!();
match ast {
ModuleAst::Script(ast) => {
GLOBALS.set(&context.meta.script.globals, || {
let unresolved_mark = ast.unresolved_mark;
let top_level_mark = ast.top_level_mark;
let cm: Arc<swc_core::common::SourceMap> = context.meta.script.cm.clone();
let origin_comments = context.meta.script.origin_comments.read().unwrap();
let is_ts = file.extname == "ts";
let is_tsx = file.extname == "tsx";
let is_jsx = file.is_content_jsx()
|| file.extname == "jsx"
|| file.extname == "js"
|| file.extname == "ts"
|| file.extname == "tsx";
// visitors
let mut visitors: Vec<Box<dyn VisitMut>> = vec![
Box::new(resolver(unresolved_mark, top_level_mark, is_ts || is_tsx)),
Box::new(FixHelperInjectPosition::new()),
Box::new(FixSymbolConflict::new(top_level_mark)),
Box::new(NewUrlAssets {
context: context.clone(),
path: file.path.clone(),
unresolved_mark,
}),
Box::new(WorkerModule::new(unresolved_mark)),
];
if is_tsx {
visitors.push(Box::new(tsx_strip(
cm.clone(),
context.clone(),
top_level_mark,
)))
}
if is_ts {
visitors.push(Box::new(ts_strip(top_level_mark)))
}
// named default export
if context.args.watch && !file.is_under_node_modules && is_jsx {
visitors.push(Box::new(DefaultExportNamer::new()));
}
// react & react-refresh
let is_dev = matches!(context.config.mode, Mode::Development);
let is_browser =
matches!(context.config.platform, crate::config::Platform::Browser);
let use_refresh = is_dev
&& context.args.watch
&& context.config.hmr.is_some()
&& !file.is_under_node_modules
&& is_browser;
if is_jsx {
visitors.push(react(
cm,
context.clone(),
use_refresh,
&top_level_mark,
&unresolved_mark,
));
}
{
let mut define = context.config.define.clone();
let mode = context.config.mode.to_string();
define
.entry("NODE_ENV".to_string())
.or_insert_with(|| format!("\"{}\"", mode).into());
let env_map = build_env_map(define, &context)?;
visitors.push(Box::new(EnvReplacer::new(
Lrc::new(env_map),
unresolved_mark,
)));
}
visitors.push(Box::new(TryResolve {
path: file.path.to_string_lossy().to_string(),
context: context.clone(),
unresolved_mark,
}));
visitors.push(Box::new(Provide::new(
context.config.providers.clone(),
unresolved_mark,
top_level_mark,
)));
visitors.push(Box::new(VirtualCSSModules {
auto_css_modules: context.config.auto_css_modules,
}));
visitors.push(Box::new(ContextModuleVisitor { unresolved_mark }));
if context.config.dynamic_import_to_require {
visitors.push(Box::new(DynamicImportToRequire { unresolved_mark }));
}
if matches!(context.config.platform, crate::config::Platform::Node) {
visitors.push(Box::new(features::node::MockFilenameAndDirname {
unresolved_mark,
current_path: file.path.clone(),
context: context.clone(),
}));
}
// folders
let mut folders: Vec<Box<dyn Fold>> = vec![];
folders.push(Box::new(decorators(decorators::Config {
legacy: true,
emit_metadata: false,
..Default::default()
})));
let comments = origin_comments.get_swc_comments().clone();
let assumptions = context.assumptions_for(file);
folders.push(Box::new(swc_preset_env::preset_env(
unresolved_mark,
Some(comments),
swc_preset_env::Config {
mode: Some(swc_preset_env::Mode::Entry),
targets: Some(swc_preset_env_targets_from_map(
context.config.targets.clone(),
)),
..Default::default()
},
assumptions,
&mut FeatureFlag::default(),
)));
folders.push(Box::new(reserved_words::reserved_words()));
folders.push(Box::new(paren_remover(Default::default())));
folders.push(Box::new(simplifier(
unresolved_mark,
SimpilifyConfig {
dce: dce::Config {
top_level: false,
..Default::default()
},
..Default::default()
},
)));
ast.transform(&mut visitors, &mut folders, file, true, context.clone())?;
Ok(())
})
}
ModuleAst::Css(ast) => {
// replace @import url() to @import before CSSUrlReplacer
import_url_to_href(&mut ast.ast);
let mut visitors: Vec<Box<dyn swc_css_visit::VisitMut>> = vec![];
visitors.push(Box::new(Compiler::new(compiler::Config {
process: swc_css_compat::feature::Features::NESTING,
})));
let path = file.path.to_string_lossy().to_string();
visitors.push(Box::new(CSSAssets {
path,
context: context.clone(),
}));
// same ability as postcss-flexbugs-fixes
if context.config.flex_bugs {
visitors.push(Box::new(CSSFlexbugs {}));
}
if context.config.px2rem.is_some() {
let context = context.clone();
visitors.push(Box::new(Px2Rem::new(
context.config.px2rem.as_ref().unwrap().clone(),
)));
}
// prefixer
visitors.push(Box::new(prefixer::prefixer(prefixer::options::Options {
env: Some(targets::swc_preset_env_targets_from_map(
context.config.targets.clone(),
)),
})));
ast.transform(&mut visitors)?;
// css modules
let is_modules = file.has_param("modules");
if is_modules {
CssAst::compile_css_modules(file.pathname.to_str().unwrap(), &mut ast.ast);
}
Ok(())
}
ModuleAst::None => Ok(()),
}
}
}analyze deps+resolve
ast解析完成後,進行依賴的分析。
依賴分析階段
有個很有意思的事情是我看到代碼中有使用oxc_resolver,一開始有點好奇,以為是什麼黑科技,因為oxc和swc是同類型的工具,一般不會出現在同一個項目中。
經過查找之後發現,是之前的resolver有點問題,作為替換才使用的oxc的resolver模塊。
也就是解析還是使用的swc,oxc只用到了resolver。
具體可參考https://github.com/umijs/mako/pull/919。
create module
ast處理完成、依賴分析完成後,將所有元數據進行合併,為一個Module,執行後續操作。
create Module階段
至此,核心編譯流程已經完成。
生成
編譯完成後,來到了整個構建流程的最後一步:生成,整體架構如下:
生成階段
五、尾聲
最開始以為Mako會像Rspack一樣,走的是Webpack的路子,看完後覺得Mako的設計思路是rollup一樣的,通過各種的plugin來完成一個構建工具的功能。
正如其官網所説:
Mako 不是為了與 Webpack 的社區加載器和插件兼容而設計的。如果你的項目嚴重依賴於 Webpack 的社區加載器和插件,你不應該使用 Mako,Rspack 是更好的選擇。
一家之言,還請各位指正。
*文/ asarua
本文屬得物技術原創,更多精彩文章請看:得物技術
未經得物技術許可嚴禁轉載,否則依法追究法律責任!