一、簡介
25/4/29 發佈的<u> Qwen3 </u>系列模型,共 8 個模型,其中六個<u> Dense 模型</u>分別為,Qwen3-32B、Qwen3-14B、Qwen3-8B、Qwen3-4B、Qwen3-1.7B 和 Qwen3-0.6B。另外兩個<u> MoE 模型</u>分別為,Qwen3-235B-A22B,擁有 2350 多億總參數和 220 多億激活參數的大模型,以及 Qwen3-30B-A3B,擁有約 300 億總參數和 30 億激活參數的小型 MoE 模型。
1.1 Qwen3-2507
在社區的反饋以及進一步研究的啓發下,僅指令(Instruct-only)和僅思考(Thinking-only)模型迴歸啦!成果就是通義千問 3-2507(Qwen3-2507),three sizes, 235B-A22B, 30B-A3B, and 4B。
Qwen3-Instruct-2507 具備以下特點:
- 泛化能力顯著提升,涵蓋 指令遵循、邏輯推理、文本理解、數學、科學、編碼以及工具使用。
- 長尾知識覆蓋在多種語言上大幅增強。
- 在主觀和開放式任務中與用户偏好的契合度明顯提高,能夠生成更有用的回覆和更高質量的文本。
- 在 25.6 萬長上下文理解方面能力增強,可擴展至 100 萬。
Qwen3-Thinking-2507 具備以下特點:
- 推理任務性能顯著提升,涵蓋邏輯推理、數學、科學、編碼以及通常需要人類專業知識的學術基準測試——在開源 thinking 模型中取得了領先的成果。
- 泛化能力顯著增強,如指令遵循、工具使用、文本生成以及與人類偏好的一致性。
- 256K 長上下文理解能力得到強化,可擴展至 1M。
1.2 Qwen3-2504( Qwen3)
- 全尺寸稠密與混合專家模型:0.6B, 1.7B, 4B, 8B, 14B, 32B and 30B-A3B, 235B-A22B
- 支持在思考模式(用於複雜邏輯推理、數學和編碼)和 非思考模式 (用於高效通用對話)之間無縫切換,確保在各種場景下的最佳性能。
- 顯著增強的推理能力,在數學、代碼生成和常識邏輯推理方面超越了之前的 QwQ(在思考模式下)和 Qwen2.5 指令模型(在非思考模式下)。
- 卓越的人類偏好對齊,在創意寫作、角色扮演、多輪對話和指令跟隨方面表現出色,提供更自然、更吸引人和更具沉浸感的對話體驗。
- 擅長智能體能力,可以在思考和非思考模式下精確集成外部工具,在複雜的基於代理的任務中在開源模型中表現領先。
- 支持 100 多種語言和方言,具有強大的多語言理解、推理、指令跟隨和生成能力。
二、Qwen 模型結構解析
本節以 qwen3\_moe 代碼為例,解析一下結構。
代碼路徑:https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/qwen3_moe/modeling_qwen3_moe.py
配置文件:https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/qwen3_moe/configuration_qwen3_moe.py
2.1 總體網絡結構
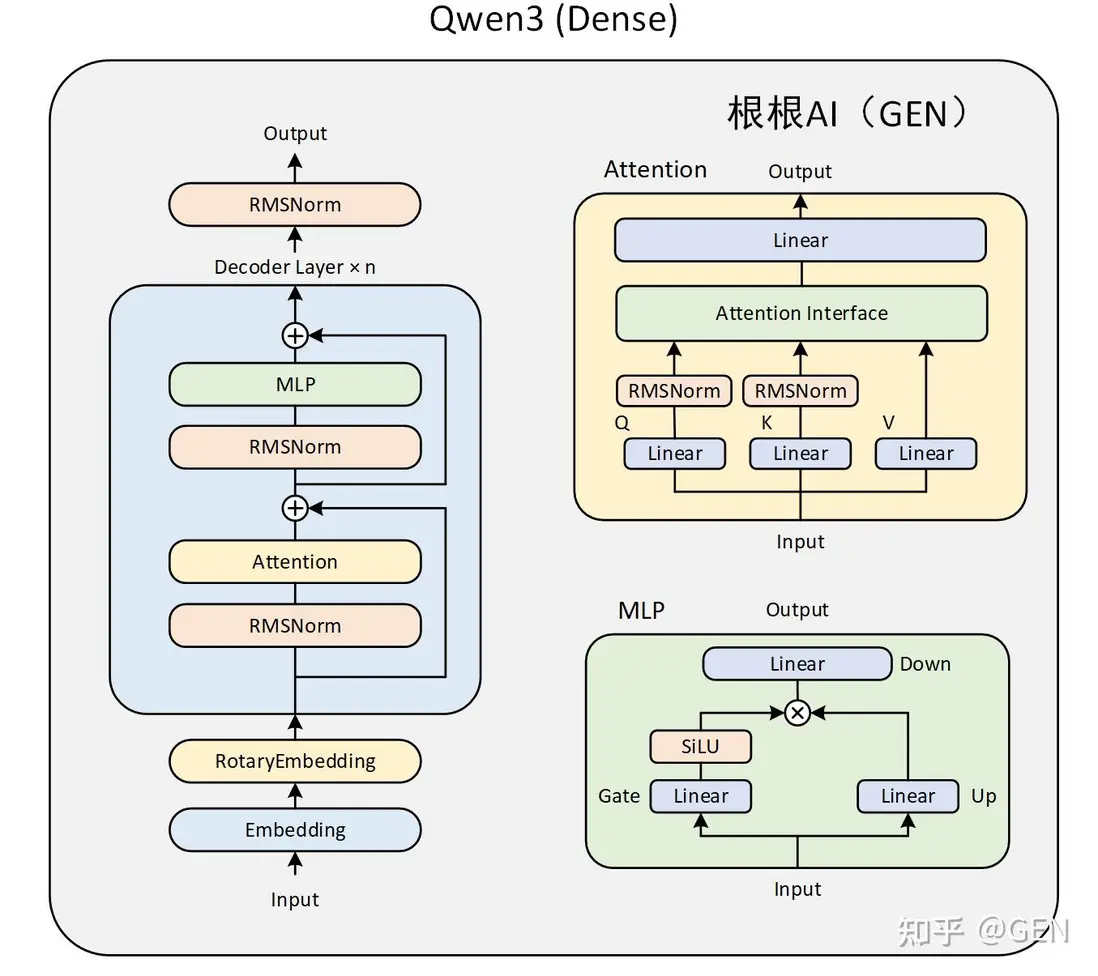
Qwen3 主要由四個部分組成:
- embed\_tokens:嵌入層。這是模型處理輸入的第一步。它的核心功能是將輸入的離散文本符號(通常是經過 Tokenizer 處理後的 Token ID)轉換為連續的、稠密的向量表示(稱為嵌入向量或 Embeddings)。
- Decoder layers:多個堆疊的解碼器。這是模型的核心計算引擎,負責理解輸入序列的上下文、提取特徵並進行深度信息處理。模型的能力(如理解、推理、生成)主要源於這些層。
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
[Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer(config, layer_idx) for layer_idx in range(config.num_hidden_layers)]
)- norm:歸一化層。處理完畢後,對最終的隱藏狀態 (Hidden States) 進行最後一次歸一化。
self.norm = Qwen3MoeRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)- rotary\_emb:旋轉位置編碼。為模型提供關於序列中 Token 位置的信息。標準 Transformer 的自注意力機制本身是排列不變的(即打亂輸入順序可能得到相同結果),因此需要顯式地注入位置信息。
self.rotary_emb = Qwen3MoeRotaryEmbedding(config=config)總體網絡結構需要結合 Qwen3MoeModel 類來看,Qwen3MoeModel 是基於混合專家(MoE)架構的語言模型,繼承自 Qwen3MoePreTrainedModel。具體代碼註解如下:
class Qwen3MoeModel(Qwen3MoePreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3MoeConfig):
super().__init__(config)
self.padding_idx = config.pad_token_id
#如 Transformer 解碼器層)的特徵向量維度,即每個 token 經過隱藏層處理後輸出的向量長度
self.vocab_size = config.vocab_size #151936,
#hidden_size:2048
self.embed_tokens = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, self.padding_idx)
#num_hidden_layers:24
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
[Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer(config, layer_idx) for layer_idx in range(config.num_hidden_layers)]
)
self.norm = Qwen3MoeRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.rotary_emb = Qwen3MoeRotaryEmbedding(config=config)
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
@check_model_inputs
@auto_docstring
def forward(
self,
#可選的整數張量,通常是輸入文本經過分詞後的索引序列(如單詞 / 子詞的 ID),是模型最常見的輸入形式。
input_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
#可選的張量,用於標記輸入序列中哪些位置是有效內容(1)、哪些是填充(0),避免模型關注無效信息。
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
#可選的整數張量,標記每個 token 在序列中的位置,輔助模型理解語序(部分模型會自動生成)。
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
#可選的緩存對象,用於存儲之前計算的鍵(key)和值(value),
#在生成式任務(如文本續寫)中加速推理,避免重複計算曆史序列
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
#可選的浮點張量,直接輸入預計算的嵌入向量(替代input_ids,適用於已處理過的特徵輸入)。
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
#指定是否採用緩存
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
#可選的整數張量,標記緩存中需要更新的位置,配合past_key_values使用。
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[TransformersKwargs],
) -> MoeModelOutputWithPast:
if (input_ids is None) ^ (inputs_embeds is not None):#異或計算,二者不可同時存在
raise ValueError("You must specify exactly one of input_ids or inputs_embeds")
#使用KV cache,DynamicCache支持靈活的序列長度變化,自動擴展容量
if use_cache and past_key_values is None:
past_key_values = DynamicCache(config=self.config)
#當inputs_embeds為None時(即用户未直接提供輸入嵌入),
#通過self.embed_tokens將input_ids(文本的整數編碼)轉換為對應的嵌入向量(inputs_embeds)。
#self.embed_tokens通常是一個nn.Embedding層,負責將離散的 token 索引映射為連續的向量表示,
#是語言模型中將文本轉換為模型可處理的數值形式的核心步驟。
if inputs_embeds is None:
inputs_embeds = self.embed_tokens(input_ids)
#確定當前輸入的每個 token 在緩存中的位置,以便後續在生成文本或處理長序列時,
#能正確關聯歷史緩存和當前輸入,實現高效的上下文關聯和緩存管理(比如 Transformer 中的 K/V 緩存)。
if cache_position is None:
past_seen_tokens = past_key_values.get_seq_length() if past_key_values is not None else 0
cache_position = torch.arange(
past_seen_tokens, past_seen_tokens + inputs_embeds.shape[1], device=inputs_embeds.device
)
if position_ids is None:
position_ids = cache_position.unsqueeze(0)
#選擇不同的掩碼函數
mask_function = create_causal_mask if self.config.sliding_window is None else create_sliding_window_causal_mask
causal_mask = mask_function(
config=self.config,
input_embeds=inputs_embeds,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
cache_position=cache_position,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
position_ids=position_ids,
)
hidden_states = inputs_embeds
# create position embeddings to be shared across the decoder layers
position_embeddings = self.rotary_emb(hidden_states, position_ids)
for decoder_layer in self.layers[: self.config.num_hidden_layers]:
hidden_states = decoder_layer(
hidden_states,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
attention_mask=causal_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
use_cache=use_cache,
cache_position=cache_position,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = self.norm(hidden_states)
return MoeModelOutputWithPast( # only diff with Mistral is the output type, we need MoE
last_hidden_state=hidden_states,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
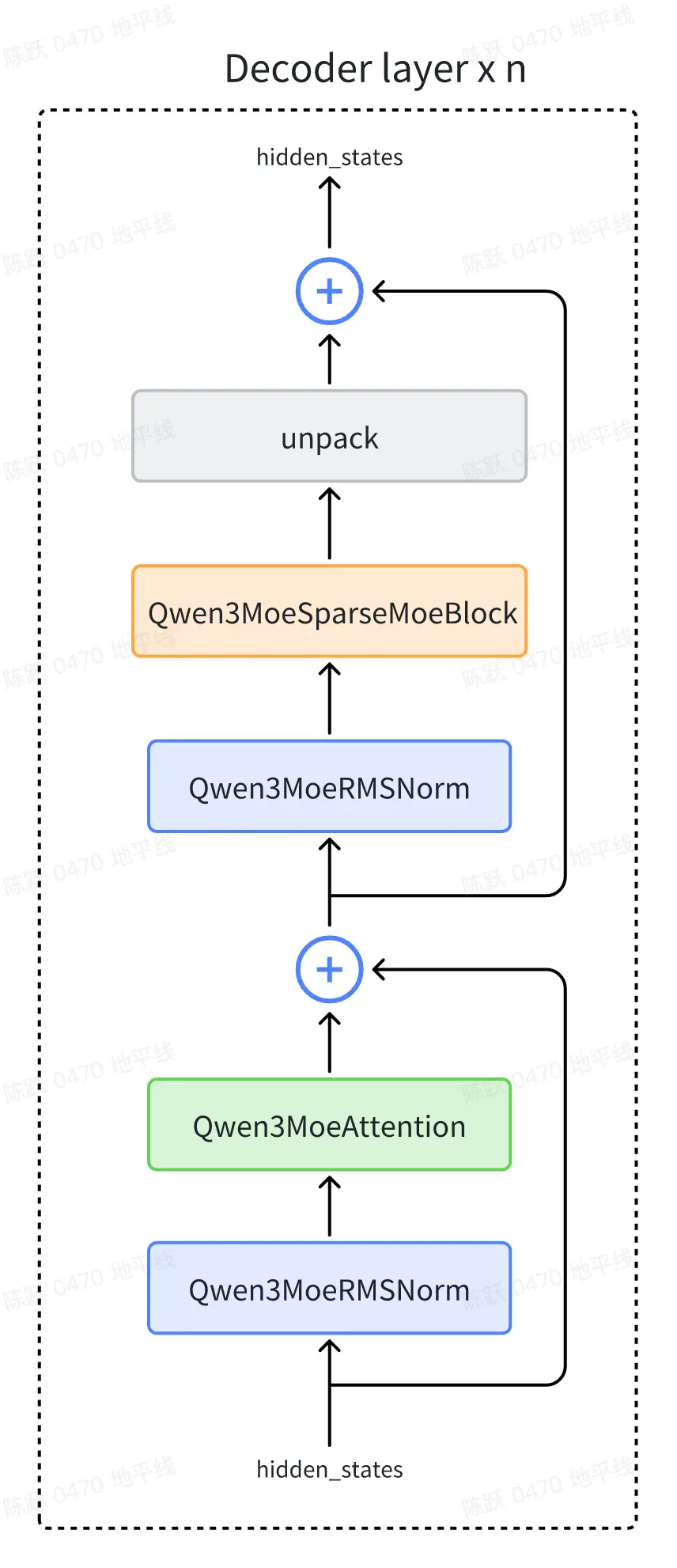
)2.2 Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer 解析
Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer 的結構圖如下所示:
下面逐個對上圖中的 block 進行解釋。
2.2.1 Qwen3MoeRMSNorm
- 功能:實現 RMS 歸一化,通過對輸入特徵的均方根進行縮放,穩定數值分佈,類似 LayerNorm 但計算更輕量(不含均值中心化)。
- 初始化:定義可學習的縮放權重
weight(維度與hidden_size一致)和數值穩定參數eps(避免除零)。 - 前向傳播:
- 裝飾器:
@use_kernel_forward_from_hub("RMSNorm")表示從 hub 加載優化的 RMSNorm 內核實現(可能是高效的 C++/CUDA 算子),提升計算速度。
@use_kernel_forward_from_hub("RMSNorm")
class Qwen3MoeRMSNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, eps=1e-6):
"""
Qwen3MoeRMSNorm is equivalent to T5LayerNorm
"""
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(hidden_size))
self.variance_epsilon = eps
def forward(self, hidden_states):
input_dtype = hidden_states.dtype
hidden_states = hidden_states.to(torch.float32)
variance = hidden_states.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
hidden_states = hidden_states * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.variance_epsilon)
return self.weight * hidden_states.to(input_dtype)
def extra_repr(self):
return f"{tuple(self.weight.shape)}, eps={self.variance_epsilon}"2.2.2 Qwen3MoeAttention
Qwen3 的注意力機制在 Qwen2 的基礎上進行了微調,在 Q、K 的線性投影后面分別加入了一個歸一化層,有助於提高穩定性。
2.2.3 Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock
我們從 Qwen3 的<u> Transformer </u>的實現來學習下優化方式。
將傳統 Transformer 模型中的全連接 MLP 層替換為新型的稀疏專家模塊(Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock)。該模塊由以下兩個關鍵組件構成:
- 包含 num\_experts 個輕量級專家網絡(Qwen3MoeMLP)的並行計算單元;
- 基於注意力機制的<u>路由網絡</u>(gate)。在計算過程中,路由網絡通過動態決策機制為每個輸入 Token 生成路由決策,篩選出匹配度最高的 top\_k 個專家節點。隨後,系統將根據路由權重對選定專家的計算結果進行加權融合,最終生成該隱層的表徵輸出。
那麼同樣我們對比<u> DeepSeekMOE</u>,Qwen3MOE 有兩個點的改變:1)沒有 shared expert。2.優化了 MLP 架構,變為 Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock。
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1902461213255925825
代碼解析:
class Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock(nn.Module):
"""
Qwen3混合專家模型中的稀疏MoE模塊,通過路由器選擇部分專家處理輸入,實現高效計算
"""
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3MoeConfig):
super().__init__()
# 1. 基礎配置參數
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size # 輸入特徵維度
self.num_experts = config.num_experts # 專家網絡總數:128
self.num_experts_per_tok = config.num_experts_per_tok # 每個token激活的專家數:8
# 2. 路由器(Router):決定每個token選擇哪些專家
# 輸入:[batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size],輸出:[batch_size, seq_len, num_experts](專家權重)
self.gate = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_experts, bias=False)
# 3. 初始化專家網絡(每個專家為獨立的MLP)
# 專家網絡通常採用與稠密MLP相同的結構(如兩次線性變換+激活函數)
self.experts = nn.ModuleList([
Qwen3MoeMLP(config) # 複用Qwen3的MLP結構作為專家
for _ in range(self.num_experts)
])
# 4. 損失函數相關(可選,用於訓練時平衡專家負載)
self.router_aux_loss_coef = config.router_aux_loss_coef # 路由器輔助損失係數
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
"""
前向傳播:輸入特徵 → 路由器選專家 → 專家計算 → 融合輸出
Args:
hidden_states: 輸入特徵,形狀為 [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size]
Returns:
output: 融合後的輸出特徵,形狀同輸入
router_aux_loss: 路由器輔助損失(用於訓練時優化專家負載均衡)
"""
# ===== 步驟1:計算路由器輸出(專家權重)=====
# 輸入通過線性層得到每個專家的原始分數(logits)
# 形狀:[batch_size, seq_len, num_experts]
router_logits = self.gate(hidden_states)
# ===== 步驟2:選擇Top-K專家並計算權重 =====
# 對每個token,選擇分數最高的num_experts_per_tok個專家
# top_k_weights: 選中專家的權重(經softmax歸一化),形狀 [batch_size, seq_len, num_experts_per_tok]
# top_k_indices: 選中專家的索引,形狀 [batch_size, seq_len, num_experts_per_tok]
top_k_weights, top_k_indices = torch.topk(router_logits, self.num_experts_per_tok, dim=-1)
top_k_weights = nn.functional.softmax(top_k_weights, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float32)
# ===== 步驟3:計算路由器輔助損失(可選,訓練用)=====
# 目的是鼓勵專家負載均衡,避免少數專家被頻繁選中
# 計算方式:對router_logits做softmax後取均值,再求負熵(簡化實現)
if self.training:
# 先對專家分數做softmax,得到每個專家被選中的概率
router_probs = nn.functional.softmax(router_logits, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float32)
# 計算每個專家的平均負載(跨batch和seq_len)
expert_load = torch.mean(router_probs, dim=(0, 1)) # 形狀 [num_experts]
# 輔助損失:鼓勵負載均衡(熵越大,分佈越均衡)
router_aux_loss = torch.sum(expert_load * torch.log(expert_load + 1e-10)) # 負熵
router_aux_loss *= self.router_aux_loss_coef # 乘以係數
else:
router_aux_loss = torch.tensor(0.0, device=hidden_states.device) # 推理時無損失
# ===== 步驟4:準備輸入,分發到選中的專家 =====
# 調整輸入形狀為 [batch_size * seq_len, hidden_size],便於批量處理
batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size = hidden_states.shape
hidden_states = hidden_states.view(-1, hidden_size) # 形狀 [total_tokens, hidden_size],total_tokens = batch_size * seq_len
# 調整選中專家索引形狀:[total_tokens, num_experts_per_tok]
top_k_indices = top_k_indices.view(-1, self.num_experts_per_tok) # [total_tokens, k]
# 調整權重形狀:[total_tokens, num_experts_per_tok, 1](便於廣播)
top_k_weights = top_k_weights.view(-1, self.num_experts_per_tok, 1) # [total_tokens, k, 1]
# ===== 步驟5:專家計算與結果融合 =====
# 初始化輸出張量
final_output = torch.zeros(
(batch_size * seq_len, hidden_size), # 與輸入同形狀
dtype=hidden_states.dtype,
device=hidden_states.device
)
# 遍歷每個專家,處理所有選中該專家的token
for expert_idx in range(self.num_experts):
# 找到所有選中當前專家的token索引
# 掩碼:[total_tokens, k] → True表示該位置選中了當前專家
expert_mask = (top_k_indices == expert_idx) # [total_tokens, k]
# 若沒有token選中當前專家,跳過
if not expert_mask.any():
continue
# 收集選中當前專家的token及其對應的權重
# 1. 提取這些token的輸入特徵
expert_input = hidden_states[expert_mask.any(dim=1)] # [num_tokens_for_this_expert, hidden_size]
# 2. 提取這些token對當前專家的權重(取第一個匹配的權重,因每個位置最多選k個專家)
expert_weights = top_k_weights[expert_mask] # [num_tokens_for_this_expert, 1]
# 3. 當前專家處理輸入
expert_output = self.experts[expert_idx](expert_input) # [num_tokens_for_this_expert, hidden_size]
# 4. 加權:用該專家的權重乘以輸出
expert_output = expert_output * expert_weights # [num_tokens_for_this_expert, hidden_size]
# 5. 將結果累加至最終輸出(對應位置)
final_output[expert_mask.any(dim=1)] += expert_output
# ===== 步驟6:恢復輸出形狀並返回 =====
final_output = final_output.view(batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size) # [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size]
return final_output, router_aux_loss三、QWen3 部署實戰
你可以在 Hugging Face Hub 的 <u>Qwen3 collection</u> 或 ModelScope 的 <u>Qwen3 collection</u> 中獲取 Qwen3 模型。
使用 huggingface-cli 命令行工具:
安裝依賴:首先確保已安裝huggingface_hub,可運行命令pip install -U huggingface_hub。
設置鏡像地址:為提高下載速度,可設置國內鏡像,如export HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com(Linux 系統)。
下載模型:使用huggingface-cli download命令下載,例如huggingface-cli download --resume-download gpt2 --local-dir gpt2,將gpt2模型下載到當前目錄下的gpt2文件夾中。若要下載特定文件,可在模型名稱後添加文件名,如huggingface-cli download gpt2 config.json。huggingface-cli download Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507 --local-dir Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507huggingface 中下載的文件:
├── config.json
├── generation_config.json
├── LICENSE
├── merges.txt
├── model-00001-of-00003.safetensors
├── model-00002-of-00003.safetensors
├── model-00003-of-00003.safetensors
├── model.safetensors.index.json
├── README.md
├── tokenizer_config.json
├── tokenizer.json
└── vocab.json文件説明
-
config.json- 模型的結構配置文件,比如隱藏層維度、層數、注意力頭數、激活函數等。
AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained()會先讀取它,決定用哪種架構初始化模型。
-
generation_config.json- 文本生成時的默認參數,例如
max_new_tokens,temperature,top_p,do_sample等。 - 如果你用
model.generate(),沒手動傳參數,就會用這裏的默認值。
- 文本生成時的默認參數,例如
-
merges.txt- BPE (Byte Pair Encoding) 分詞的合併規則文件。
- 跟
vocab.json一起定義了 tokenizer 的詞表。
-
vocab.json- tokenizer 的詞表文件,存儲了 token 到 ID 的映射。
- 例如
"hello" -> 1234。
-
tokenizer.json- Hugging Face 的標準 tokenizer 文件,包含 vocab 和 merges 的完整定義。
- 用
AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained()會加載它。
-
tokenizer_config.json- Tokenizer 的額外參數,比如是否大小寫敏感、padding/truncation 策略等。
-
model-00001-of-00003.safetensors, model-00002-of-00003.safetensors, model-00003-of-00003.safetensors- 模型的權重文件,分成了多個分片,每個幾 GB。
safetensors是一種比pytorch_model.bin更安全和高效的格式。
-
model.safetensors.index.json- 權重索引文件,指明每個參數在分片文件中的位置。
- 加載模型時,transformers 會先讀這個文件,再去對應分片里加載。
將 huggingface 中的文件全部下載到 "。/Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507"文件夾
在 docker 環境中安裝(torch 2.3.0):
pip3 install transformers==4.55.0
pip3 install accelerate部署代碼:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
#下載的權重文件的路徑
model_name = "./Qwen/Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507"
# load the tokenizer and the model
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "你怎麼認為普京"
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
enable_thinking=True, # Switches between thinking and non-thinking modes. Default is True.
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=32768
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
# parse thinking content
try:
# rindex finding 151668 (</think>)
index = len(output_ids) - output_ids[::-1].index(151668)
except ValueError:
index = 0
thinking_content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[:index], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[index:], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
print("thinking content:", thinking_content)
print("content:", content)四、參考鏈接
https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1901014191235633835
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1902019286836449827
https://qwen.readthedocs.io/zh-cn/latest/
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers