2025-11-28:統計特殊三元組。用go語言,給定一個整數數組 nums。我們把滿足 i<j<k(索引從 0 開始)且 nums[i] 和 nums[k] 都等於 nums[j] 的兩倍的三個不同索引 (i, j, k) 稱為“一組特殊三元組”。要求計算數組中所有這樣的三元組數量,並將結果對 1000000007 取模後返回。
3 <= n == nums.length <= 100000。
0 <= nums[i] <= 100000。
輸入: nums = [6,3,6]。
輸出: 1。
解釋:
唯一的特殊三元組是 (i, j, k) = (0, 1, 2),其中:
nums[0] = 6, nums[1] = 3, nums[2] = 6
nums[0] = nums[1] * 2 = 3 * 2 = 6
nums[2] = nums[1] * 2 = 3 * 2 = 6
題目來自力扣3583。
過程分步説明
-
初始化階段
代碼使用了三個映射(map)來動態跟蹤計數:cnt1:記錄每個數字作為三元組中第一個元素nums[i]出現的次數。鍵是數字本身,值是該數字在遍歷過程中作為nums[i]的累計次數。cnt12:記錄每個數字作為中間值nums[j]時,當前已存在的有效(i, j)對數量。具體來説,對於給定的nums[j],cnt12[nums[j]]表示之前已遇到多少對(i, j)滿足nums[i] = 2 * nums[j]且i < j。cnt123:直接統計完整三元組(i, j, k)的數量。初始值為 0,最終結果需對1_000_000_007取模。
-
遍歷數組並動態更新計數
代碼從左到右遍歷數組nums,將每個元素x依次視為三元組中的潛在k、j或i:- 步驟一:檢查
x作為nums[k]的可能性
如果x是偶數(即x % 2 == 0),則計算x / 2作為候選的nums[j]值。此時,若cnt12中已存在鍵x/2,説明之前已記錄過滿足nums[i] = 2 * nums[j]的(i, j)對,且這些對的nums[j]正好是x/2。當前x作為nums[k]可與這些(i, j)組合成完整三元組,因此將cnt12[x/2]的值累加到cnt123中。 - 步驟二:更新
x作為nums[j]的計數
接下來,將x視為nums[j]。需要找到所有滿足nums[i] = 2 * x且i < j的nums[i]。這些nums[i]的數量已記錄在cnt1[2*x]中(即之前遍歷時作為i出現的次數)。因此,將cnt1[2*x]的值加到cnt12[x]中,表示新增了cnt1[2*x]個有效的(i, j)對。 - 步驟三:更新
x作為nums[i]的計數
最後,將x視為nums[i],簡單增加cnt1[x]的計數,為後續j或k的匹配做準備。
- 步驟一:檢查
-
最終處理
遍歷完成後,cnt123即為所有滿足條件的三元組總數。返回cnt123 % 1_000_000_007以確保結果在模數範圍內。
複雜度分析
- 總的時間複雜度:
O(n),其中n是數組長度。代碼僅對數組進行一次線性遍歷,每個元素處理過程中對映射的查詢、插入和更新操作均攤時間複雜度為O(1)(基於哈希映射實現)。 - 總的額外空間複雜度:
O(n)。主要來自三個映射cnt1、cnt12和cnt123的存儲。在最壞情況下,映射中的鍵數量與數組長度n成正比(例如所有元素互異時),因此空間複雜度為線性。
補充説明
- 算法的關鍵洞察:通過單次遍歷和巧妙的計數映射,避免了暴力枚舉所有三元組(否則複雜度為
O(n³)),實現了高效統計。這種方法類似於動態規劃中“用空間換時間”的策略,逐步構建子問題的解。 - 與其他三元組問題的區別:不同於搜索和排序類三元組問題(如三數之和),本題專注於特定算術關係的計數,且數組元素無需排序。
Go完整代碼如下:
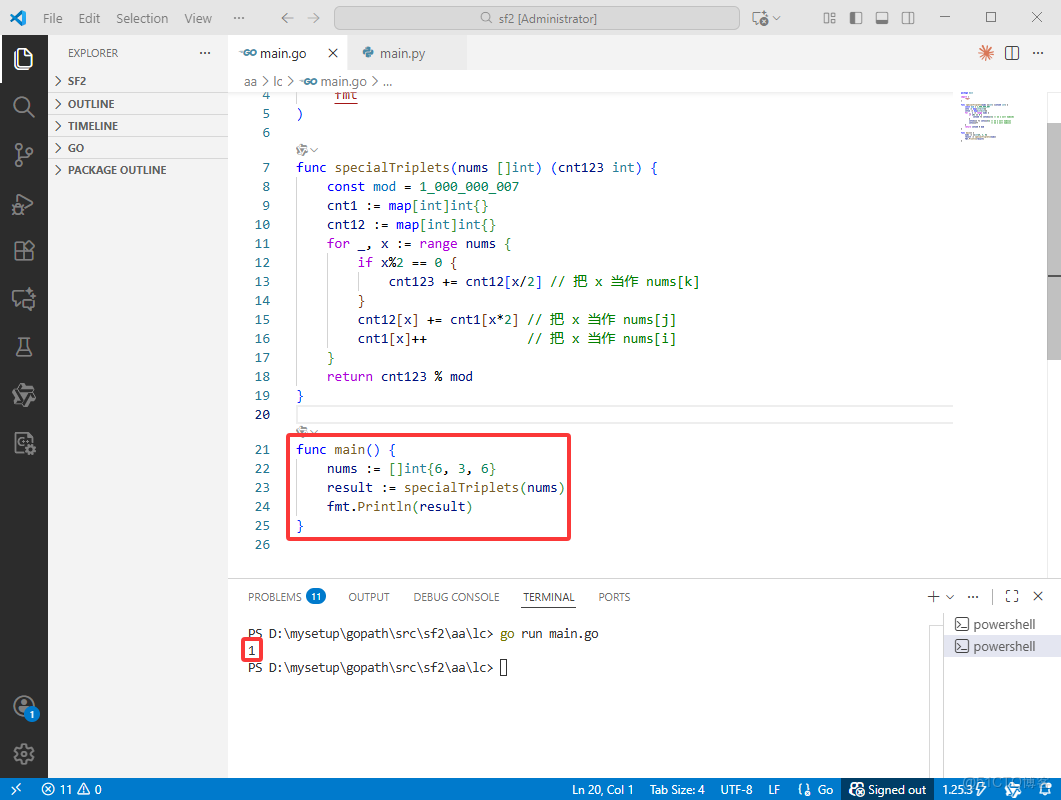
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func specialTriplets(nums []int) (cnt123 int) {
const mod = 1_000_000_007
cnt1 := map[int]int{}
cnt12 := map[int]int{}
for _, x := range nums {
if x%2 == 0 {
cnt123 += cnt12[x/2] // 把 x 當作 nums[k]
}
cnt12[x] += cnt1[x*2] // 把 x 當作 nums[j]
cnt1[x]++ // 把 x 當作 nums[i]
}
return cnt123 % mod
}
func main() {
nums := []int{6, 3, 6}
result := specialTriplets(nums)
fmt.Println(result)
}
Python完整代碼如下:
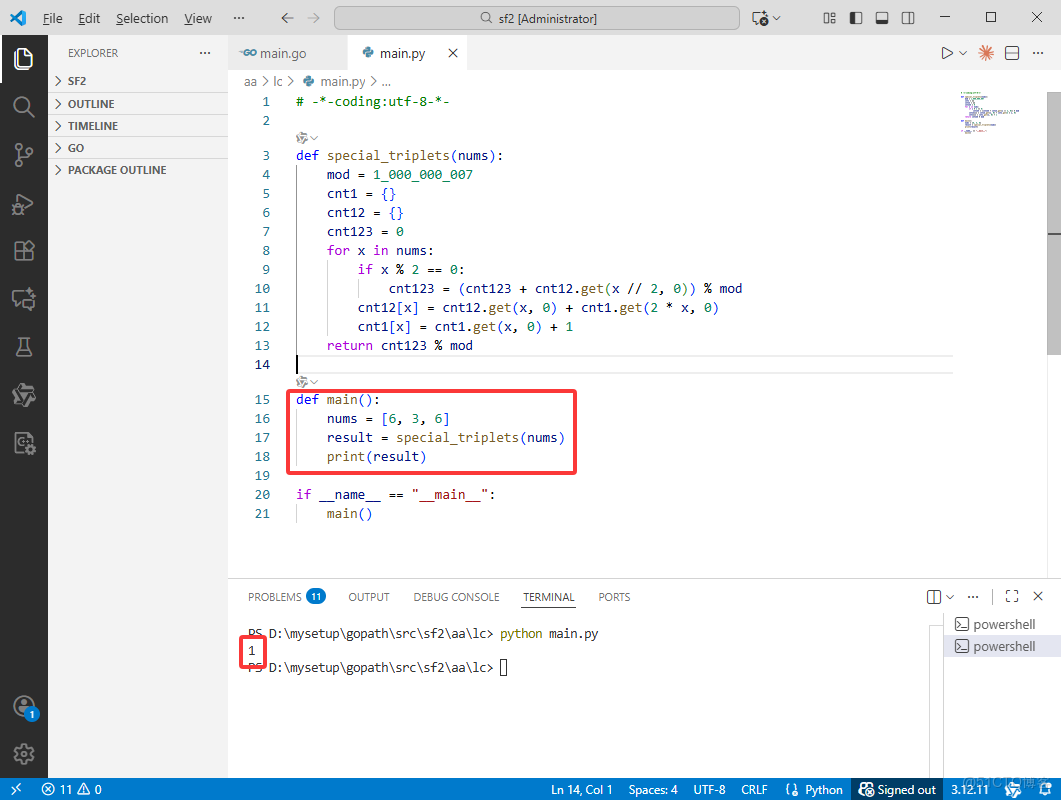
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
def special_triplets(nums):
mod = 1_000_000_007
cnt1 = {}
cnt12 = {}
cnt123 = 0
for x in nums:
if x % 2 == 0:
cnt123 = (cnt123 + cnt12.get(x // 2, 0)) % mod
cnt12[x] = cnt12.get(x, 0) + cnt1.get(2 * x, 0)
cnt1[x] = cnt1.get(x, 0) + 1
return cnt123 % mod
def main():
nums = [6, 3, 6]
result = special_triplets(nums)
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++完整代碼如下:
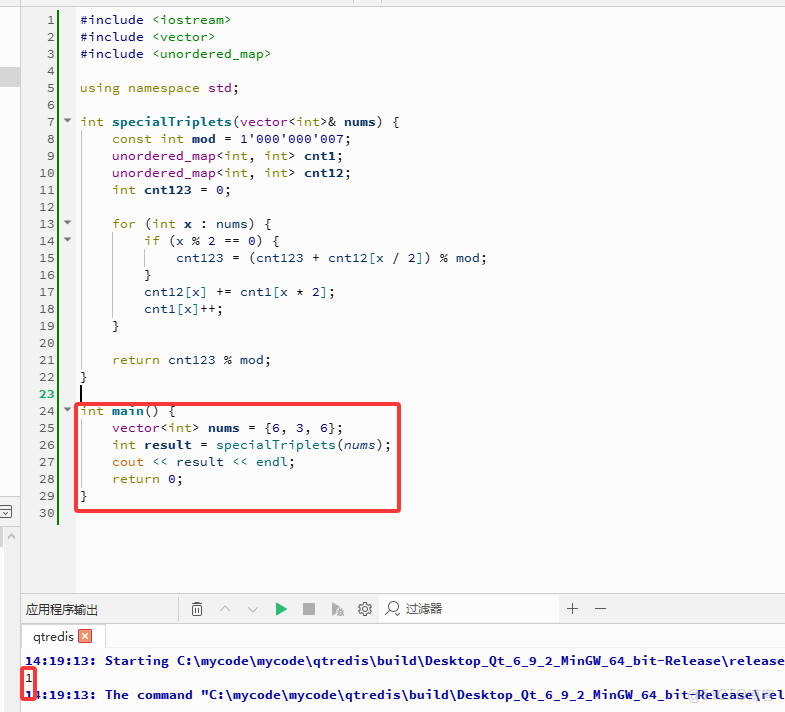
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int specialTriplets(vector<int>& nums) {
const int mod = 1'000'000'007;
unordered_map<int, int> cnt1;
unordered_map<int, int> cnt12;
int cnt123 = 0;
for (int x : nums) {
if (x % 2 == 0) {
cnt123 = (cnt123 + cnt12[x / 2]) % mod;
}
cnt12[x] += cnt1[x * 2];
cnt1[x]++;
}
return cnt123 % mod;
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {6, 3, 6};
int result = specialTriplets(nums);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}