本文內容包含所有的Crypto,四道PIoTS,兩道Re以及兩個系列的Misc題,主要用於記錄
Crypto
高位攻擊
完全用不到pq高位信息,因為d大概是n的0.2544次冪,所以直接套boneh donfee板子就可
# SageMath 9.3
N = 28384198625234311024055591508760545859772557962616705058087134570313766078246339432810722251075770426155260882976548948745855775802466082136886198916308950895091350291804323083377746723426585662829956721593008069417593656058519847917141571157423337000995823498275338699783892359735051369928648561714630161425631668045643208548745557419257154201912621422125784538013535319473974771074731705230991582524865280419594116357454200441743555890216903447536600103202560201259871803992219002685757605178878578265090068993111854329728311196716695934142083541791762952464173221834117578210442075243829228771641151482461878395681
e = 24233198590433138929759046268361507704173924810200652679220620112938468106193887274039561623781677698718659545011949842007599587857513820908529013019054134965026341908641820214813864848590705039503962393544485942577593170832200318338048424938687583902593193451991009036073079376645787351773806712023712043915544661222738699918976674231029998684765476662313863475966304161444465282825845046504385175046765187829943107254178661647191288636247051016225997643316505985860750972663378492448313338846037936997542245777268091759458108263910160659565995588095034641162401363842335174968680271594738396192872825937509377247217
c = 940844774044002760041224401562703091111426466612866082339966140841639939444648025078973826624076043358296937037021610358779157680065548800768654725751103021962957103161713314365598234258437018412919647354775780700585758075623352776449216395723630660676425946215835561424716152933938854890964273887565373627808873987131623770696128641766795559659984456300489545944324461938795805156161909329750290251725440271617055330398638953715159135274381585663770711778978803710571670536163056904818086237979881559953073139720433782186818163069926281641109314202702006420384137994982480163260679548223758917067813649186512456317
"""
Setting debug to true will display more informations
about the lattice, the bounds, the vectors...
"""
debug = False
"""
Setting strict to true will stop the algorithm (and
return (-1, -1)) if we don't have a correct
upperbound on the determinant. Note that this
doesn't necesseraly mean that no solutions
will be found since the theoretical upperbound is
usualy far away from actual results. That is why
you should probably use `strict = False`
"""
strict = False
"""
This is experimental, but has provided remarkable results
so far. It tries to reduce the lattice as much as it can
while keeping its efficiency. I see no reason not to use
this option, but if things don't work, you should try
disabling it
"""
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # stop removing if lattice reaches that dimension
############################################
# Functions
##########################################
# display stats on helpful vectors
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii, ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
print(nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# display matrix picture with 0 and X
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii, jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
print(a)
# tries to remove unhelpful vectors
# we start at current = n-1 (last vector)
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# end of our recursive function
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# we start by checking from the end
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# if it is unhelpful:
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# let's check if it affects other vectors
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if another vector is affected:
# we increase the count
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# level:0
# if no other vectors end up affected
# we remove it
if affected_vectors == 0:
# print("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii - 1)
return BB
# level:1
# if just one was affected we check
# if it is affecting someone else
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if it is affecting even one vector
# we give up on this one
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# remove both it if no other vector was affected and
# this helpful vector is not helpful enough
# compared to our unhelpful one
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(
bound - BB[ii, ii]):
# print("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii - 1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 if `strict=true`, and determinant doesn't bound
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
finds a solution if:
* d < N^delta
* |x| < e^delta
* |y| < e^0.5
whenever delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.<u,x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
Q = PR.quotient(x * y + 1 - u) # u = xy + 1
polZ = Q(pol).lift()
UU = XX * YY + 1
# x-shifts
gg = []
for kk in range(mm + 1):
for ii in range(mm - kk + 1):
xshift = x ^ ii * modulus ^ (mm - kk) * polZ(u, x, y) ^ kk
gg.append(xshift)
gg.sort()
# x-shifts list of monomials
monomials = []
for polynomial in gg:
for monomial in polynomial.monomials():
if monomial not in monomials:
monomials.append(monomial)
monomials.sort()
# y-shifts (selected by Herrman and May)
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm / tt) * jj, mm + 1):
yshift = y ^ jj * polZ(u, x, y) ^ kk * modulus ^ (mm - kk)
yshift = Q(yshift).lift()
gg.append(yshift) # substitution
# y-shifts list of monomials
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm / tt) * jj, mm + 1):
monomials.append(u ^ kk * y ^ jj)
# construct lattice B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0, 0)
for jj in range(1, ii + 1):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](UU, XX, YY)
# Prototype to reduce the lattice
if helpful_only:
# automatically remove
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus ^ mm, nn - 1)
# reset dimension
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print("failure")
return 0, 0
# check if vectors are helpful
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus ^ mm)
# check if determinant is correctly bounded
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus ^ (mm * nn)
if det >= bound:
# print("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
# print("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
# print("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus ^ mm)
# LLL
if debug:
print("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print("LLL is done!")
# transform vector i & j -> polynomials 1 & 2
if debug:
print("looking for independent vectors in the lattice")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# for i and j, create the two polynomials
PR.<w,z> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](w * z + 1, w, z) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU, XX, YY)
pol2 += monomials[jj](w * z + 1, w, z) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU, XX, YY)
# resultant
PR.<q> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
# are these good polynomials?
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
# print("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
# print("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
# print("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
#
return solx, soly
delta = .255 # this means that d < N^delta
m = 4 # size of the lattice (bigger the better/slower)
t = int((1 - 2 * delta) * m) # optimization from Herrmann and May
X = 2 * floor(N ^ delta) # this _might_ be too much
Y = floor(N ^ (1 / 2)) # correct if p, q are ~ same size
P.<x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
A = int((N + 1) / 2)
pol = 1 + x * (A + y)
solx, soly = boneh_durfee(pol, e, m, t, X, Y)
from Crypto.Util.number import *
d = int(pol(solx, soly) / e)
print(d)
m = pow(c,d,n)
print(long_to_bytes(int(m)).decode())
'''
det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)
6432702586977117047058127731915006203091953449046589982066699955250631372024238906597725462193228046982264362352356406213727451958618792246270372719793156453
flag{please-put-this-one-in-sagamath}
'''
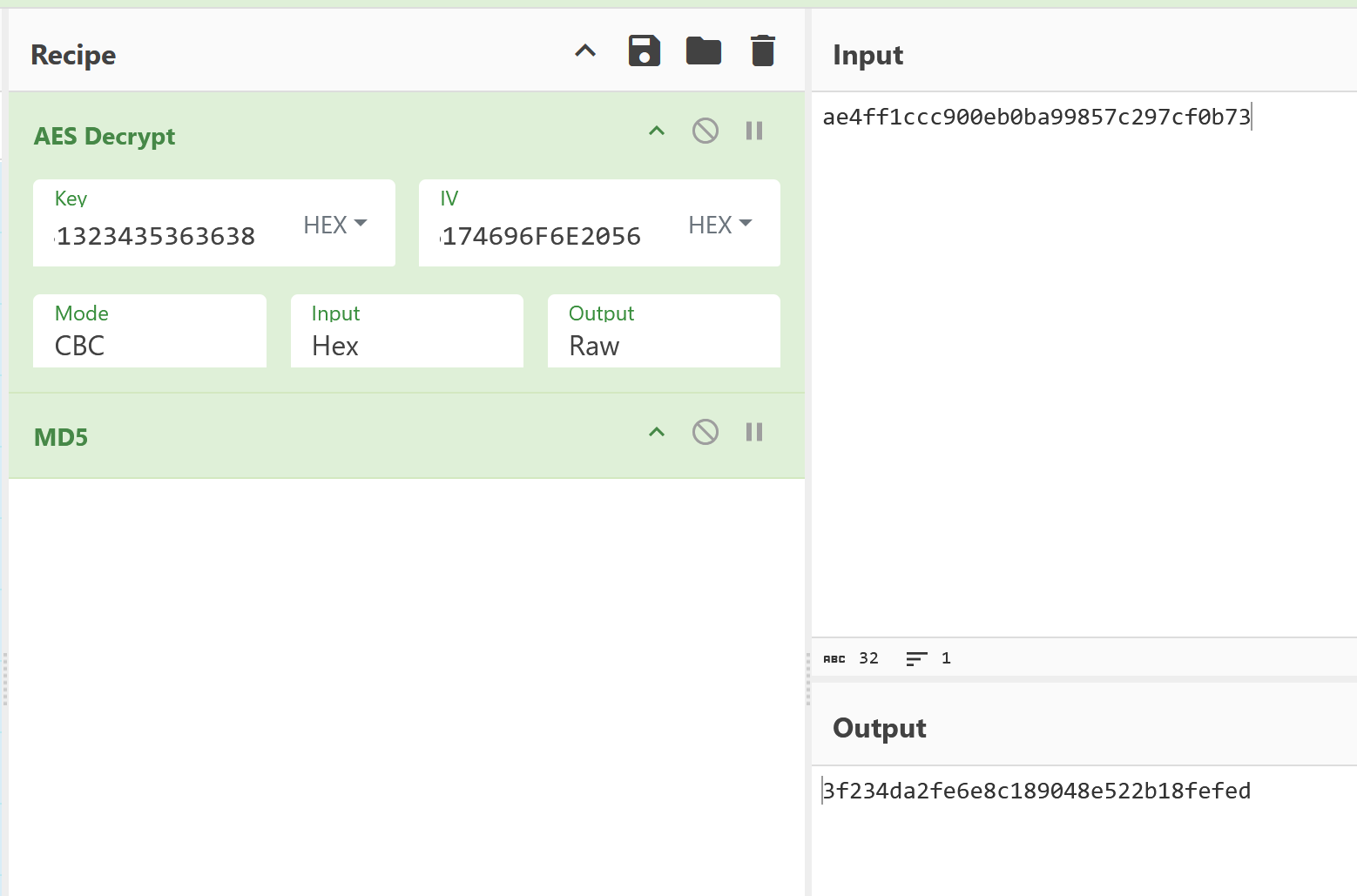
EzAES
key、IV、c均已知,直接AES解密即可,然後再套一層MD5,帶上flag{}殼提交
trod
import sys
def Sn(i):
s = ''
while i != 0:
digit = i & 0xff
i >>= 8
s += chr(digit)
return s
def In(s):
val = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
digit = ord(s[len(s) - i - 1])
val <<= 8
val |= digit
return val
def egcd(a, b):
if a == 0:
return b, 0, 1
else:
g, y, x = egcd(b % a, a)
return g, x - (b // a) * y, y
def mod_inv(a, p):
a %= p
g, x, y = egcd(a, p)
if g != 1:
raise Exception('No inverse exists')
else:
return x % p
def add(a, b, p):
if b == -1: return a
if a == -1: return b
x1, y1 = a
x2, y2 = b
# 分母
denom = (x1 + x2 - y1 - y2 - 1) % p
inv_denom = mod_inv(denom, p)
x3 = ((x1 * x2 - x1 * y2 - x2 * y1 + 2 * y1 * y2) * inv_denom) % p
y3 = ((y1 * y2) * inv_denom) % p
return x3, y3
def double_add(a, p):
return add(a, a, p)
def mod_mul(m, g, p):
r = -1
while m != 0:
if m & 1:
r = add(r, g, p)
m >>= 1
g = double_add(g, p)
return r
# --- 破解邏輯 ---
from sympy.ntheory import discrete_log
p = 518176062457782304884612410952519332834134329945067733347561865398388593
g = (36787147675581394808139907493983017478037802710811666907537030656, 9196786918895348702034976873495754369509450677702916726884257664)
A = (123420721694594649929479399223574107534344333995718594245237838243095171, 441474954859299544474995920494435026572932663211423760492509380991644019)
B = (201033191494423227078517457992052009778645182262306784843547224098182904, 218648529653244920425405172206343059964354475824649267929238496666580596)
encrypted_message = 100093982037856112608548215034731454533357581263010216959659834987333181487918721876307552567021052798183868853477600221794005089397754541179893146978
def map_point(P, p):
"""
同態映射函數 phi(x, y) = (x - y - 1) / (x - y) mod p
"""
x, y = P
u = (x - y) % p
# phi = 1 - 1/u = (u-1)/u
num = (u - 1) % p
den = mod_inv(u, p)
return (num * den) % p
def solve():
print("[*] Calculating mapped values...")
val_g = map_point(g, p)
val_A = map_point(A, p)
print("[*] Solving Discrete Logarithm (this might take a moment depending on p-1 smoothness)...")
# 求解: val_g ^ a = val_A (mod p)
# sympy.discrete_log 能夠自動處理 Pohlig-Hellman 算法
aliceSecret = discrete_log(p, val_A, val_g)
print(f"[+] Found Alice's Secret: {aliceSecret}")
print("[*] Calculating Shared Secret...")
# S = aliceSecret * B (using custom group mul)
S = mod_mul(aliceSecret, B, p)
# 根據題目邏輯計算 masterSecret
masterSecret = (S[0] * S[1]) # 注意這裏是普通乘法,不是模 p 乘法,根據題目邏輯 masterSecret = aliceMS[0] * aliceMS[1]
print("[*] Decrypting...")
decrypted_int = encrypted_message ^^ masterSecret
flag = Sn(decrypted_int)
print(f"\n[SUCCESS] Flag: {flag}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
solve()
'''
[*] Calculating mapped values...
[*] Solving Discrete Logarithm (this might take a moment depending on p-1 smoothness)...
[+] Found Alice's Secret: 5893410662100511584121728146593578127178145692816888878
[*] Calculating Shared Secret...
[*] Decrypting...
[SUCCESS] Flag: flag{Who_has_the_computer_organization_principle_in_the_exam?}
'''
創造lcg
一開始沒想到一個點,flag並不是由反推的初始的LCG狀態列表得出來的,而是由當前狀態再經過一次lcg變換得到的下一狀態得出來的。通過打印並觀察每一輪對應的假的flag看出來的,然後就只需要對當前狀態進行一次lcg變化然後讀出對應flag即可
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, inverse
final_lcg = [
531812496965714475754459274425954913,
573493247306997567791036597408132959,
531874692922906583591521900672740733
]
a = 678292774844628690689951
b = 799218428050845578943269
c = 871991670671866736323531
p = 226554022535584634512578046463759712133
current_state = list(final_lcg)
new_state = (a*current_state[0] + b*current_state[1] + c*current_state[2]) % p
current_state = current_state[1:] + [new_state]
val_nplus1 = current_state[0]
val_nplus2 = current_state[1]
val_nplus3 = current_state[2]
inv_a = inverse(a, p)
val_n = (inv_a * (val_nplus3 - b * val_nplus1 - c * val_nplus2)) % p
current_state = [val_n] + current_state[:2]
flag_bytes = b""
for part in current_state:
flag_bytes += long_to_bytes(part)
print(flag_bytes.decode())
# flag{try_to_transform_it_into_formulaic_form}
xiaoji的RSA
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from math import gcd
c = 18062960292926203405106631570645792887346762710596094595946201638145269792362432970619678514073768330282072122297774770846723026262793638145140252714036118255298935496782643261099997757452005888950084317572578983859160308143219449311014720216597693717833093096186064214815571678655104145532183363580096161113659794514705540535423432576540755810113817779577012494191762397204056012915596163266097092210799790994886142736276356044755057247863118120000651380079123033610186723297866795705886993017274323290850712391555552018597217459748407996232225971214252337750534257640641166056960137653051788480104937847471213865531
leak = 29786109562795434767286575222202920392934698151772733519827029723076564127577506924725472620552207928305324807071633980845799428305323747287497587012814817694240321762385052643719779704776885137653915759833442842418374852111545817139388092965791383085268376283252367393215830021523854878152740193684532064211244526477475872824124551317767515936013314015487953976823909663377712672258700701049790904432754196590520755614551428222850284265995888579989169357385240073615572407415594868320441237551194011351100321407974631166974196395240849462596136681294133772802147270429624576958515766511950802469230517874955000694776
h1 = 14598570770570369251044298637863318854969244053819114954671895416691350802920687681668270301378543649113252159681469894140327953343981428435557763783575047421073785093934100988516182011757805151301552786226747639175213248064364104458391503594386384710007637410647669428289271030281975860741433987188926890687769189330536656978907095466736760156091550669274865538908426382007469741745093518762985240171234021436305408209014615992584706412209748494302146308826117702351113891442300797965409831595569786933763773967575744129781374727612526423706127336276048951135368854093017991855415497273999713365969103371554004824509
h2 = 11655430400126708521266628893465012008156070100550313215125940102411494976112918677189030755406554269846801368688286768397687408859238412058773272768466345174217960738213084397497134648104645110774595383007722678343723326165844773931623583737649558732929341710652376370393000666923877685083880991816166675473675993119565288119886891401337292448811477124318462203416303782364411201690259713617106545395093938159021072322598644028525378190756212177234492649667270787158675885995463312527798325191816554894434526912762675422186788558909636033206644624947398671285555871818986699430277747968998624440765160214625508302582
n = 16117539256891249484718413429700173002583084988861340273782389608188420881800342876872775121756821301056788500260045796850939585388076522939011021777251658702207624594144564384121357888401608404641571728859619754015070281985119363898471820577703197516678288716301039869441770173970562352919565912788016889342101896134309321994797037369608180360632790282197647969119609543804552490560372790883065970972189091831856508916272396614853136857081227250153104695845022919856333090412792344985816893032033703744649648621089458783293225651830841418574525258165458710362104364949367148707705685722700758399918195168711661909001
# solve linear system for c1,c2:
c1 = (c + leak) // 3
c2 = c - c1
K = 7717*8859
a = pow(h1, 8859, n)
b = pow(h2, 7717, n)
t2024 = pow(2024, K, n)
t2025 = pow(2025, K, n)
X = (a * t2025 - b * t2024) % n
g = gcd(X, n)
p = g
q = n // p
e = 0x10001
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
d = inverse(e, phi)
m1 = pow(c1, d, n)
m2 = pow(c2, d, n)
print((long_to_bytes(m1)+long_to_bytes(m2)).decode())
# flag{fc08e137-5be9-4677-a1f5-4e640223df0e}
漸增套娃
cryisc題,通過觀察,注意到本題涉及到qwerty座標密碼,具體來説,這個24292125,其中的22代表第二行第二列,經過驗證flag拼在一起為24292125與題目一致,對三段密文開始解密,第一段結果為stepwise,第二段為nwlahycrxw,無意義單詞,Rot枚舉一下偏移量,發現為9時得到有意義文本encryption,第三段為nomziboc,Rot枚舉偏移量為21時得到有意義文本strength,最後根據題目説明拼出flag為flag{stepwise encryption strength}
PIoTS
默認密鑰漏洞xor
題目提到數據使用了出廠未修改的默認全局鏈路密鑰“ZigBeeAlliance09”,因此通信負載可被直接解密。將 payload 與該默認密鑰循環 XOR 後,可在正確偏移3處還原出可讀明文。最終明文中包含的字符串即為題目flag
data = open(r"E:\Downloads\zigbee_traffic.pcap","rb").read()
payload = data[0x28:]
key_hex = "5A6967426565416C6C69616E63653039".lower()
key = bytes.fromhex(key_hex)
def score_plain(b):
printable = 0
for c in b:
if 32 <= c <= 126:
printable += 1
return printable/len(b)
candidates = []
for s in range(len(payload)):
out = bytearray(payload) # full
for i in range(s,len(payload)):
out[i] ^= key[(i-s)%len(key)]
sc = score_plain(out[s:]) # only encrypted tail
candidates.append((sc,s,out))
sorted(candidates, reverse=True)[:10][:3]
cands=[]
for s in range(len(payload)):
out = bytearray(payload)
for i in range(s,len(payload)):
out[i] ^= key[(i-s)%len(key)]
sc = score_plain(out)
cands.append((sc,s,out))
if b'flag' in out:
print(out)
break
sorted(cands, reverse=True)[:10]
# bytearray(b'\x00\x08\x01SensorData: flag{thepolarinthezigbee}')
點擊挑戰
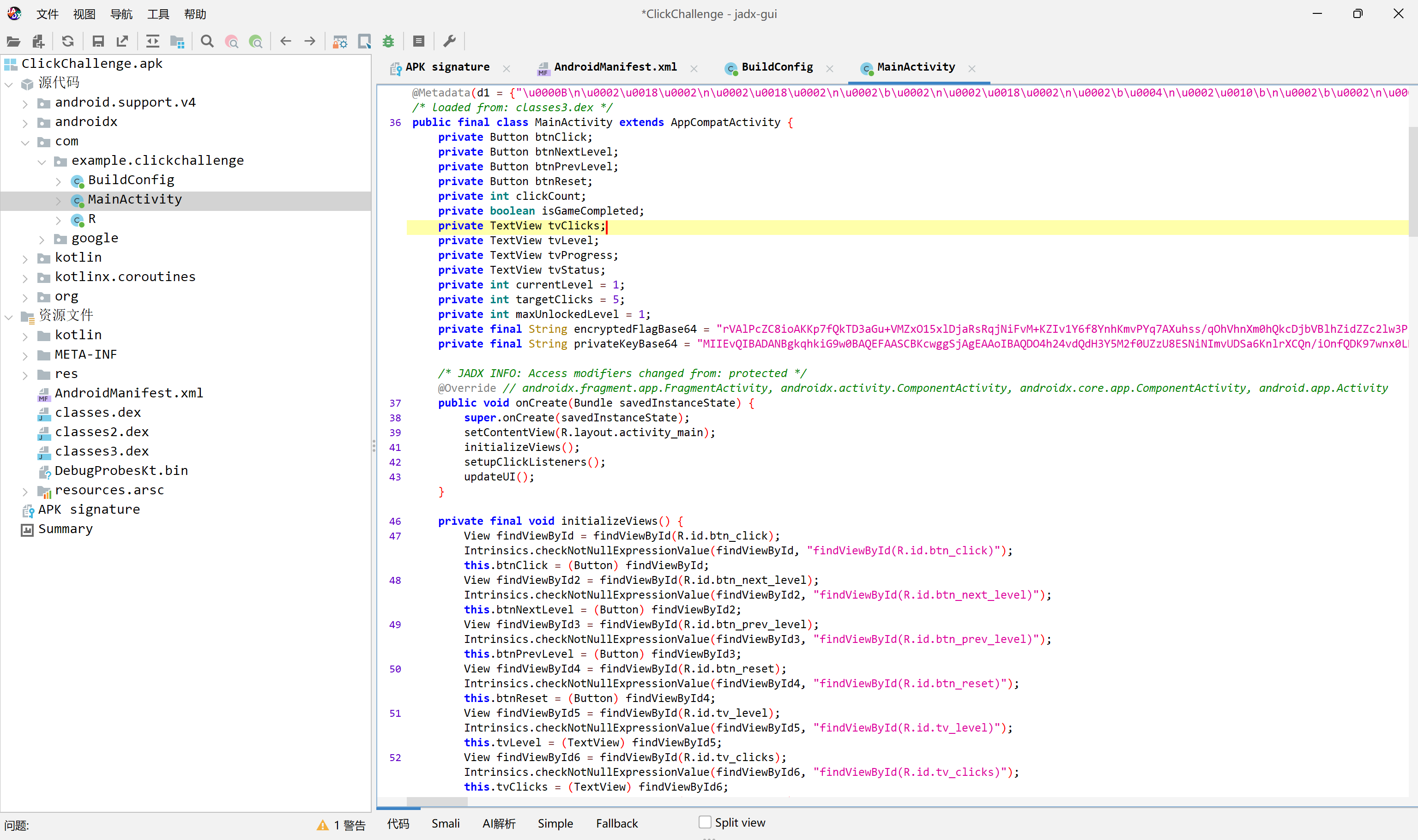
首先解包 APK,使用 jadx 查看代碼,在 MainActivity 中發現RSA私鑰、密文以及用於顯示flag的邏輯。觀察到程序會用內置私鑰解密內置密文,並直接在隱藏關卡中顯示flag。從 APK 中提取 Base64 私鑰和密文,在本地復現相同的解密過程,獲得flag
import base64
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
from Crypto.Cipher import PKCS1_v1_5
def main():
# APK 中提取出的 Base64 私鑰
key_b64 = """
MIIEvQIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKcwggSjAgEAAoIBAQDO4h24vdQdH3Y5M2f0UZzU8ESNiNImvUDSa6KnlrXCQn/iOnfQDK97wnx0LDibNlMAE50AizHGXwlWClBqtMohObbiFgZrpONbw1Xyg6sGVPPjDHpqgZkV7iXpAnQdphkeEkp2YVYWPaAwFj+lIQl9IuyW1uaGqYKcAzI4xd9juzA1h9wZjXSVyAo77q/HbNVgM1RFw0zQuUJ8qV1rAZv1zrkv7bRO4O4EC00fxzcvbOdos8WwjKvBwSWI52oJEQ6rhYk471o9YkE6pWxuWWORnjLmmI/Eb66BrVUwLZSyTxtUWNrMqyOmtNlkH6H9HL3MrnrPLRiu6m2BrsOnPDmrAgMBAAECggEAIyqEata5q4mhiu+WCA2nXvrIbFaJglRBJINvTpVrp+2t10KhAxhk6+CPTyAFLzz4ttaepW0DtPiKmbl/GeRJR4SL9bpQtRN+Iib+AQ8ojxb5rep9FIWbBANLJmRoYHHPazEovx6kh3tKM2JUxzjqZ/77wFgfL1y4+tQAQW5BHq5wsnKgW5/kysZf1tNhBvyNCowJF0JxisoGvx5nx63J+d+TAM0XPpQ8RBVFjoR3W2odWdpeAmbMl1Aa4ZihcskBbp4EqYr1QZYGuONzLBLaqtwu+E+uC0JPU3dxy9te3Yjs33Dd41gcg8v6HnTrNFntsfR9TojLmEL5N8q+DWvKgQKBgQDlxYmlfefj+b5+FOuokJWX3ioYhFxM4OVF2WkTirAcydm+b7Teacmc3YL9xr0If+88trjb7b8BXCwiterpFi0Pax/z5u7ZIJ8BA1MwybC0CIBzy2i0tMU0qCPCaMYkrEHjKBrYmSIXAy3jqyZ4V9QMkO4pcJoEPNCSyBPr3cZVewKBgQDmf7oglk890b0CVdFNYzPN2Du01OZ5y7aJbzKGlo/H+xx8Qkm/eUeaIOPTWemZaJYCHOQHKHMN/Zp50qE/g7OkQifrvHSJR+PgLv+YN/Y0Our2zIiY5wdZRNZj6k6l9eDbsR65lDC3bhwahuYBQ1yvHzSdaRjeMCJ2Agod6z69kQKBgCrlTQQ7VC5ocprBNxmaHINks4EuPLkRh1wZ8Zb3XleRi3gVDLQ1FbGWXR0ZnDLZB4XTKwHMCcusNIUqZzeqrzDgs+9p3o9kmqqqvz4teTKzH5/+ioap9OMWvM5PlyZDjm1lEFX9iLK5IjkNu7nd07Wg3QWZgvdljx7IAYgYOC2/AoGADXeG82J0zMLVTS6gZOoX2733dxA9Sv5o8sypYg2n5uI3/taMooA+e7XSOcX2DP18TjFL7VMirb2UaeuxehmCxGUNGgvPrzmhCbcVPdp/KvwKQFMg4/YTitanw/yrjay4730As40B76WiRLZ+97Hs11p2Y4ABcPHVAZoK50aYStECgYEAxktu0YJ2By/rRPB1kAkttSb6PvEAuIwuwUFmttYiNuO8dQktpLjCoi62eyUzPxHWcY0Hxi92IAqfS697e9skEMKrepRZ6ysAkKjOMaJhVAwA+XAdRhaPimy4miDFa5dSFPxcc0JwfCAXkX2C/jjYc9s7t4jOMDnYhGszlzGdjNU=
""".strip()
# APK 中提取出的 Base64 密文
cipher_b64 = """
rVAlPcZC8ioAKKp7fQkTD3aGu+VMZxO15xlDjaRsRqjNiFvM+KZIv1Y6f8YnhKmvPYq7AXuhss/qOhVhnXm0hQkcDjbVBlhZidZZc2lw3PIc1mphUVgj+rd1hu3xwDY8Gsh1CNEx0H878B93T+OVshWh6IygFi6VFHEnfYOh99vPcA6MbeaRFMb4ZhWvr122X0/dxsrP1KXlQEWcnLXtPpbIB7aXjwHb1nqUNaD4EaDqNoouF+CxA4YOt4Oh8sHqh8BtNsD2khSrz6rS5mi7DRff4A4RxRvW4SVU0p7z5v6/KXgdhPe7df9k9duKDUgJ8BooPbMJnG/RuqljK3MR3g==
""".strip()
# 解碼並導入私鑰
key_der = base64.b64decode(key_b64)
rsa_key = RSA.import_key(key_der)
# 初始化 PKCS1Padding 解密器
cipher = PKCS1_v1_5.new(rsa_key)
# 解密
ciphertext = base64.b64decode(cipher_b64)
plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext, None)
if plaintext is None:
print("解密失敗,請檢查數據。")
else:
print(plaintext.decode())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# flag{8baf11bb16c9c14a5577e3ed0658bed3}
ESP32_AP
非預期,直接在附件中搜索 flag{ 即可得到本題的flag為 flag{MAC_2_PWD_Is_C00L!}
NFC水卡
首先理解題意,題目所要求的應該是第 1 張卡中“總金額+對應校驗位”所在扇區的扇區內容 ,首先觀察兩張原卡的結構,顯然只有第 0 扇區和第 2 扇區中數據較多。題目明確指出金額和校驗位在同一扇區,因而可以確定為第二扇區。對比觀察可以發現第 1 行和第 3 行完全對稱,明顯是金額塊和其備份,特徵包括前 9 個字節全是 00 、第 10 字節固定是 FF、第 11–12 字節變化、第 13 字節為 00、第 14–15 字節變化、第 16 字節固定 FD 等等。從而確定了具體的金額的位置,可以計算檢驗,對於原卡 1,金額為 0x0578,校驗為 0xFA87, 有 0xFFFF-0X0578=0XFA87 校驗通過,説明推理正確。然後看轉賬,相加之後得到新的金額為 0x09CB,新的校驗為 0xF634,據此可以寫出轉賬之後卡 1 第二扇區的內容,然後就是一點格式問題
多提交驗證幾次,嘗試不同的提交格式,得到正確的結果為如下字段,flag為flag{46FEED7D708C39B9C843768F0559F1C0}
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF F6 34 00 09 CB FD
58 00 00 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 59
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF F6 34 00 09 CB FD
12 63 22 33 53 13 FF 07 80 69 12 63 22 33 53 13
Re
練習1
先從二進制中提取到偽裝的模板串 flag{PbkD7j4x|8Wz::z_01},隨後在代碼段中找到對該字符串的所有引用,定位到其所在的變換函數。通過分析棧上緩衝區的讀寫與多段循環控制邏輯,可還原出程序對模板串執行了分段異或(前 5 字不變、接下 7 字 XOR 0x07、再 7 字 XOR 0x08、剩餘直接複製)的生成規則。將此規則應用到模板串即可求得真實 flag
templ = b"flag{PbkD7j4x|8Wz::z_01}"
def transform(t):
t = list(t)
out = ['\x00']*0x32
idx = 0
# first 5
for b4 in range(5):
out[idx] = chr(t[b4])
idx+=1
# next 7 XOR 7
for d4 in range(7):
ch = t[idx]
out[idx] = chr(ch ^ 0x7)
idx += 1
# next 7 XOR 8
for f4 in range(7):
ch = t[idx]
out[idx] = chr(ch ^ 0x8)
idx+=1
# remaining until idx reaches len(t)
while idx < len(t):
out[idx] = chr(t[idx])
idx+=1
out[idx] = '\0'
return "".join(out[:idx])
print(transform(templ))
# flag{WelC0m3pt0_r22z_01}
peek_stack
程序要求輸入中文口令“秘密口令2025”,若匹配則進入生成 flag 的函數。該函數會先輸出固定前綴“flag{”,然後將口令的 UTF-8 字節逐字節與 0x5A 異或並輸出,最後添加“}”。因此只需提取口令字節並 XOR 0x5A,即可得到最終 flag
secret_utf8 = "秘密口令2025".encode("utf-8")
flag_hex_middle = ''.join(f"{b^0x5a:02x}" for b in secret_utf8)
print(f'flag{{{flag_hex_middle}}}')
# flag{bdfdc2bff5dcbfd5f9bee1fe686a686f}
Misc
Source of danger系列
網站 IP
用 strings 1.pcapng 找到 Host: 192.168.27.15,並結合其後大量 /source/ecshop/... 請求,可判斷這是受害者訪問的本地購物站點 IP
瀏覽器及版本
在同一主機 192.168.27.15 的 HTTP 請求附近找到: User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 ... Chrome/142.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edge/142.0.0.0 。説明是 Edge 瀏覽器,版本號 142.0.0.0
圖片上寫的內容
搜索圖片名 138_thumb_G_1763621518921.jpg,在返回的 HTML 裏有:
<img src=".../138_thumb_G_1763621518921.jpg" alt="ChatGPT" ...>
<a href="goods.php?id=138" title="ChatGPT5">ChatGPT</a>
商品名/圖片文字為 ChatGPT
木馬使用的庫版本
在流量中找到木馬回連 C2: POST /upload.php HTTP/1.1其中 User-Agent: python-requests/2.32.5,可知惡意程序使用 requests 庫,版本號為 2.32.5
木馬竊取信息中的網站 URL
在該 POST 請求的 multipart 裏,有上傳文件名: filename="edge_passwords_2025-11-26_12-44-41.txt"
進一步截取該文件內容(在邊界與下一次 boundary 中間的明文部分),可看到:
網站: http://192.168.27.15/source/ecshop/admin/privilege.php
用户名: admin
密碼: ...
題目要求完整url,所以 flag 填 http://192.168.27.15/source/ecshop/admin/privilege.php
Virtual_currency系列
檢材只用到了兩個數據,一個是polar文件夾,一個是polarCTF.exe,只需要對這兩個展開分析即可
虛擬貨幣的名稱
前端頁面 index.html 的標題為“Polar幣交易平台”,且餘額顯示單位為 “POL”。服務端區塊鏈邏輯中未定義其他幣名,因此平台所使用的虛擬貨幣即為 Polar幣。因而虛擬貨幣名稱為 Polar幣
黑客的地址
從日誌分析可見,該地址頻繁被查詢餘額並參與交易,是平台主要操作者使用的主賬號。結合客户/中間賬號行為分佈可知,該地址對應題目所述的“黑客本人”。因而黑客地址為 9598f90b557fdf01558f9061c09195647f3ca9261264485319279e1da7a7ac48
黑客和客户使用的中間賬號地址
logs 顯示此地址先被客户端頁面訪問,又被黑客側查詢,是雙方共同使用的賬號。結合題意“黑客與客户交互的中轉賬户”,可確定這是中間賬號。因而中間賬號地址為 9004ddca99ff4aa70ef6cd27d2f3b81103c25d33c1384549a4f3bb0fdc035ef4
客户的 IP
從訪問日誌可見,192.168.192.129 進行頁面登錄、交易發送、手動挖礦等典型“前端用户”操作。與後台礦機(192.168.192.130)區分後,129 明顯對應題目描述的“客户”。因而客户 IP 為 192.168.192.129
黑客植入的礦機木馬是什麼?
逆向 miner.py 顯示木馬直接將自身註冊為 Windows 服務 “polarCTF”,作為後台挖礦程序運行。程序未釋放其他挖礦文件,因此木馬本體即為 EXE 本身。因而木馬文件名為 polarCTF.exe