ffmpeg-python幀處理終極指南:像素級視頻控制
你還在為逐幀處理視頻而編寫冗長的FFmpeg命令行嗎?還在為像素級操作與Python數據科學工具銜接而煩惱嗎?本文將通過ffmpeg-python庫實現從視頻解碼到幀數據提取的全流程控制,無需複雜命令行知識,即可讓你在5分鐘內掌握視頻幀的精準操作。讀完本文你將獲得:
- 從視頻中提取指定幀的完整代碼方案
- 幀數據與NumPy數組的無縫轉換技巧
- 實時幀處理與視頻重建的高效工作流
- 基於AI模型的幀內容分析實戰案例
核心原理:ffmpeg-python幀處理架構
ffmpeg-python通過聲明式API將複雜的FFmpeg命令圖轉化為可讀性強的Python代碼。幀處理的核心在於通過filter()方法鏈實現視頻流的精準控制,其內部通過 Directed Acyclic Graph(DAG,有向無環圖)管理數據流,如dag.py中定義的拓撲排序算法確保幀處理的順序性。
關鍵模塊協作流程:
- 輸入模塊:ffmpeg/_ffmpeg.py的
input()函數創建視頻源節點 - 過濾模塊:ffmpeg/_filters.py提供
select、trim等幀操作濾鏡 - 輸出模塊:通過
output('pipe:')將幀數據重定向到內存管道 - 執行模塊:ffmpeg/_run.py的
run()方法啓動進程並捕獲輸出
基礎操作:單幀提取實戰
提取視頻中指定幀是最常見的幀處理需求。examples目錄下的read_frame_as_jpeg.py提供了完整實現,核心代碼僅需6行:
def read_frame_as_jpeg(in_filename, frame_num):
out, err = (
ffmpeg
.input(in_filename) # 創建輸入流
.filter('select', 'gte(n,{})'.format(frame_num)) # 選擇第N幀
.output('pipe:', vframes=1, format='image2', vcodec='mjpeg') # 輸出到管道
.run(capture_stdout=True) # 執行並捕獲輸出
)
return out關鍵參數解析
vframes=1:僅輸出1幀數據format='image2':啓用單幀圖像輸出模式capture_stdout=True:將幀數據捕獲到Python字節流
運行示例:
python examples/read_frame_as_jpeg.py examples/in.mp4 15 > frame15.jpg該示例從examples/in.mp4中提取第15幀,並保存為JPEG圖像。實際應用中可通過調整filter('select', ...)的表達式實現複雜選擇邏輯,如提取I幀(關鍵幀)或特定時間點的幀。
進階技巧:幀數據與NumPy集成
對於計算機視覺任務,通常需要將幀數據轉換為NumPy數組進行處理。ffmpeg-python與NumPy的結合可通過管道輸出原始像素數據實現:
import numpy as np
def extract_frame_as_numpy(in_filename, frame_num):
# 輸出原始RGB24格式數據
out, _ = (
ffmpeg
.input(in_filename)
.filter('select', f'eq(n,{frame_num})')
.output('pipe:', format='rawvideo', pix_fmt='rgb24', vframes=1)
.run(capture_stdout=True)
)
# 獲取視頻分辨率
probe = ffmpeg.probe(in_filename)['streams'][0]
width, height = probe['width'], probe['height']
# 轉換為NumPy數組 (height, width, 3)
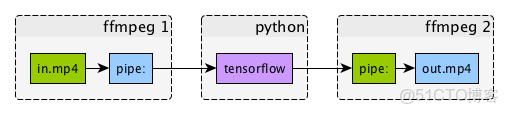
return np.frombuffer(out, np.uint8).reshape([height, width, 3])上述代碼使用ffmpeg/_probe.py中的probe()函數獲取視頻元數據,確保數組維度正確。轉換後的NumPy數組可直接輸入OpenCV、TensorFlow等框架進行後續處理,如examples/tensorflow_stream.py所示的實時視頻流推理。
高級應用:AI驅動的幀內容分析
結合幀提取與AI模型可實現智能視頻分析。以下案例使用預訓練的ResNet50模型對視頻幀進行分類:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.applications.resnet50 import ResNet50, preprocess_input
def analyze_frame_content(frame_array):
# 預處理幀數據
img = tf.image.resize(frame_array, (224, 224))
img = preprocess_input(img)
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
# 加載模型並預測
model = ResNet50(weights='imagenet')
preds = model.predict(img)
# 返回Top-3預測結果
from tensorflow.keras.applications.resnet50 import decode_predictions
return decode_predictions(preds, top=3)[0]
# 使用前面定義的extract_frame_as_numpy獲取幀數據
frame = extract_frame_as_numpy('examples/in.mp4', 42)
print(analyze_frame_content(frame))該流程利用ffmpeg-python高效解碼與TensorFlow強大的圖像識別能力,實現了從視頻到內容理解的端到端解決方案。更多類似案例可參考examples/ffmpeg-numpy.ipynb的Jupyter筆記本教程。
性能優化:批量幀處理最佳實踐
處理長視頻或高分辨率素材時,需採用批處理策略提升效率。推薦使用以下模式:
- 時間分片處理:使用
trim(start=10, end=20)濾鏡截取視頻片段 - 多線程執行:通過
run_async()實現非阻塞幀提取 - 內存控制:定期清理未使用幀數據,避免內存溢出
def batch_extract_frames(in_filename, start_frame, end_frame, step=5):
frames = []
# 創建異步處理進程
process = (
ffmpeg
.input(in_filename)
.filter('select', f'between(n,{start_frame},{end_frame})')
.filter('select', f'not(mod(n,{step}))') # 每隔step幀提取一次
.output('pipe:', format='rawvideo', pix_fmt='rgb24')
.run_async(pipe_stdout=True)
)
# 讀取所有幀數據
while True:
in_bytes = process.stdout.read(width * height * 3)
if not in_bytes:
break
frames.append(np.frombuffer(in_bytes, np.uint8).reshape([height, width, 3]))
process.wait()
return frames總結與擴展
通過ffmpeg-python庫,我們實現了視頻幀的精準控制,從簡單提取到AI分析的全流程覆蓋。核心優勢在於:
- 聲明式API:將複雜濾鏡鏈轉化為可讀的Python代碼
- 內存高效:直接通過管道獲取幀數據,避免中間文件
- 生態集成:與NumPy、TensorFlow等數據科學工具無縫銜接
官方文檔doc/src/index.rst提供了更多高級濾鏡的使用方法,建議結合examples目錄下的12個實戰案例深入學習。如需處理音頻幀,可參考asplit()濾鏡和音頻相關示例。