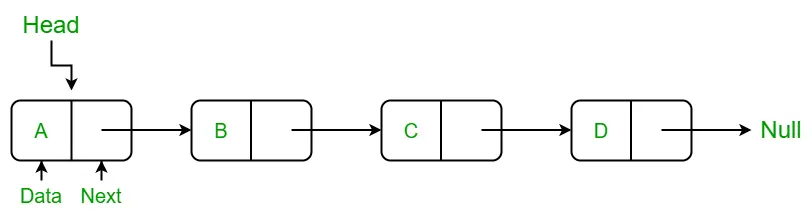
一、什麼是鏈表
動態的線性數據結構。
二、鏈表的增刪改查
(一)非遞歸實現
<?php
class LinkedList
{
// protected Node $head;
protected Node $dummyHead; // 虛擬頭結點
private $size;
public function __construct()
{
// $this->head = null;
$this->dummyHead = new Node();
$this->size = 0;
}
public function getSize(): int
{
return $this->size;
}
public function isEmpty(): bool
{
return $this->size == 0;
}
// 在鏈表頭添加新的元素
public function addFirst($e)
{
$this->add(0, $e);
}
// 在鏈表的 index (0-based) 位置添加新的元素 e
public function add($index, $e)
{
// 判斷 index 的合法性
if ($index < 0 || $index > $this->size) {
// 注意 index 可以取到 size 的,因為可以在最後一個節點添加元素
throw new \Exception('Add failed. illegal index');
}
$prev = $this->dummyHead;
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$prev = $prev->next;
}
// 順序很重要
$node = new Node($e);
$node->next = $prev->next;
$prev->next = $node;
// 更優雅的寫法
// $prev->next = new Node($e, $prev->next);
$this->size ++;
}
// 在鏈表末尾添加元素 e
public function addLast($e)
{
$this->add($this->size, $e);
}
// 獲得鏈表中第 index 個位置的元素:
public function get($index)
{
if ($index < 0 && $index >= $this->size) {
throw new \Exception('Get failed, Illeal index');
}
$cur = $this->dummyHead->next;
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$cur = $cur->next;
}
return $cur->e;
}
// 獲得鏈表的第一個元素
public function getFrist()
{
return $this->get(0);
}
// 獲得鏈表的最後一個元素
public function getLast()
{
return $this->get($this->size - 1);
}
// 修改鏈表的第 index 個位置的元素
public function set($index, $e)
{
if ($index < 0 && $index >= $this->size) {
throw new \Exception('Set failed, Illeal index');
}
$cur = $this->dummyHead->next;
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$cur = $cur->next;
}
$cur->e = $e;
}
// 查找鏈表中是否存在元素 e
public function contains($e)
{
$cur = $this->dummyHead->next;
while ($cur != null) {
if ($e == $cur->e) {
return true;
}
$cur = $cur->next;
}
return false;
}
// 從鏈表中刪除第 index 個元素,並返回刪除元素的值
public function remove($index)
{
if ($index < 0 || $index >= $this->size) {
throw new \Exception('Delete failed, illegal index');
}
$prev = $this->dummyHead;
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$prev = $prev->next;
}
$retNode = $prev->next;
$prev->next = $retNode->next;
$retNode->next = NULL;
$this->size--;
return $retNode->e;
}
// 從鏈表中刪除第一個元素,返回刪除元素
public function removeFirst()
{
return $this->remove(0);
}
// 從鏈表中刪除最後一個元素,返回刪除元素
public function removeLast()
{
return $this->remove($this->size - 1);
}
public function toString()
{
$cur = $this->dummyHead->next;
$ret = '';
while ($cur != null) {
$ret .= $cur->e . '->';
$cur = $cur->next;
}
$ret .= 'NULL';
return $ret;
}
}
class Node
{
public $e;
public $next;
public function __construct($e = null, $next = null)
{
$this->e = $e;
$this->next = $next;
}
}1. 虛擬頭結點(dummy head)
為什麼要使用虛擬頭結點?詳情參考 鏈表問題:虛擬節點dummy
因為頭結點的上一個節點不存在,很多對於其他節點,需要用上上一個節點的操作對頭結點就不適合,因此,就需要單獨考慮頭結點。
虛擬頭結點的目的就是消除頭結點的特殊性,把頭結點當做一個普通的節點來處理。即在頭結點的前面加上了一個虛擬頭結點。
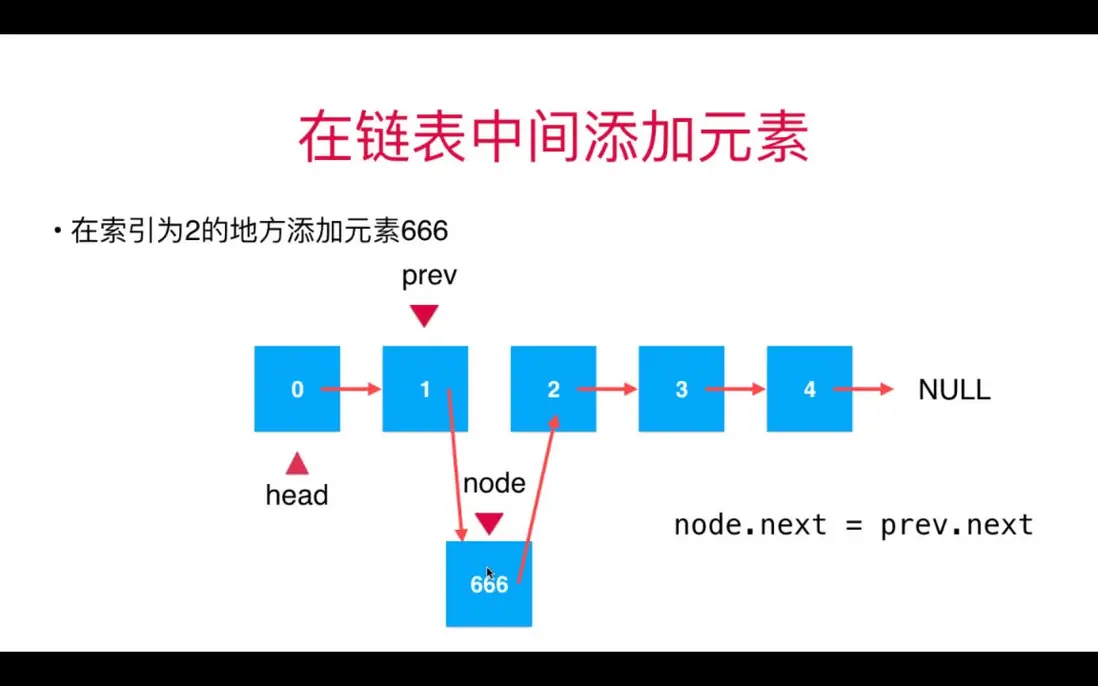
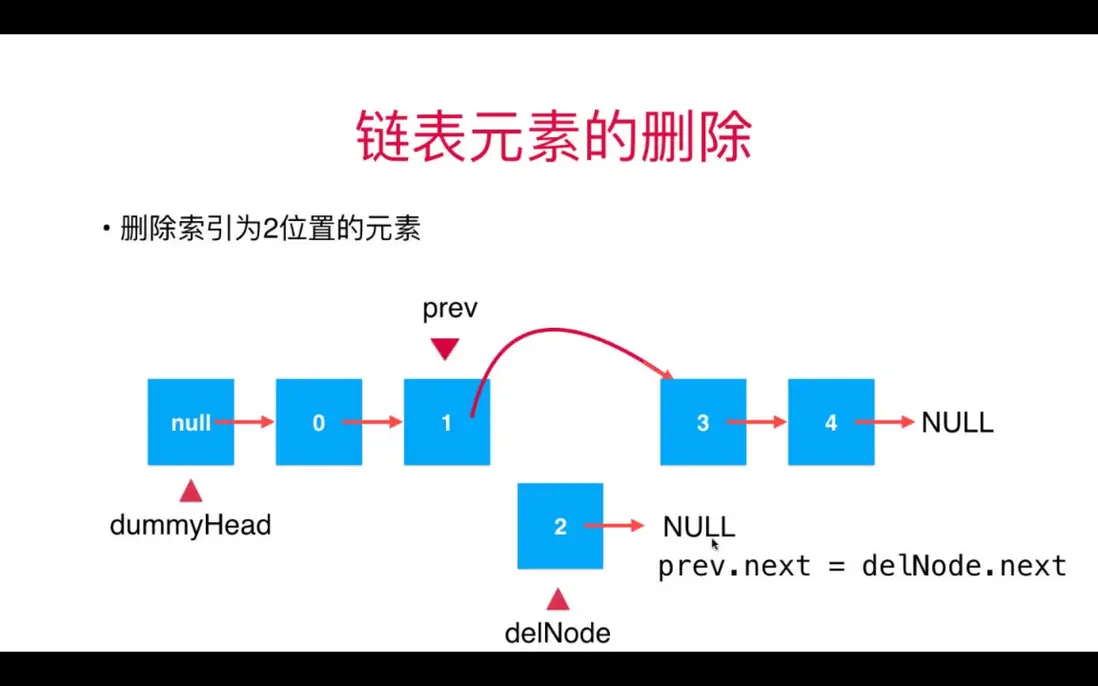
2. 增刪
在鏈表中間添加和刪除元素的關鍵:找到要添加或刪除的節點的前一個節點。
增加元素示意圖:
刪除元素示意圖:
這也是用虛擬頭結點的原因:假如想要在頭結點增加一個元素或者刪除頭結點,那麼就需要找到頭結點的前一個節點,但是頭結點前面是沒有節點的,比較常見的做法是分情況討論;更好的做法是使用虛擬頭結點這種技巧,把頭結點也當做普通元素來處理,最終也不會對結果產生影響,避免了分類討論。
值得一提的是,在增加或刪除元素時遍歷鏈表時,是從虛擬頭結點開始遍歷的,而非鏈表的第一個元素開始,代碼如下:
// 在鏈表的 index (0-based) 位置添加新的元素 e
public function add($index, $e)
{
...
// 從 dummyHead 開始遍歷
$prev = $this->dummyHead;
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$prev = $prev->next;
}
$node = new Node($e);
$node->next = $prev->next;
$prev->next = $node;
$this->size ++;
}
// 從鏈表中刪除第 index 個元素,並返回刪除元素的值
public function remove($index)
{
...
// 從 dummyHead 開始遍歷
$prev = $this->dummyHead;
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$prev = $prev->next;
}
$retNode = $prev->next;
$prev->next = $retNode->next;
$retNode->next = NULL;
$this->size--;
return $retNode->e;
}為什麼要從 dummyHead 開始遍歷呢?就不得不再提一遍增加或者刪除元素的重點了:找到要添加或刪除的節點的前一個節點,即我們要找到的前一個節點而非目標節點。
舉個例子,在鏈表 L 中位置為 2 的地方添加一個節點 6,鏈表 L 如下:
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | next |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| val | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | null |
現在在頭結點前面加上一個虛擬頭結點:
| index | dummyHead | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | next |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| val | null | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | null |
遍歷的目標節點是 L[1]。
dummyHead -> next = L[0]
L[0] -> next = L[1]兩次就找到了目標節點的前一個節點,和待添加的位置 2 統一。
3. 改查
遍歷找到目標節點即可。但是與增刪有些許不同,改查並不是從 dummyHead 開始遍歷,而是從鏈表的頭結點開始。
舉個例子,獲取 L 中索引為 2 的元素的值,L 鏈表如下:
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | next |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| val | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | null |
如果從 dummyHead 開始遍歷,循環兩次,找到的是 L[1] 這個元素,那麼如果是從頭結點開始遍歷,那麼遍歷兩次就可以找到目標元素了。
L[0] -> next = L[1];
L[1] -> next = L[2];查和改的代碼如下:
// 修改鏈表的第 index 個位置的元素
public function set($index, $e)
{
...
// 從頭結點開始遍歷
$cur = $this->dummyHead->next;
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$cur = $cur->next;
}
$cur->e = $e;
}
// 獲得鏈表中第 index 個位置的元素:
public function get($index)
{
...
// 從頭結點開始遍歷
$cur = $this->dummyHead->next;
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$cur = $cur->next;
}
return $cur->e;
}三、遞歸刪除鏈表中指定元素
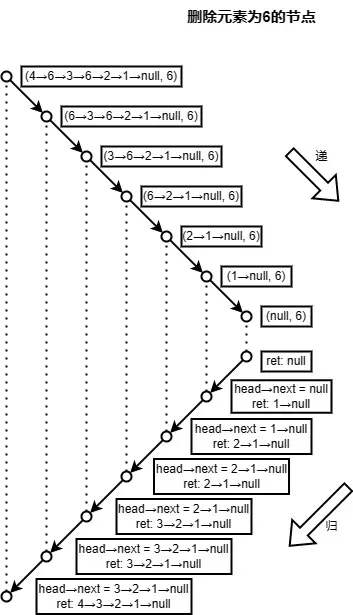
問題描述:給定單向鏈表的頭指針和一個要刪除的節點的值,定義一個函數刪除該節點;返回刪除後的鏈表的頭節點。詳情參考 劍指 Offer 18. 刪除鏈表的節點。
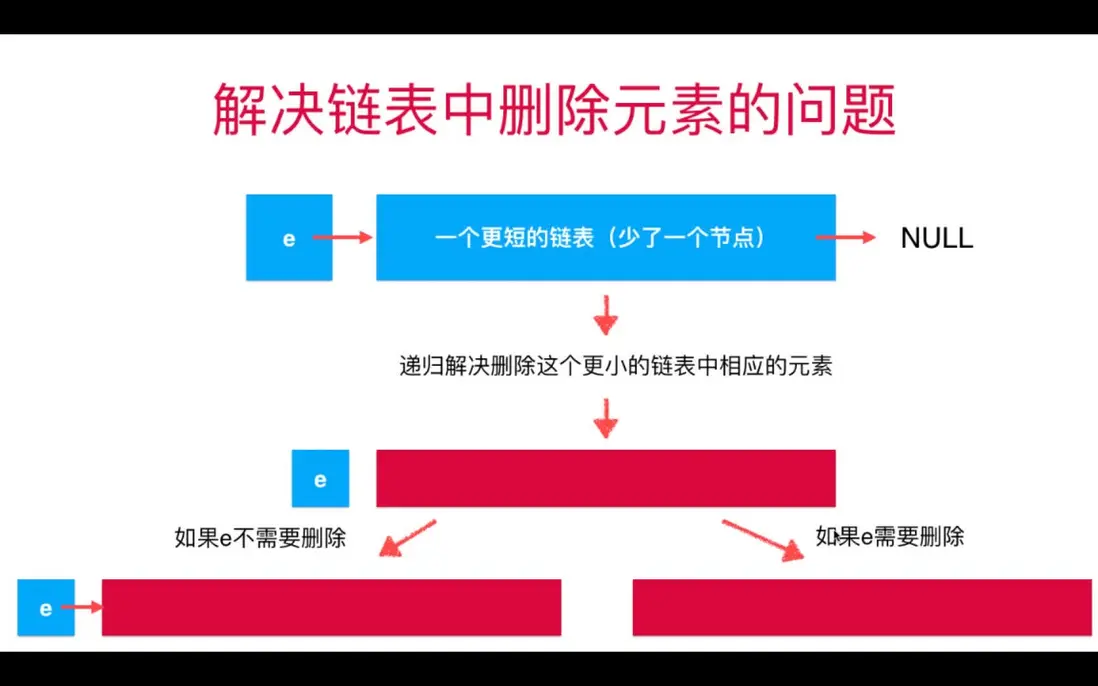
解題思路:利用鏈表天然的遞歸性。
遞歸藴含的思想其實是數學歸納法:為了求解問題p(n),首先解決基礎情形p(1),然後假定p(n-1)已經解決,在此基礎上若p(n)得解,那所有問題均得解。
參考代碼如下:
<?php
class RemoveElements{
public function removeEles($head, $e)
{
if ($head == null) {
return null;
}
$head->next = $this->removeEles($head->next, 6);
return $head->val == $e ? $head->next : $head;
}
public static function main()
{
$arr = [4, 6, 3, 6, 2, 1];
$head = new ListNode($arr);
dump($head);
$ret = (new RemoveElements())->removeEles($head, 6, 0);
dump($ret);
}
}
class ListNode
{
public $val;
public $next;
public function __construct($x)
{
if (is_int($x)) {
$this->val = $x;
} elseif (is_array($x)) {
if ($x == null || count($x) == 0) {
throw new \Exception("arr cannot be empty");
}
$this->val = $x[0];
$cur = $this;
for ($i = 1; $i < count($x); $i ++) {
$cur->next = new ListNode($x[$i]);
$cur = $cur->next;
}
}
}
public function __toString()
{
$str = '';
$cur = $this;
while ($cur != null) {
$str .= "{$cur->val}->";
$cur = $cur->next;
}
$str .= 'NULL';
return $str;
}
}測試:
<?php
$solution = new RemoveElements();
$solution->main();
/*
結果:
4->6->3->6->2->1->NULL
4->3->2->1->NULL
*/一種可視化的,可快速得到遞歸結果的手段:
四、翻轉鏈表
第一版:
public function reverseList($head)
{
if ($head->next == null) {
return $head;
}
$reversedList = $this->reverseList($head->next);
$head->next = null;
$tail = $reversedList;
while ($tail->next != null) {
$tail = $tail->next;
}
$tail->next = $head;
return $reversedList;
}改進:
<?php
/**
* Definition for a singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* public $val = 0;
* public $next = null;
* function __construct($val) { $this->val = $val; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @return ListNode
*/
function reverseList($head) {
if ($head->next == null) {
return $head;
}
$reversedList = $this->reverseList($head->next);
$head->next->next = $head;
$head->next = null;
return $reversedList;
}
}第一版是我用了三個小時自己想出來的,雖然用的時間有點久,但是自己獨立解決了這個問題,還是有點小成就感的。
回顧這個過程,感覺是可以用更短的時間解決這個問題的,花的時間比較久的地方是在思考如何用遞歸得到的結果構建出最終的結果。
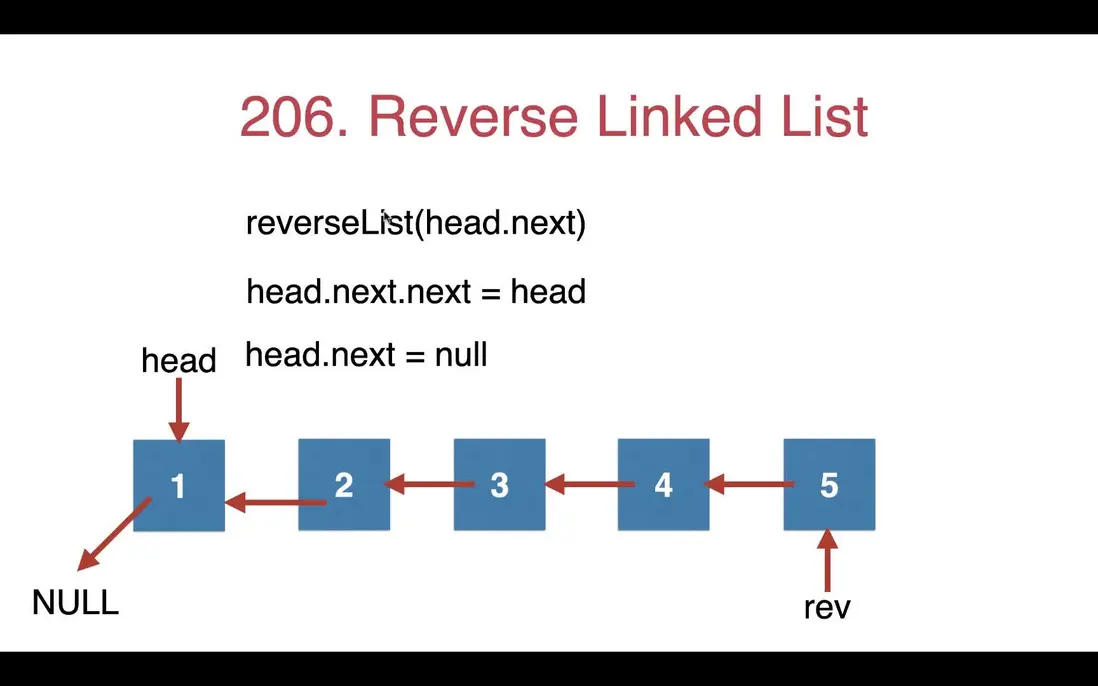
舉個例子,翻轉鏈表 L。鏈表 L :1->2->3->4->5->null。
把鏈表 L 看成頭結點 1 後面接了一個更短的鏈表 L1:2->3->4->5->null,翻轉 L1 得到的結果是 5->4->3->2->null。現在的問題是如何把鏈表 L 的頭結點 1 和遞歸得到的結果 L1(5->4->3->2->null)組合起來得到最終的結果。
一開始我放了一個錯誤,即把 L1 頭結點的下一個節點指向 L 的頭結點,導致一直無法得到正確的答案,正確的做法是把 L1 的尾結點指向 L 的頭結點。
錯誤的代碼:
public function reverseList($head)
{
if ($head->next == null) {
return $head;
}
$reversedList = $this->reverseListWrong($head->next);
$head->next = null;
$reversedList->next = $head;
return $reversedList;
}
/*
測試:1->2->3->4->5->null
結果:
5->1->NULL
*/
正確的代碼:
public function reverseList($head)
{
...
$reversedList = $this->reverseList($head->next);
$head->next = null;
$tail = $reversedList;
while ($tail->next != null) {
$tail = $tail->next;
}
$tail->next = $head;
return $reversedList;
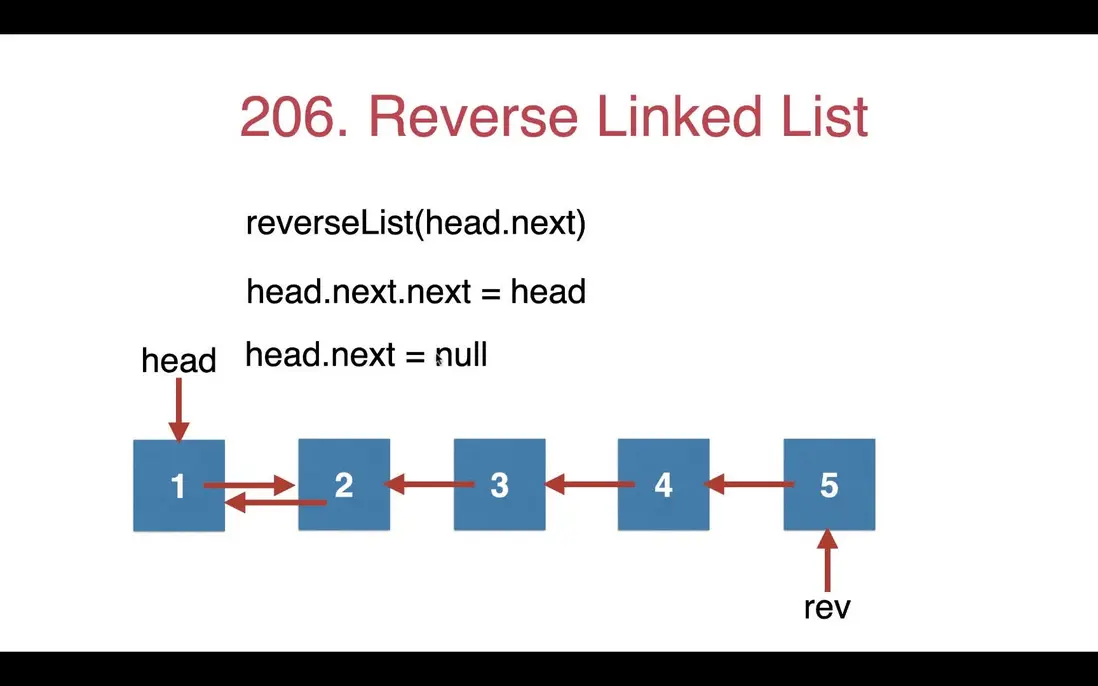
}雖然用循環就能找到鏈表 L1 的尾結點,但是還有更好更簡潔的方法。
鏈表 L1 的尾結點就是鏈表 L 頭結點的下一個結點。即可以通過鏈表 L 頭結點的下一個結點找到鏈表 L1 的尾結點,再讓鏈表 L1 尾結點的下一個結點指向鏈表 L 的頭結點。
改進後的代碼如下:
function reverseList($head) {
...
$reversedList = $this->reverseList($head->next);
$head->next->next = $head;
$head->next = null;
return $reversedList;
}過程:
需要繼續深入學習的內容:
- 引用
- 指針
- 遞歸