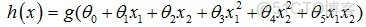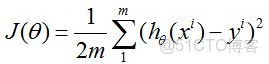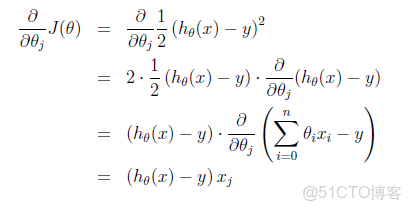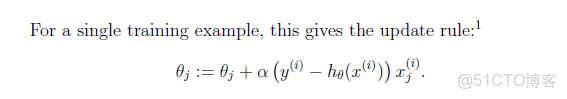斯坦福大學公開課 :機器學習課程 [第2集] 監督學習應用.梯度下降
http://v.163.com/movie/2008/1/B/O/M6SGF6VB4_M6SGHJ9BO.html
Matlab實現線性迴歸和邏輯迴歸: Linear Regression & Logistic Regression
octave入門教程
關於非線性優化fminbnd函數的説明(僅供新手參考)(也可作為fmincon函數的參考)
http://www.docin.com/p-214776767.html
由於是剛開始接觸ML和MATLAB,所以記錄一些比較簡單的筆記。
個人實驗中未使用MATLAB,而是使用了Octave作為替代,區別只是把函數結束的end改成endfunction即可,其他部分和matlab保持一致。
文中主要框架內容參考
第一部分:基本模型
在解決擬合問題的解決之前,我們首先回憶一下線性迴歸基本模型。
設待擬合參數 θn*1 和輸入參數[ xm*n, ym*1 ] 。
對於各類擬合我們都要根據梯度下降的算法,給出兩部分:
① cost function(指出真實值y與擬合值h<hypothesis>之間的距離):給出cost function 的表達式,每次迭代保證cost function的量減小;給出梯度gradient,即cost function對每一個參數θ的求導結果。
function
② Gradient_descent(主函數):用來運行梯度下降算法,調用上面的cost function進行不斷迭代,直到最大迭代次數達到給定標準或者cost function返回值不再減小。
function
線性迴歸:擬合方程為hθ(x)=θ0x0+θ1x1+…+θnxn,當然也可以有xn的冪次方作為線性迴歸項(如
),這與普通意義上的線性不同,而是類似多項式的概念。其cost function 為:
第二部分:Y=θ0+θ1X1型---線性迴歸(直線擬合)
在Matlab 線性擬合 & 非線性擬閤中我們已經講過如何用matlab自帶函數fit進行直線和曲線的擬合,非常實用。而這裏我們是進行ML課程的學習,因此研究如何利用前面講到的梯度下降法(gradient descent)進行擬合。
cost function:
[cpp] view plain copy
1. function [ jVal,gradient ] = costFunction2( theta )
2. %COSTFUNCTION2 Summary of this function goes here
3. % linear regression -> y=theta0 + theta1*x
4. % parameter: x:m*n theta:n*1 y:m*1 (m=4,n=1)
5. %
6.
7. %Data
8. x=[1;2;3;4];
9. y=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8];
10. m=size(x,1);
11.
12. hypothesis = h_func(x,theta);
13. delta = hypothesis - y;
14. jVal=sum(delta.^2);
15.
16. gradient(1)=sum(delta)/m;
17. gradient(2)=sum(delta.*x)/m;
18.
19. end
其中,h_func是hypothesis的結果:
[cpp] view plain copy
1. function [res] = h_func(inputx,theta)
2. %H_FUNC Summary of this function goes here
3. % Detailed explanation goes here
4.
5.
6. %cost function 2
7. res= theta(1)+theta(2)*inputx;
8. end
Gradient_descent:
[cpp] view plain copy
1. function [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag]=Gradient_descent( )
2. %GRADIENT_DESCENT Summary of this function goes here
3. % Detailed explanation goes here
4.
5. 'GradObj','on','MaxIter',100);
6. initialTheta = zeros(2,1);
7. [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction2,initialTheta,options);
8.
9. endresult:
[cpp] view plain copy
1. >> [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = Gradient_descent()
2.
3. Local minimum found.
4.
5. Optimization completed because the size of the gradient is less than
6. the default value of the function tolerance.
7.
8. <stopping criteria details>
9.
10.
11. optTheta =
12.
13. 0.3000
14. 0.8600
15.
16.
17. functionVal =
18.
19. 0.0720
20.
21.
22. exitFlag =
23.
24. 1
驗證:
[cpp] view plain copy
1. function [ parameter ] = checkcostfunc( )
2. %CHECKC2 Summary of this function goes here
3. % check if the cost function works well
4. % check with the matlab fit function as standard
5.
6. %check cost function 2
7. x=[1;2;3;4];
8. y=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8];
9.
10. EXPR= {'x','1'};
11. p=fittype(EXPR);
12. parameter=fit(x,y,p);
13.
14. end運行結果:
[cpp] view plain copy
1. >> checkcostfunc()
2.
3. ans =
4.
5. Linear model:
6. ans(x) = a*x + b
7. Coefficients (with 95% confidence bounds):
8. a = 0.86 (0.4949, 1.225)
9. b = 0.3 (-0.6998, 1.3)和我們的結果一樣。下面畫圖:
[cpp] view plain copy
1. function PlotFunc( xstart,xend )
2. %PLOTFUNC Summary of this function goes here
3. % draw original data and the fitted
4.
5.
6.
7. %===================cost function 2====linear regression
8. %original data
9. x1=[1;2;3;4];
10. y1=[1.1;2.2;2.7;3.8];
11. %plot(x1,y1,'ro-','MarkerSize',10);
12. plot(x1,y1,'rx','MarkerSize',10);
13. hold on;
14.
15. %fitted line - 擬合曲線
16. x_co=xstart:0.1:xend;
17. y_co=0.3+0.86*x_co;
18. %plot(x_co,y_co,'g');
19. plot(x_co,y_co);
20.
21. hold off;
22. end
註解:
1 single training example公式
More than one training example:
θ:θ(i)-=gradient(i),其中gradient(i)是J(θ)對θi求導的函數式,此處令α=1/m,並且gradient(1)在matlab程序中實際對應x(0),而x(0)=1,把代入上面的公式可以得到gradient(1)=sum(delta)/m;
註解2
1. options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',100);
2. initialTheta = zeros(2,1);
3. [optTheta,functionVal,exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction2,initialTheta,options);初學matlab優化,迭代中止後,經常一頭霧水。參看幫助後仍似懂非懂。下面關於fminbnd函數的説明(也可作為fmincon函數的參考)對於新手也許會有幫助,不當之處請指正。
目標函數fun:
需要最小化的目標函數。fun函數需要輸入標量參數x,返回x處的目標函數標量值f。可以將fun函數指定為命令行,如
x = fminbnd(inline('sin(x*x)'),x0)
同樣,fun參數可以是一個包含函數名的字符串。對應的函數可以是M文件、內部函數或MEX文件。若fun='myfun',則M文件函數myfun.m必須有下面的形式:
function f = myfun(x)
f = ... %計算x處的函數值。
若fun函數的梯度可以算得,且options.GradObj設為'on'(用下式設定),
options = optimset('GradObj','on')
則fun函數必須返回解x處的梯度向量g到第二個輸出變量中去。注意,當被調用的fun函數只需要一個輸出變量時(如算法只需要目標函數的值而不需要其梯度值時),可以通過核對nargout的值來避免計算梯度值。
function [f,g] = myfun(x)
f = ... %計算x處得函數值。
if nargout > 1 %調用fun函數並要求有兩個輸出變量。
g = ... %計算x處的梯度值。
end