項目背景
最近我們團隊自研了一個基於 React 的 H5 前端框架,領導讓我來負責編寫框架的使用文檔。我選擇了 dumi 來搭建文檔站點,大部分內容都是手動寫 Markdown 來介紹各種功能,包括:初始化、目錄結構、生命週期、狀態管理、插件系統 等等。
框架裏有個很重要的子包,主要負責多個 App 的橋接能力,深度集成了各端環境的監測和橋接邏輯。這個子包對外提供了一個 App 實例對象,裏面封裝了很多原生能力,比如: 設置導航欄、錄音、保存圖片到相冊 等
這些 API 代碼格式都比較統一,領導希望避免在框架源碼和文檔裏重複定義相同的接口,最好能直接從源代碼自動生成文檔內容。需要提取的信息包括:API支持的App版本、功能描述、開發狀態、使用方式,如果是函數的話還要有參數説明和返回值説明。
我的解決方案
經過一番思考,我想到了一個方案:
核心思路:在不改動源代碼邏輯的前提下,通過增加註釋信息來補充文檔需要的元數據
具體實現路徑:
- 定義一套規範的註釋標籤
- 編寫解析腳本提取信息,生成 JSON 文件
- 在文檔項目中讀取 JSON,動態渲染成 API 文檔
定義註釋規範
我定義了一系列標準的註釋標籤:
- @appVersion —— 支持該API的App版本
- @description —— API的功能描述
- @apiType —— API類型,默認是函數,可選property(屬性)和function(函數)
- @usage —— 使用示例
- @param —— 函數參數説明(只有函數類型需要)
- @returns —— 函數返回值説明(只有函數類型需要)
- @status —— 發佈狀態
在實際代碼中這樣使用,完全不會影響原來的業務邏輯:
const app = {
/**
* @appVersion 1.0.0
* @description 判斷設備類型
* @apiType property
* @usage app.platform // notInApp | ios | android | HarmonyOS
* @status 已上線
*/
platform: getPlatform(),
/**
* @appVersion 1.0.6
* @description 註冊事件監聽
* @param {Object} options - 配置選項
* @param {string} options.title - 事件名稱
* @param {Function} options.callback - 註冊事件時的處理函數邏輯
* @param {Function} options.onSuccess - 設置成功的回調函數(可選)
* @param {Function} options.onFail - 設置失敗的回調函數(可選)
* @param {Function} options.onComplete - 無論成功失敗都會執行的回調函數(可選)
* @usage app.monitor({ eventName: 'onOpenPage', callback: (data)=>{ console.log('端上push消息', data ) } })
* @returns {String} id - 綁定事件的id
* @status 已上線
*/
monitor: ({ onSuccess, onFail, onComplete, eventName = "", callback = () => { } }) => {
let _id = uuid();
// 業務代碼省略
return _id;
},
}解析腳本
接下來要寫一個解析腳本,把註釋內容提取成鍵值對格式,主要用正則表達式來解析註釋:
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
/**
* 解析參數或返回值標籤
* @param {string} content - 標籤內容
* @param {string} type - 類型 ('param' 或 'returns')
* @returns {Object} 解析後的參數或返回值對象
*/
function parseParamOrReturn(content, type = 'param') {
const match = content.match(/{([^}]+)}\s+(\w+)(?:\.(\w+))?\s*-?\s*(.*)/);
if (!match) return null;
const paramType = match[1];
const parentName = match[2];
const childName = match[3];
const description = match[4].trim();
const isParam = type === 'param';
if (childName) {
// 嵌套參數或返回值 (options.title 或 data.result 格式)
return {
name: parentName,
type: 'Object',
description: isParam ? `${parentName} 配置對象` : `${parentName} 返回對象`,
required: isParam ? true : undefined,
children: [{
name: childName,
type: paramType,
description: description,
required: isParam ? (!paramType.includes('?') && !description.includes('可選')) : undefined
}]
};
} else {
// 普通參數或返回值
return {
name: parentName,
type: paramType,
description: description,
required: isParam ? (!paramType.includes('?') && !description.includes('可選')) : undefined
};
}
}
/**
* 合併嵌套對象
* @param {Array} items - 參數或返回值數組
* @returns {Array} 合併後的數組
*/
function mergeNestedItems(items) {
const merged = {};
items.forEach(item => {
if (item.children) {
// 嵌套對象
if (!merged[item.name]) {
merged[item.name] = { ...item };
} else {
// 合併子元素
if (!merged[item.name].children) merged[item.name].children = [];
merged[item.name].children.push(...item.children);
}
} else {
// 普通參數
if (!merged[item.name]) {
merged[item.name] = item;
}
}
});
return Object.values(merged);
}
/**
* 保存標籤內容到註解對象
*/
function saveTagContent(annotation, tag, content) {
// 確保 parameters 和 returns 數組存在
if (!annotation.parameters) annotation.parameters = [];
if (!annotation.returns) annotation.returns = [];
switch (tag) {
case 'appVersion':
annotation.appVersion = content;
break;
case 'sxzVersion':
annotation.sxzVersion = content;
break;
case 'mddVersion':
annotation.mddVersion = content;
break;
case 'description':
annotation.description = content;
break;
case 'status':
annotation.status = content;
break;
case 'usage':
annotation.usage = content.trim();
break;
case 'apiType':
// 解析類型:property 或 method
annotation.type = content.toLowerCase();
break;
case 'param':
const param = parseParamOrReturn(content, 'param');
if (param) {
annotation.parameters.push(param);
// 合併嵌套對象
annotation.parameters = mergeNestedItems(annotation.parameters);
}
break;
case 'returns':
const returnItem = parseParamOrReturn(content, 'returns');
if (returnItem) {
annotation.returns.push(returnItem);
// 合併嵌套對象
annotation.returns = mergeNestedItems(annotation.returns);
}
break;
}
}
/**
* 解析 JSDoc 註釋中的註解信息 - 逐行解析
*/
function parseJSDocAnnotation(comment) {
if (!comment) return null;
const annotation = {};
// 按行分割註釋
const lines = comment.split('\n');
let currentTag = '';
let currentContent = '';
for (const line of lines) {
// 清理行內容,移除 * 和首尾空格,但保留內部的換行意圖
const cleanLine = line.replace(/^\s*\*\s*/, '').trimRight();
// 跳過空行和註釋開始結束標記
if (!cleanLine || cleanLine === '/' || cleanLine === '*/') continue;
// 檢測標籤開始
const tagMatch = cleanLine.match(/^@(\w+)\s*(.*)$/);
if (tagMatch) {
// 保存前一個標籤的內容
if (currentTag) {
saveTagContent(annotation, currentTag, currentContent);
}
// 開始新標籤
currentTag = tagMatch[1];
currentContent = tagMatch[2];
} else if (currentTag) {
// 繼續當前標籤的內容,但保留換行
// 對於 @usage 標籤,我們保留原始格式
if (currentTag === 'usage') {
currentContent += '\n' + cleanLine;
} else {
currentContent += ' ' + cleanLine;
}
}
}
// 保存最後一個標籤的內容
if (currentTag) {
saveTagContent(annotation, currentTag, currentContent);
}
// 確保 parameters 和 returns 數組存在(即使為空)
if (!annotation.parameters) annotation.parameters = [];
if (!annotation.returns) annotation.returns = [];
return Object.keys(annotation).length > 0 ? annotation : null;
}
/**
* 使用 @apiType 標籤指定類型
*/
function extractAnnotationsFromSource(sourceCode) {
const annotations = { properties: {}, methods: {} };
// 使用更簡單的邏輯:按行分析
const lines = sourceCode.split('\n');
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
const line = lines[i].trim();
// 檢測 JSDoc 註釋開始
if (line.startsWith('/**')) {
let jsdocContent = line + '\n';
let j = i + 1;
// 收集完整的 JSDoc 註釋
while (j < lines.length && !lines[j].trim().startsWith('*/')) {
jsdocContent += lines[j] + '\n';
j++;
}
if (j < lines.length) {
jsdocContent += lines[j] + '\n'; // 包含結束的 */
// 查找註釋後面的代碼行
for (let k = j + 1; k < lines.length; k++) {
const codeLine = lines[k].trim();
if (codeLine && !codeLine.startsWith('//') && !codeLine.startsWith('/*')) {
// 解析註解
const annotation = parseJSDocAnnotation(jsdocContent);
if (annotation) {
// 從註解中獲取類型(property 或 method)
let itemType = annotation.type;
let name = null;
// 如果沒有明確指定類型,默認設為 method
if (!itemType) {
itemType = 'method';
}
// 提取名稱
const nameMatch = codeLine.match(/^(\w+)\s*[:=]/);
if (nameMatch) {
name = nameMatch[1];
} else {
// 如果沒有匹配到名稱,嘗試其他模式
const funcMatch = codeLine.match(/^(?:async\s+)?(\w+)\s*\(/);
if (funcMatch) {
name = funcMatch[1];
}
}
if (name) {
if (itemType === 'property') {
annotations.properties[name] = annotation;
} else if (itemType === 'method') {
annotations.methods[name] = annotation;
} else {
console.warn(`未知的類型: ${itemType},名稱: ${name}`);
}
} else {
console.warn(`無法提取名稱: ${codeLine.substring(0, 50)}`);
}
}
break;
}
}
i = j; // 跳過已處理的行
}
}
}
return annotations;
}
/**
* 從文件提取註解
*/
function extractAnnotationsFromFile(filePath) {
if (!fs.existsSync(filePath)) {
console.error('文件不存在:', filePath);
return { properties: {}, methods: {} };
}
const sourceCode = fs.readFileSync(filePath, 'utf-8');
return extractAnnotationsFromSource(sourceCode);
}
/**
* 提取所有文件的註解
*/
function extractAllAnnotations(filePaths) {
const allAnnotations = {};
filePaths.forEach(filePath => {
if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) {
const fileName = path.basename(filePath, '.js');
console.log(`\n=== 處理文件: ${fileName} ===`);
const annotations = extractAnnotationsFromFile(filePath);
if (Object.keys(annotations.properties).length > 0 ||
Object.keys(annotations.methods).length > 0) {
allAnnotations[fileName] = {
fileName,
...annotations
};
}
}
});
return allAnnotations;
}
module.exports = {
parseJSDocAnnotation,
extractAnnotationsFromSource,
extractAnnotationsFromFile,
extractAllAnnotations
};集成到構建流程
然後創建一個腳本,指定要解析的源文件,把生成的 JSON 文件 輸出到 build 目錄裏:
const { extractAllAnnotations } = require('./jsdoc-annotations');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
/**
* 主函數 - 提取註解並生成JSON文件
*/
function main() {
const filePaths = [
path.join(process.cwd(), './app.js'),
path.join(process.cwd(), './xxx.js'),
path.join(process.cwd(), './yyy.js'),
].filter(fs.existsSync);
if (filePaths.length === 0) {
console.error('未找到任何文件,請檢查文件路徑');
return;
}
const annotations = extractAllAnnotations(filePaths);
const outputPath = path.join(process.cwd(), './build/api-annotations.json');
// 保存為JSON文件
fs.writeFileSync(outputPath, JSON.stringify(annotations, null, 2));
}
main();在 package.json 裏定義構建指令,確保 build 的時候自動運行解析腳本:
{
"scripts": {
"build:annotations": "node scripts/extract-annotations.js",
"build": "(cd template/main-app && npm run build) && npm run build:annotations"
},
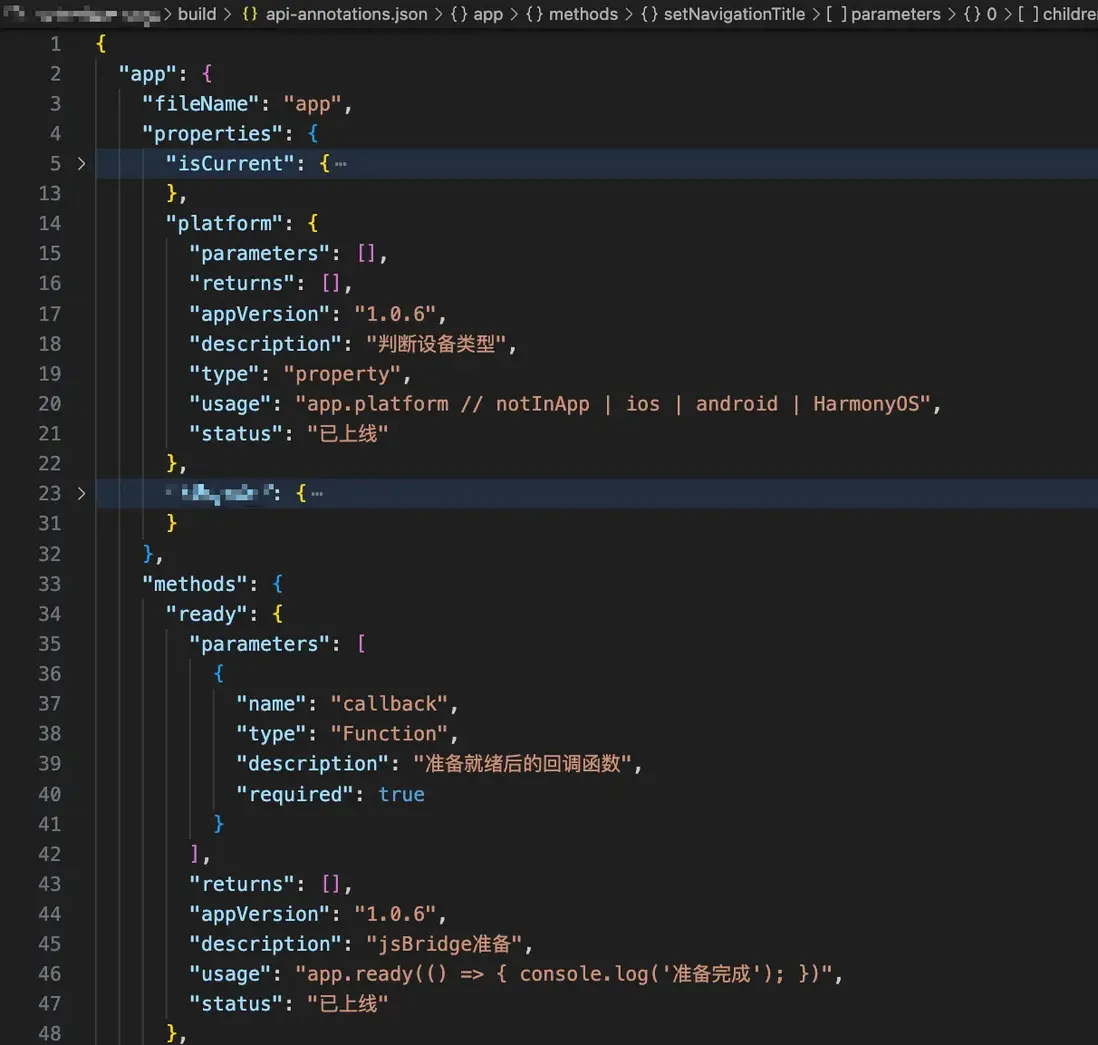
} 執行效果:運行 npm run build 後,會生成結構化的 JSON 文件:
## 在文檔中展示
框架項目和文檔項目是分開的,把 JSON 文件生成到 build 文件夾,上傳到服務器後提供固定訪問路徑。
有了結構化的 JSON 數據,生成文檔頁面就很簡單了。在 dumi 文檔裏,把解析邏輯封裝成組件:
---
title: xxx
order: 2
---
```jsx
/**
* inline: true
*/
import JsonToApi from '/components/jsonToApi/index.jsx';
export default () => <JsonToApi type="app" title="xxx" desc="App原生 api 對象"/>;
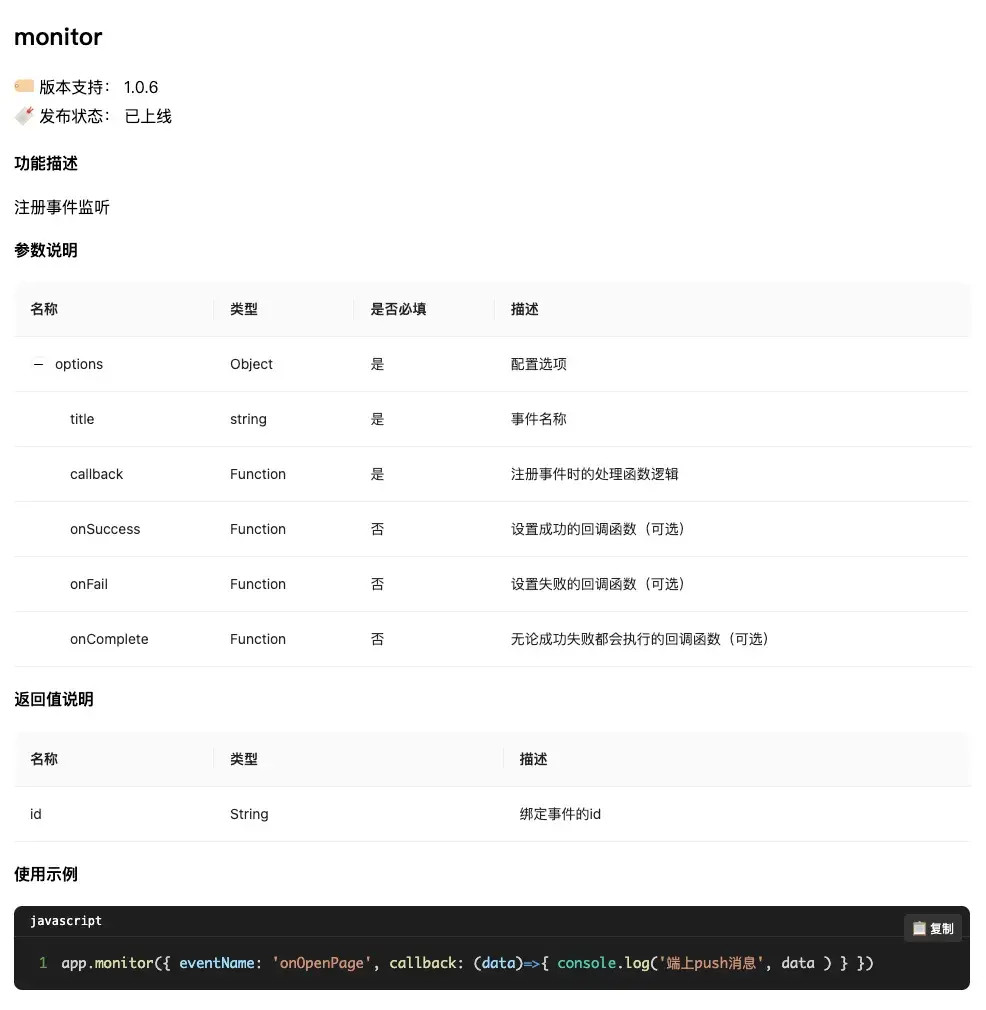
```渲染效果如圖所示
在將 JSON 數據解析並渲染到頁面的過程中,有兩個關鍵的技術點需要特別關注:
要點一:優雅的代碼展示體驗
直接使用 dangerouslySetInnerHTML 來呈現代碼片段會導致頁面樣式簡陋、缺乏可讀性。我們需要藉助代碼高亮工具來提升展示效果,同時添加便捷的複製功能,讓開發者能夠輕鬆複用示例代碼。
import React from 'react';
import { Prism as SyntaxHighlighter } from 'react-syntax-highlighter';
import { vscDarkPlus } from 'react-syntax-highlighter/dist/esm/styles/prism';
const CodeBlock = ({
children,
language = 'javascript',
showLineNumbers = true,
highlightLines = []
}) => {
const [copied, setCopied] = React.useState(false);
// 可靠的複製方法
const copyToClipboard = async (text) => {
try {
// 方法1: 使用現代 Clipboard API
if (navigator.clipboard && window.isSecureContext) {
await navigator.clipboard.writeText(text);
return true;
} else {
// 方法2: 使用傳統的 document.execCommand(兼容性更好)
const textArea = document.createElement('textarea');
textArea.value = text;
textArea.style.position = 'fixed';
textArea.style.left = '-999999px';
textArea.style.top = '-999999px';
document.body.appendChild(textArea);
textArea.focus();
textArea.select();
const success = document.execCommand('copy');
document.body.removeChild(textArea);
return success;
}
} catch (err) {
console.error('複製失敗:', err);
// 方法3: 備用方案 - 提示用户手動複製
prompt('請手動複製以下代碼:', text);
return false;
}
};
const handleCopy = async () => {
const text = String(children).replace(/\n$/, '');
const success = await copyToClipboard(text);
if (success) {
setCopied(true);
setTimeout(() => setCopied(false), 2000);
}
};
return (
<div className="code-container" style={{ position: 'relative', margin: '20px 0' }}>
{/* 語言標籤 */}
<div style={{
background: '#1e1e1e',
color: '#fff',
padding: '8px 16px',
borderTopLeftRadius: '8px',
borderTopRightRadius: '8px',
borderBottom: '1px solid #333',
fontSize: '12px',
fontFamily: 'monospace',
display: 'flex',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
alignItems: 'center'
}}>
<span>{language}</span>
<button
onClick={handleCopy}
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: '8px',
right: '8px',
background: copied ? '#52c41a' : '#333',
color: 'white',
border: 'none',
padding: '4px 8px',
borderRadius: '4px',
fontSize: '12px',
cursor: 'pointer',
zIndex: 10,
transition: 'all 0.3s'
}}
>
{copied ? '✅ 已複製' : '📋 複製'}
</button>
</div>
{/* 代碼區域 */}
<SyntaxHighlighter
language={language}
style={vscDarkPlus}
showLineNumbers={showLineNumbers}
wrapLines={true}
lineProps={(lineNumber) => ({
style: {
backgroundColor: highlightLines.includes(lineNumber)
? 'rgba(255,255,255,0.1)'
: 'transparent',
padding: '2px 0'
}
})}
customStyle={{
margin: 0,
borderTopLeftRadius: 0,
borderTopRightRadius: 0,
borderBottomLeftRadius: '8px',
borderBottomRightRadius: '8px',
padding: '16px',
fontSize: '14px',
lineHeight: '1.5',
background: '#1e1e1e',
border: 'none',
borderTop: 'none'
}}
codeTagProps={{
style: {
fontFamily: '"Fira Code", "Monaco", "Consolas", "Courier New", monospace',
fontSize: '14px'
}
}}
>
{String(children).replace(/\n$/, '')}
</SyntaxHighlighter>
</div>
);
};
export default CodeBlock;要點二:錨點導航方案
由於我們是通過組件方式動態渲染內容,無法直接使用 dumi 內置的錨點導航功能。這就需要我們自主實現一套導航系統,並確保其在不同屏幕尺寸下都能保持良好的可用性,避免出現佈局錯亂的問題。
import React, { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import { Anchor } from 'antd';
export default function readJson(props){
const anchorRef = useRef(null);
const anchorWrapperRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
// 使用更長的延遲確保 DOM 完全渲染
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
const contentElement = document.querySelector('.dumi-default-content');
const anchorElement = anchorRef.current;
if (!contentElement || !anchorElement) return;
// 創建錨點容器
const anchorWrapper = document.createElement('div');
anchorWrapper.className = 'custom-anchor-wrapper';
Object.assign(anchorWrapper.style, {
position: 'sticky',
top: '106px',
width: '184px',
marginInlineStart: '24px',
maxHeight: '80vh',
overflow: 'auto',
overscrollBehavior: 'contain'
});
// 插入到內容元素後面
if (contentElement.nextSibling) {
contentElement.parentNode.insertBefore(anchorWrapper, contentElement.nextSibling);
} else {
contentElement.parentNode.appendChild(anchorWrapper);
}
// 移動錨點
anchorWrapper.appendChild(anchorElement);
// 記錄錨點容器,用於清理
anchorWrapperRef.current = anchorWrapper;
}, 500); // 500ms 延遲,確保 DOM 完全渲染
return <div ref={anchorRef}>
<Anchor
targetOffset={80}
items={[
{
key: 'properties',
href: '#properties',
title: '屬性',
children: Object.keys(properties).map(item => ({
key: item,
href: `#${item}`,
title: item
}))
},
{
key: 'methods',
href: '#methods',
title: '方法',
children: Object.keys(methods).map(item => ({
key: item,
href: `#${item}`,
title: item
}))
}
]}
/>
</div>
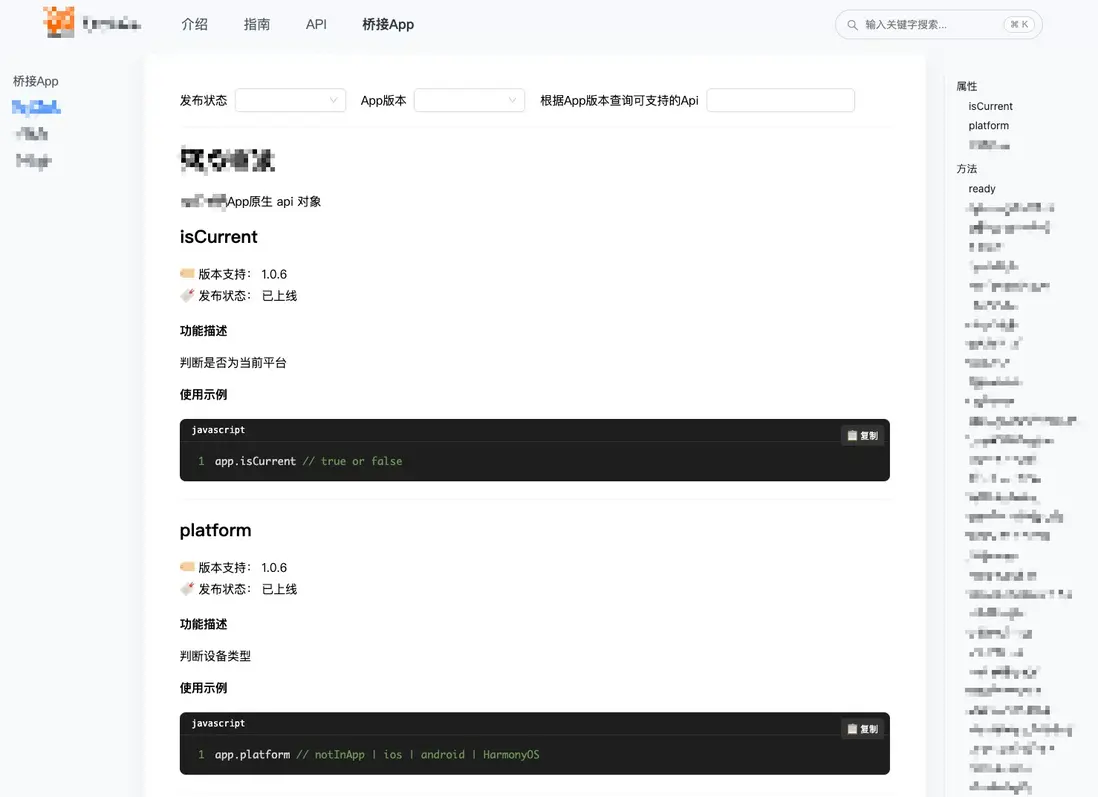
}當然,在頁面功能上我們還可以進一步豐富,比如增加實用的篩選功能。比如快速查看特定 App 版本支持的 API、篩選"已上線"、"開發中"或"已廢棄"的接口,這些篩選能力讓文檔不再是靜態的參考手冊,而變成了一個API 探索工具,最終呈現效果如下:
通過這套自動化文檔方案,我們實現了代碼和文檔的實時同步,大大減少了維護成本,同時給開發者提供了出色的使用體驗。現在開發同學只需要在代碼裏寫好註釋,文檔就會自動更新,再也不用擔心文檔落後於代碼了。
如果你對前端工程化有興趣,或者想了解更多前端相關的內容,歡迎查看我的其他文章,這些內容將持續更新,希望能給你帶來更多的靈感和技術分享~