1、數據倉庫
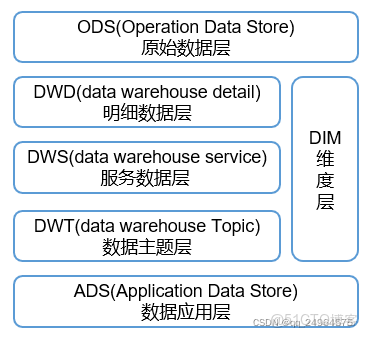
數倉分層:ODS(Operational Data Store)直接存放原始數據,DWD(Data Warehouse Detail)對數據進行清洗 ,DWS(Data Warehouse Service)輕度彙總(存儲每天數據的彙總),DWT(Data Warehouse Topic)重度彙總(存儲一段時間數據的彙總),DIM維度層(事實表的描述信息,何人、何時、何地,即分析時所站的角度),ADS(Application Data Store)提供報表數據;
分層原因:簡化複雜問題,減少重複開發,隔離原始數據;
幾個概念:1)數據集市部門級的,2)數據倉庫公司級的,3)數據湖包含各種類型的數據;
一文看懂:什麼是數據庫、數據湖、數據倉庫、湖倉一體、智能湖倉?
2、關係建模與維度建模
三大範式:1NF消除非原子性,2NF消除部分依賴,3NF消除傳遞依賴,BCNF消除主屬性對碼的部分依賴。符合3NF要求的數據庫設計,基本上解決了數據冗餘過大,插入異常,修改異常,刪除異常的問題。
詳解第一範式、第二範式、第三範式、BCNF範式
關係模型嚴格遵循第三範式(3NF),數據冗餘程度低,數據的一致性容易得到保證。由於數據分佈於眾多的表中,查詢會相對複雜,在大數據的場景下,查詢效率相對較低。
維度模型以數據分析作為出發點,不遵循三範式,故數據存在一定的冗餘。維度模型面向業務,將業務用事實表和維度表呈現出來。表結構簡單,故查詢簡單,查詢效率較高。
雪花模型、星型模型和星座模型
在DWD層,以業務過程為建模驅動,基於每個具體業務過程的特點,構建最細粒度的明細層事實表。DWS層、DWT層和ADS層都是以需求為驅動,和維度建模已經沒有關係了。事實表可做適當的寬表化處理。ADS層對特定系統各大主題指標分別進行分析。
Hive on Spark大體與Spark on Hive結構類似,只是SQL引擎(SQL的解析優化)不同,但是計算引擎都是Spark、存儲引擎都是Hive!
大數據Hadoop之——Spark on Hive 和 Hive on Spark的區別與實現
Oracle只有一個數據庫名,一般對應一個實例(數據庫名和實例名不一定相同),但是Oracle的真正應用集羣(Real Application Clusters,RAC)有多個實例同時裝載並打開一個數據庫,允許在集羣環境中的多台計算機上操作數據庫;使用Oracle_SID來標識一個實例,使用Service_name來標識一個數據庫;一個實例下面有多個Schema,一個Schema下面有多張表,Oracle中Schema與User同名、同量。連接Oracle數據庫:sqlplus 用户名/密碼@ip地址[:端口]/service_name。
MySQL可以配置多個實例(默認情況是一個實例),使用IP:PORT區分不同實例,一個實例下有多個Schema(與Database等效),一個Schema下面有多張表。
在Oracle、MySql中,特定IP:PORT下對應多個Schema,Oracle中Database與Schema是一對多的關係(口語就是,一個IP:PORT對應一個數據庫),Mysql中Database與Schema是等效關係(口語就是,一個IP:PORT對應多個數據庫)。Oracle中的多個實例通過SID標識(RAC時訪問同一份數據,其他情況不一定),MySql中多個實例通過IP:PORT標識(用於主從架構時訪問同一份數據,其他情況不一定)
如果系統在非常大的數據集中包含多個索引表,則很難在索引表與原始數據之間保持一致性。可能圍繞最終一致性模型設計應用程序。例如,要插入,更新或刪除數據,應用程序可以將消息發佈到隊列,並讓單獨的任務執行操作並維護異步引用此數據的索引表。有關實現最終一致性的更多信息,請參閲數據一致性入門。
索引表模式
ORACLE索引表學習
數據庫實例名是用於和操作系統之間的聯繫,用於對外部連接時使用。在操作系統中,要取得於數據庫之間的聯繫必須通過實例名。比如:要和某一個數據庫Server進行連接,必須通過實例名,只知道數據庫名是沒用的,與數據庫名不同的是,數據庫實例名在數據庫的安裝或者創建之後,是可以被修改的。數據庫在安裝之後,對應的實例名會被寫入到數據庫控制參數文件pfile(格式如下代碼塊)中,可以通過修改這個文件,來修改Oracle數據庫的實例名,當然,數據庫名是不能修改的!在很多情況下,對於數據庫實例名的描述,有些時候使用(instance_name)參數,有些時候使用Oracle_SID參數,這兩個都是數據庫實例名參數,但是以下是他們的區別:
a、Oracle_SID是操系統環境變量
b、instance_name是Oracle數據庫配置文件參數
c、操作系統想要獲得數據庫實例名必須通過系統環境變量Oracle_SID,而Oracle數據庫如果想獲得數據庫實例名,則可以通過參數文件得到。
db_name="orcl" #(數據庫名:不允許修改)
db_domain=dbcenter.toys.com
instance_name=orcl #(數據庫實例名:可以修改,可以與db_name相同也可不同)
service_names=orcl.dbcenter.toys.com
control_file=(...............
.........一鍵獲取完整項目代碼
powershell
Oracle 數據庫名、實例名、Oracle_SID
實例就是一組操作系統進程(或者是一個多線程的進程)以及一些內存。這些進程可以操作數據庫;而數據庫只是一個文件集合(包括數據文件、臨時文件、重做日誌文件和控制文件)。在任何時刻,一個實例只能有一組相關的文件(與一個數據庫關聯)。大多數情況下,反過來也成立:一個數據庫上只有一個實例對其進行操作。不過,Oracle的真正應用集羣(Real Application Clusters,RAC)是一個例外,這是Oracle提供的一個選項,允許在集羣環境中的多台計算機上操作,這樣就可以有多台實例同時裝載並打開一個數據庫(位於一組共享物理磁盤上)。由此,我們可以同時從多台不同的計算機訪問這個數據庫。Oracle RAC能支持高度可用的系統,可用於構建可擴縮性極好的解決方案。
15.Oracle的用户、Schema、數據庫、表空間、數據文件的相互關係
在8i以前,使用SID來表示標識數據庫的一個實例,但是在Oracle的並行環境中,一個數據庫對應多個實例,這樣就需要多個網絡服務名,設置繁瑣。為了方便並行環境中的設置,引進了Service_name參數,該參數對應一個數據庫,而不是一個實例。一句話來説就是:SID是對內的,是實例級別的一個名字,用來內部之間稱呼用。SERVICE_name是對外的,是數據庫級別的一個名字,用來告訴外面的人,我數據庫叫"SERVICE_NAME"。
Oracle 服務名/實例名,Service_name 和Sid的區別
不用進行網絡配置,其實就是tnsname.ora文件,但只支持oracle10G以上。
命令:sqlplus 用户名/密碼@ip地址[:端口]/service_name [as sysdba]
示例:sqlplus sys/pwd@ip:1521/test as sysdba (注意這裏的test是tnsnames.ora中的SERVICE_NAME,而非其它)
備註:使用默認1521端口時可省略輸入
一鍵獲取完整項目代碼
格式一: Oracle JDBC Thin using a ServiceName:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//<host>:<port>/<service_name>
Example: jdbc:oracle:thin:@//192.168.2.1:1521/XE
注意這裏的格式,@後面有//, 這是與使用SID的主要區別。
這種格式是Oracle 推薦的格式,因為對於集羣來説,每個節點的SID 是不一樣的,
但是SERVICE_NAME 確可以包含所有節點。
格式二: Oracle JDBC Thin using an SID:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@<host>:<port>:<SID>
Example: jdbc:oracle:thin:@192.168.2.1:1521:X01A
Note:
Support for SID is being phased out. Oracle recommends that users switch over to usingservice names.
格式三:Oracle JDBC Thin using a TNSName:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@<TNSName>
Example: jdbc:oracle:thin:@GL
Note:
Support for TNSNames was added in the driver release 10.2.0.1``一鍵獲取完整項目代碼
在關係型數據庫中,分三級:database.schema.table。即一個數據庫下面可以包含多個schema,一個schema下可以包含多個數據庫對象,比如表、存儲過程、觸發器等。但並非所有數據庫都實現了schema這一層,比如mysql直接把schema和database等效了,PostgreSQL、Oracle、SQL server等的schema也含義不太相同。
在Oracle數據庫中不能新建一個schema,要想創建一個schema,只能通過創建一個用户的方法解決,在創建一個用户的同時為這個用户創建一個與用户名同名的schem並作為該用户的缺省shcema。即schema的個數同user的個數相同,而且schema名字同user名字一一 對應並且相同。
MySQL實例指的是MySQL進程及其所持有的內存結構,我們對數據的操作實際上是通過MySQL實例來訪問物理數據庫文件的。在實際生產中,可以用一個IP:PORT組合來表示一個實例。如“192.168.7.101:3307”這個MySQL實例表示在主機上起了一個MySQL服務,它的服務端口是3307。
mysql有實例名這個概念,MySQL的一些概念筆記
mysql中建立一個會話,不是和具體的數據庫相連接,而是跟instance建立會話,在一個實體機上可以建立多個instance,通過port來區分實例。而一個實例可以建立多個數據庫。即一個會話可以操作一個實例上的多個數據庫。MySQL 中 Schema 等價於數據庫。
mysql中數據庫database、Schema、實例instance、會話session的關係
mysql 多實例配置記錄(多配置文件)
3、數倉環境搭建
啓動Spark歷史服務器
[atguigu@hadoop102 conf]$ hadoop dfs -mkdir /directory
[atguigu@hadoop102 conf]$ start-history-server.sh一鍵獲取完整項目代碼
啓動Spark的thriftserver(Spark對HiveServer2的實現),使用DBeaver連接Hive。Spark Thrift Server本身的Server服務就是一個Driver,直接接收sql執行,也就是所有的session都共享一個Application,因此它能使用的集羣資源就和單個Application直接掛鈎。
Spark On Yarn的兩種模式yarn-cluster和yarn-client深度剖析
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop]$ start-thriftserver.sh一鍵獲取完整項目代碼
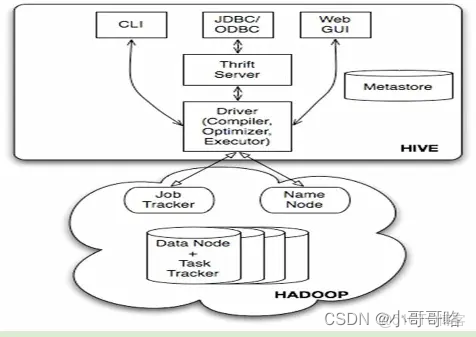
hive與hiveserver關係圖
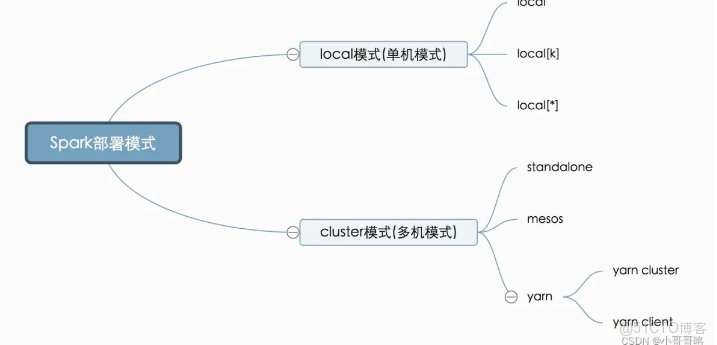
我們要部署Spark這套計算框架,有多種方式,可以部署到一台計算機,也可以是多台(cluster)。我們要去計算數據,就必須要有計算機幫我們計算,當然計算機越多(集羣規模越大),我們的計算力就越強。但有時候我們只想在本機做個試驗或者小型的計算,因此直接部署在單機上也是可以的。Spark部署方式可以用如下圖形展示:
Spark啓動時的master參數以及Spark的部署方式
通過Spark Thrift Server創建Hive表:hive -e,spark-sql -e (Spark通過Spark-SQL使用hive語句,操作hive,底層運行的還是 spark rdd)
Hive中的內部表、外部表、分區表和分桶表
Spark on Hive & Hive on Spark,傻傻分不清楚
Spark SQL 與 Hive 的區別簡介【學習筆記】
Hive on Spark配置
hive 的註釋(comment) 中文亂碼的解決方法(親測有效)[記得重啓hadoop、hive、Spark Thrift Server]
4、數倉實戰
In Spark 3.0, SHOW CREATE TABLE table_identifier always returns Spark DDL, even when the given table is a Hive SerDe table. For generating Hive DDL, use SHOW CREATE TABLE table_identifier AS SERDE command instead.
sql-migration-guide
hive的serde解析與應用
增量表:記錄更新週期內新增的數據,即在原表中數據的基礎上新增本週期內產生的新數據;
全量表:記錄更新週期內的全量數據,無論數據是否有變化都需要記錄;
拉鍊表:一種數據存儲和處理的技術方式,可以記錄數據的歷史信息,記錄數據從開始一直到當前所有變化的信息。
真正秒懂增量表、全量表和拉鍊表
Spark為了提高性能會緩存Parquet的元數據信息。當更新了Parquet表時,緩存的元數據信息未更新,導致Spark SQL查詢不到新插入的數據作業執行報錯,報錯信息參考如下:
SQL 錯誤: Error running query: java.io.FileNotFoundException: File does not exist:
更新hive的metastore信息:Hive 修復分區 MSCK REPAIR TABLE的使用
更新Spark-sql的metastore:REFRESH TABLE刷新表元數據
根據ORC和parquet的要求,一般有如下配合
① ORC格式存儲,Snappy壓縮
② Parquet格式存儲,Lzo壓縮
③ Parquet格式存儲,Snappy壓縮
在實際生產中,使用Parquet存儲,lzo壓縮的方式更為常見,這種情況下可以避免由於讀取不可分割大文件引發的數據傾斜(實際上能不能切片是看文件格式的,parquet本身支持切片採用lzo只是它的內部在進行壓縮,切片只看文件格式,parquet支持切片所以沒問題的)。 但是,如果數據量並不大(預測不會有超大文件,若干G以上)的情況下,使用ORC存儲,snappy壓縮的效率還是非常高的。
Hive數倉建表該選用ORC還是Parquet,壓縮選LZO還是Snappy?
LZO是一個適合實時解壓、壓縮的壓縮庫,LZOP基於LZO庫的壓縮解壓工具,有了壓縮解壓庫LZO,還不能直接操作文件壓縮解壓,需要LZOP;LZOP輸出後綴文件就是.lzo,而且LZOP支持通過DistributedLzoIndexer生成index切片索引,而LZO本身是不支持索引的。
關於lzop和lzo區別,以及lzop文件格式和parquet文件格式加lzo壓縮區別
lateral view UDTF(expression) tableAliasName as colAliasName
其中UDTF(expression)表示行轉列的生成函數,即一行變為多行的函數,比如explode,當然也可以通過UDF自定義函數把一行轉為多行,或者UDF返回Array再通過explode炸成多行。
Hive中explode和lateral view組合的用法
解決:FAILED: SemanticException [Error 10096]: Dynamic partition strict mode requires at least one static partition column. To turn this off set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict
因為要做動態分區, 所以要先設定partition參數,由於default是false, 需要額外下指令打開這個開關,default是strick, 表示不允許動態分區, 所以要改成nostrick
解決方法:
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true;
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nostrick;Hive動態分區
5、數倉表的設計
數倉建模—寬表的設計
附錄
PS:針對Spark on Hive(Spark Thrift Server)的一些配置
[atguigu@hadoop102 conf]$ cat /opt/module/spark-3.0.0-bin-hadoop3.2/conf/hive-site.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?>
<configuration>
<!-- 修改Hive的計算引擎 -->
<property>
<name>hive.execution.engine</name>
<value>tez</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.container.size</name>
<value>1024</value>
</property>
<!-- hive窗口打印默認庫和表頭 -->
<property>
<name>hive.cli.print.header</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.print.current.db</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<!-- 指定hiveserver2連接的host -->
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.bind.host</name>
<value>hadoop102</value>
</property>
<!-- 指定hiveserver2連接的端口號 -->
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.port</name>
<value>10000</value>
</property>
<!-- jdbc連接的URL -->
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://hadoop102:3306/metastore?useSSL=false</value>
</property>
<!-- jdbc連接的Driver-->
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value>
</property>
<!-- jdbc連接的username-->
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name>
<value>root</value>
</property>
<!-- jdbc連接的password -->
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name>
<value>root</value>
</property>
<!-- Hive默認在HDFS的工作目錄 -->
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.warehouse.dir</name>
<value>/user/hive/warehouse</value>
</property>
<!-- Hive元數據存儲的驗證 -->
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.schema.verification</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<!-- 元數據存儲授權 -->
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.event.db.notification.api.auth</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<!-- 開啓動態分區 -->
<property>
<name>hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode</name>
<value>nonstrict</value>
</property>
</configuration>一鍵獲取完整項目代碼
xml
[atguigu@hadoop102 conf]$ cat /opt/module/spark-3.0.0-bin-hadoop3.2/conf/spark-defaults.conf
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
# Default system properties included when running spark-submit.
# This is useful for setting default environmental settings.
# Example:
# spark.master spark://master:7077
#是否記錄Spark任務日誌
spark.eventLog.enabled true
#Spark任務日誌的存儲路徑
spark.eventLog.dir hdfs://hadoop102:9820/directory
# spark.serializer org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer
# spark.driver.memory 5g
# spark.executor.extraJavaOptions -XX:+PrintGCDetails -Dkey=value -Dnumbers="one two three"
#Spark歷史服務器地址
spark.yarn.historyServer.address=hadoop102:18080
spark.history.ui.port=18080
#------------------------------------
#指定Spark master為yarn
spark.master=yarn
#Spark歷史服務器讀取歷史任務日誌的路徑
spark.history.fs.logDirectory=hdfs://hadoop102:9820/directory
#開啓Spark-sql自適應優化
spark.sql.adaptive.enabled=true
#開啓Spark-sql中Reduce階段分區數自適應
spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.enabled=true
#使用Hive提供的Parquet文件的序列化和反序列化工具,以兼容Hive
spark.sql.hive.convertMetastoreParquet=false
#使用老版的Parquet文件格式,以兼容Hive
spark.sql.parquet.writeLegacyFormat=true
#解決SPARK-21725問題
spark.hadoop.fs.hdfs.impl.disable.cache=true
#降低Spark-sql中類型檢查級別,兼容Hive
spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy=LEGACY
[atguigu@hadoop102 conf]$ cat /opt/module/hadoop-3.1.3/etc/hadoop/capacity-scheduler.xml
<!--
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License. See accompanying LICENSE file.
-->
<configuration>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-applications</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>
Maximum number of applications that can be pending and running.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-am-resource-percent</name>
<!-- 學習環境調大Application Master可以獲得的最大資源百分比,生產使用默認的0.1就可以 -->
<value>0.8</value>
<description>
Maximum percent of resources in the cluster which can be used to run
application masters i.e. controls number of concurrent running
applications.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.resource-calculator</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.yarn.util.resource.DefaultResourceCalculator</value>
<description>
The ResourceCalculator implementation to be used to compare
Resources in the scheduler.
The default i.e. DefaultResourceCalculator only uses Memory while
DominantResourceCalculator uses dominant-resource to compare
multi-dimensional resources such as Memory, CPU etc.
</description>
</property>
<!-- 指定hive隊列的資源額定容量 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.capacity</name>
<value>50</value>
</property>
<!-- 指定隊列中,用户提交job佔用集羣資源的百分比-->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.user-limit-factor</name>
<value>2</value>
</property>
<!-- 指定hive隊列的資源最大容量 -->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.maximum-capacity</name>
<value>100</value>
</property>
<!--指定隊列的工作狀態-->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.state</name>
<value>RUNNING</value>
</property>
<!--訪問權限,設定那些用户可以提交應用,*表示所有用户-->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_submit_applications</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<!--訪問權限,設定那些用户是管理者,*表示所有用户-->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_administer_queue</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<!--訪問權限,設定那些用户有優先,*表示所有用户平等-->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_application_max_priority</name>
<value>*</value>
</property>
<!--訪問權限,設定job的最大存活時間,-1表示沒有限定-->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.maximum-application-lifetime</name>
<value>-1</value>
</property>
<!--訪問權限,設定job的默認存活時間,-1表示沒有限定-->
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.default-application-lifetime</name>
<value>-1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.queues</name>
<value>default,hive</value>
<description>
The queues at the this level (root is the root queue).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.capacity</name>
<value>50</value>
<description>Default queue target capacity.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.user-limit-factor</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>
Default queue user limit a percentage from 0.0 to 1.0.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-capacity</name>
<value>60</value>
<description>
The maximum capacity of the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.state</name>
<value>RUNNING</value>
<description>
The state of the default queue. State can be one of RUNNING or STOPPED.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.acl_submit_applications</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can submit jobs to the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.acl_administer_queue</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can administer jobs on the default queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.acl_application_max_priority</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>
The ACL of who can submit applications with configured priority.
For e.g, [user={name} group={name} max_priority={priority} default_priority={priority}]
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-application-lifetime
</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
Maximum lifetime of an application which is submitted to a queue
in seconds. Any value less than or equal to zero will be considered as
disabled.
This will be a hard time limit for all applications in this
queue. If positive value is configured then any application submitted
to this queue will be killed after exceeds the configured lifetime.
User can also specify lifetime per application basis in
application submission context. But user lifetime will be
overridden if it exceeds queue maximum lifetime. It is point-in-time
configuration.
Note : Configuring too low value will result in killing application
sooner. This feature is applicable only for leaf queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.default-application-lifetime
</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
Default lifetime of an application which is submitted to a queue
in seconds. Any value less than or equal to zero will be considered as
disabled.
If the user has not submitted application with lifetime value then this
value will be taken. It is point-in-time configuration.
Note : Default lifetime can't exceed maximum lifetime. This feature is
applicable only for leaf queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.node-locality-delay</name>
<value>40</value>
<description>
Number of missed scheduling opportunities after which the CapacityScheduler
attempts to schedule rack-local containers.
When setting this parameter, the size of the cluster should be taken into account.
We use 40 as the default value, which is approximately the number of nodes in one rack.
Note, if this value is -1, the locality constraint in the container request
will be ignored, which disables the delay scheduling.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.rack-locality-additional-delay</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
Number of additional missed scheduling opportunities over the node-locality-delay
ones, after which the CapacityScheduler attempts to schedule off-switch containers,
instead of rack-local ones.
Example: with node-locality-delay=40 and rack-locality-delay=20, the scheduler will
attempt rack-local assignments after 40 missed opportunities, and off-switch assignments
after 40+20=60 missed opportunities.
When setting this parameter, the size of the cluster should be taken into account.
We use -1 as the default value, which disables this feature. In this case, the number
of missed opportunities for assigning off-switch containers is calculated based on
the number of containers and unique locations specified in the resource request,
as well as the size of the cluster.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.queue-mappings</name>
<value></value>
<description>
A list of mappings that will be used to assign jobs to queues
The syntax for this list is [u|g]:[name]:[queue_name][,next mapping]*
Typically this list will be used to map users to queues,
for example, u:%user:%user maps all users to queues with the same name
as the user.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.queue-mappings-override.enable</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If a queue mapping is present, will it override the value specified
by the user? This can be used by administrators to place jobs in queues
that are different than the one specified by the user.
The default is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.per-node-heartbeat.maximum-offswitch-assignments</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>
Controls the number of OFF_SWITCH assignments allowed
during a node's heartbeat. Increasing this value can improve
scheduling rate for OFF_SWITCH containers. Lower values reduce
"clumping" of applications on particular nodes. The default is 1.
Legal values are 1-MAX_INT. This config is refreshable.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>yarn.scheduler.capacity.application.fail-fast</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether RM should fail during recovery if previous applications'
queue is no longer valid.
</description>
</property>
</configuration>