書籍完整目錄
3.3 理解 Redux 中間件
這一小節會講解 redux 中間件的原理,為下一節講解 redux 異步 action 做鋪墊,主要內容為:
-
Redux 中間件是什麼
-
使用 Redux 中間件
-
logger 中間件結構分析
-
applyMiddleware
-
中間件的執行過程
3.3.1 Redux 中間件是什麼
Redux moddleware provides a third-party extension point between dispatching an action, and the moment it reaches the reducer.
redux 提供了類似後端 Express 的中間件概念,本質的目的是提供第三方插件的模式,自定義攔截
action -> reducer 的過程。變為 action -> middlewares -> reducer 。這種機制可以讓我們改變數據流,實現如異步 action ,action 過濾,日誌輸出,異常報告等功能。
3.3.2 使用 Redux 中間件
Redux 提供了一個叫 applyMiddleware 的方法,可以應用多箇中間件,以日誌輸出中間件為例
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import createLogger from 'redux-logger'
import rootReducer from './reducers'
const loggerMiddleware = createLogger()
const initialState = {}
return createStore(
rootReducer,
initialState,
applyMiddleware(
loggerMiddleware
)
)3.3.3 logger 中間件結構分析
看看 redux-logger 的源碼結構
function createLogger(options = {}) {
/**
* 傳入 applyMiddleWare 的函數
* @param {Function} { getState }) [description]
* @return {[type]} [description]
*/
return ({ getState }) => (next) => (action) => {
let returnedValue;
const logEntry = {};
logEntry.prevState = stateTransformer(getState());
logEntry.action = action;
// ....
returnedValue = next(action);
// ....
logEntry.nextState = stateTransformer(getState());
// ....
return returnedValue;
};
}
export default createLogger;Logger 中這樣的結構 ({ getState }) => (next) => (action) => {} 看起來是很奇怪的,這種設計如果沒有 es6 的箭頭函數,擴展下來就是
/**
* getState 可以返回最新的應用 store 數據
*/
function ({getState}) {
/**
* next 表示執行後續的中間件,中間件有可能有多個
*/
return function (next) {
/**
* 中間件處理函數,參數為當前執行的 action
*/
return function (action) {...}
}
}這樣的結構本質上就是為了將 middleware 串聯起來執行,為了分析 middleware 的執行順序,還得看看 applyMiddleware 的實現
3.3.4 applyMiddleware 分析
下面是 applyMiddleware 完整的代碼,參數為 middlewares 數組:
import compose from './compose'
/**
* Creates a store enhancer that applies middleware to the dispatch method
* of the Redux store. This is handy for a variety of tasks, such as expressing
* asynchronous actions in a concise manner, or logging every action payload.
*
* See `redux-thunk` package as an example of the Redux middleware.
*
* Because middleware is potentially asynchronous, this should be the first
* store enhancer in the composition chain.
*
* Note that each middleware will be given the `dispatch` and `getState` functions
* as named arguments.
*
* @param {...Function} middlewares The middleware chain to be applied.
* @returns {Function} A store enhancer applying the middleware.
*/
export default function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
return (createStore) => (reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) => {
var store = createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer)
var dispatch = store.dispatch
var chain = []
var middlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (action) => dispatch(action)
}
chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI))
dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch)
return {
...store,
dispatch
}
}
}-
applyMiddleware執行過後返回一個閉包函數,目的是將創建store的步驟放在這個閉包內執行,這樣middleware就可以共享store對象。 -
middlewares數組 map 為新的middlewares數組,包含了middlewareAPI -
compose方法將新的middlewares和store.dispatch結合起來,生成一個新的dispatch方法 -
返回的
store新增了一個dispatch方法, 這個新的dispatch方法是改裝過的dispatch,也就是封裝了中間件的執行。
所以關鍵點來到了 compose 方法了,下面來看一下 compose 的設計:
export default function compose(...funcs) {
if (funcs.length === 0) {
return arg => arg
}
if (funcs.length === 1) {
return funcs[0]
}
const last = funcs[funcs.length - 1]
const rest = funcs.slice(0, -1)
return (...args) => rest.reduceRight((composed, f) => f(composed), last(...args))
}可以看到 compose 方法實際上就是利用了 Array.prototype.reduceRight 。如果對 reduceRight 不是很熟悉,來看看下面的一個例子就清晰了:
/**
* [description]
* @param {[type]} previousValue [前一個項]
* @param {[type]} currentValue [當前項]
*/
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4].reduceRight(function(previousValue, currentValue, index, array) {
return previousValue + currentValue;
}, 10);執行結果:
| # | previousValue | currentValue | return value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 第一次 | 10 | 4 | 14 |
| 第二次 | 14 | 3 | 17 |
| 第三次 | 17 | 2 | 19 |
| 第四次 | 19 | 1 | 20 |
| 第五次 | 20 | 0 | 20 |
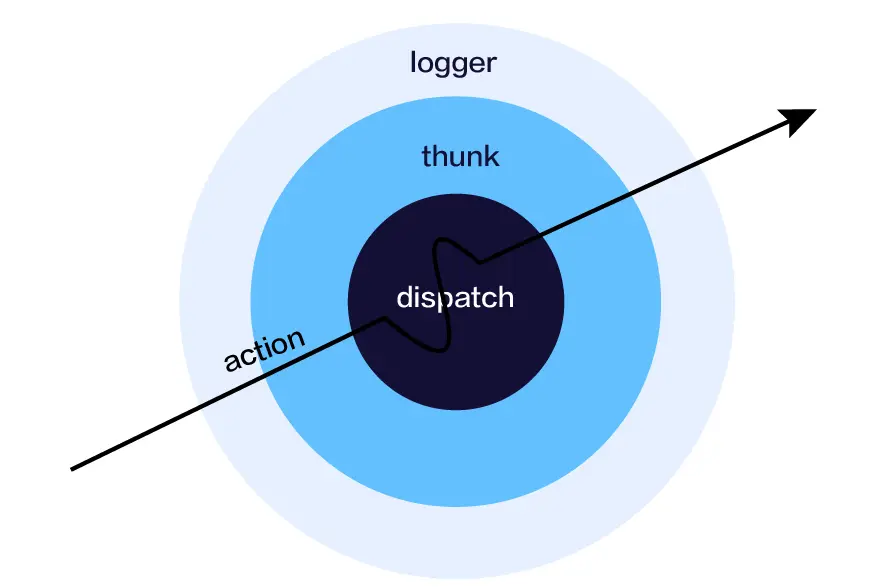
3.3.5 理解中間件的執行過程
通過上面的 applyMiddleware 和 中間件的結構,假設應用瞭如下的中間件: [A, B, C],一個 action 的完整執行流程
初始化階段
一箇中間件的結構為
function ({getState}) {
return function (next) {
return function (action) {...}
}
}初始化階段一:middlewares map 為新的 middlewares
chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI))執行過後,middleware 變為了
function (next) {
return function (action) {...}
}初始化階段二:compose 新的 dispatch
const newDispatch = compose(newMiddlewares)(store.dispatch)dispatch 的實現為 reduceRight, 當一個新的 action 來了過後
/**
* 1. 初始值為: lastMiddleware(store.dispatch)
* 2. previousValue: composed
* 3. currentValue: currentMiddleware
* 4. return value: currentMiddleware(composed) => newComposed
*/
rest.reduceRight((composed, f) => f(composed), last(...args))composed 流程
reduceRight 的執行過程:
初始時候
-
initialValue: composedC = C(store.dispatch) = function C(action) {}
-
next 閉包: store.dispatch
第一次執行:
-
previousValue(composed): composedC
-
currentValue(f): B
-
return value: composedBC = B(composedC) = function B(action){}
-
next 閉包 composedC
第二次執行:
-
previousValue(composed): composedBC
-
currentValue(f): A
-
return value: composedABC = A(composedBC) = function A(action){}
-
next 閉包 composedBC
最後的返回結果為 composedABC
執行階段
-
dispatch(action)等於composedABC(action)等於執行function A(action) {...} -
在函數 A 中執行
next(action), 此時 A 中next為composedBC,那麼等於執行composedBC(action)等於執行function B(action){...} -
在函數 B 中執行
next(action), 此時 B 中next為composedC,那麼等於執行composedC(action)等於執行function C(action){...} -
在函數 C 中執行
next(action), 此時 C 中next為store.dispatch即 store 原生的 dispatch, 等於執行store.dispatch(action) -
store.dispatch 會執行 reducer 生成最新的 store 數據
-
所有的 next 執行完過後開始回溯
-
執行函數 C 中 next 後的代碼
-
執行函數 B 中 next 後的代碼
-
執行函數 A 中 next 後的代碼
整個執行 action 的過程為 A -> B -> C -> dispatch -> C -> B -> A