分佈式事務實操與原理深度解析
文章目錄
- 分佈式事務實操與原理深度解析
- 引言
- 第一章:分佈式事務概述與理論基礎
- 1.1 分佈式事務的定義與挑戰
- 1.1.1 什麼是分佈式事務
- 1.1.2 分佈式事務面臨的挑戰
- 1.2 ACID特性在分佈式環境下的挑戰
- 1.2.1 傳統ACID特性回顧
- 1.2.2 分佈式環境下的ACID挑戰
- 1.3 CAP定理與BASE理論
- 1.3.1 CAP定理詳解
- 1.3.2 BASE理論
- 1.4 分佈式事務的分類
- 1.4.1 剛性事務 vs 柔性事務
- 第二章:分佈式事務核心算法與協議
- 2.1 兩階段提交協議(2PC)
- 2.1.1 2PC協議原理
- 2.1.2 2PC參與者實現
- 2.1.3 2PC協議的優缺點
- 2.2 三階段提交協議(3PC)
- 2.2.1 3PC協議改進
- 2.3 TCC(Try-Confirm-Cancel)模式
- 2.3.1 TCC模式原理與實現
- 2.3.2 TCC事務管理器
- 第三章:分佈式事務實現方案詳解
- 3.1 基於消息隊列的最終一致性
- 3.1.1 本地消息表模式
- 3.1.2 消息消費者實現
- 第四章:主流分佈式事務框架實戰
- 4.1 Spring Cloud Alibaba Seata實戰
- 4.1.1 Seata架構與核心組件
- 4.1.2 Seata事務模式詳解
- 4.2 Apache ShardingSphere分佈式事務
- 4.2.1 ShardingSphere-Transaction集成
- 4.3 RocketMQ事務消息實踐
- 4.3.1 RocketMQ事務消息機制
- 4.4 框架選型對比分析
- 4.4.1 各框架特性對比
- 第五章:分佈式事務性能優化與最佳實踐
- 5.1 性能瓶頸分析與優化策略
- 5.1.1 常見性能瓶頸識別
- 5.1.2 緩存策略優化
- 5.2 監控與故障排查
- 5.2.1 全鏈路監控實現
- 5.2.2 故障診斷工具
- 5.3 生產環境部署最佳實踐
- 5.3.1 部署架構設計
- 5.3.2 配置管理最佳實踐
- 5.4 常見問題與解決方案
- 5.4.1 事務超時處理
- 5.4.2 死鎖檢測與處理
- 第六章:總結與展望
- 6.1 知識點總結回顧
- 6.1.1 分佈式事務核心概念
- 6.1.2 分佈式事務解決方案對比
- 6.1.3 主流框架實戰經驗
- 6.2 技術發展趨勢
- 6.2.1 雲原生分佈式事務
- 6.2.2 新興技術融合
- 6.3 擴展閲讀推薦
- 6.3.1 經典論文與書籍
- 6.3.2 開源項目與工具
- 6.4 思考問題與討論
- 6.4.1 深度思考題
- 6.4.2 實戰練習建議
- 6.5 結語
引言
在微服務架構日益普及的今天,分佈式事務已成為後端開發中不可迴避的技術挑戰。當業務邏輯跨越多個服務、多個數據庫時,如何保證數據的一致性和事務的完整性,成為了架構師和開發者必須深入理解和掌握的核心技能。
本文將從理論基礎到實戰應用,全面解析分佈式事務的核心概念、實現原理和最佳實踐。我們將深入探討2PC、3PC、TCC、Saga等經典算法,結合Spring Cloud Alibaba Seata、Apache ShardingSphere等主流框架,通過豐富的代碼示例,幫助讀者構建完整的分佈式事務知識體系。
無論你是初入分佈式系統的新手,還是希望深化理解的資深開發者,這篇文章都將為你提供有價值的技術洞察和實踐指導。
第一章:分佈式事務概述與理論基礎
1.1 分佈式事務的定義與挑戰
1.1.1 什麼是分佈式事務
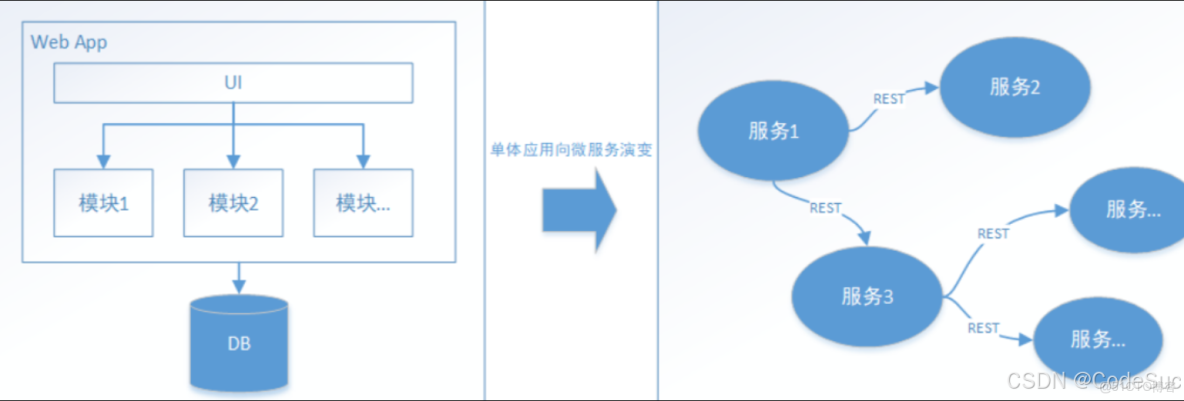
分佈式事務是指事務的參與者、支持事務的服務器、資源服務器以及事務管理器分別位於不同的分佈式系統的不同節點之上。簡單來説,就是一次大的操作由不同的小操作組成,這些小操作分佈在不同的服務器上,且屬於不同的應用,分佈式事務需要保證這些小操作要麼全部成功,要麼全部失敗。
// 典型的分佈式事務場景:電商下單
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private InventoryService inventoryService;
@Autowired
private PaymentService paymentService;
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
/**
* 下單操作涉及多個服務的數據變更
* 1. 扣減庫存 (inventory-service)
* 2. 扣減賬户餘額 (account-service)
* 3. 創建支付記錄 (payment-service)
* 4. 創建訂單記錄 (order-service)
*/
@GlobalTransactional // Seata全局事務註解
public void createOrder(OrderRequest request) {
// 1. 扣減庫存
inventoryService.deductStock(request.getProductId(), request.getQuantity());
// 2. 扣減賬户餘額
accountService.deductBalance(request.getUserId(), request.getAmount());
// 3. 創建支付記錄
paymentService.createPayment(request.getUserId(), request.getAmount());
// 4. 創建訂單
createOrderRecord(request);
// 如果任何一步失敗,整個事務都會回滾
}
private void createOrderRecord(OrderRequest request) {
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(request.getUserId());
order.setProductId(request.getProductId());
order.setQuantity(request.getQuantity());
order.setAmount(request.getAmount());
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.CREATED);
orderRepository.save(order);
}
}1.1.2 分佈式事務面臨的挑戰
- 網絡分區問題:網絡不可靠,可能出現延遲、丟包、分區等問題
- 節點故障:參與事務的節點可能隨時宕機
- 性能開銷:分佈式事務的協調機制會帶來額外的性能開銷
- 複雜性增加:相比單機事務,分佈式事務的實現和調試更加複雜
1.2 ACID特性在分佈式環境下的挑戰
1.2.1 傳統ACID特性回顧
// 單機事務的ACID特性示例
@Service
@Transactional
public class BankTransferService {
/**
* 傳統的銀行轉賬操作
* ACID特性在單機環境下很容易保證
*/
public void transfer(String fromAccount, String toAccount, BigDecimal amount) {
// Atomicity: 原子性 - 要麼全部成功,要麼全部失敗
Account from = accountRepository.findByAccountNo(fromAccount);
Account to = accountRepository.findByAccountNo(toAccount);
// Consistency: 一致性 - 轉賬前後總金額不變
if (from.getBalance().compareTo(amount) < 0) {
throw new InsufficientBalanceException("餘額不足");
}
// Isolation: 隔離性 - 併發事務不會相互影響
from.setBalance(from.getBalance().subtract(amount));
to.setBalance(to.getBalance().add(amount));
accountRepository.save(from);
accountRepository.save(to);
// Durability: 持久性 - 事務提交後數據持久化
}
}1.2.2 分佈式環境下的ACID挑戰
在分佈式環境下,傳統的ACID特性面臨以下挑戰:
// 分佈式環境下的轉賬操作
@Service
public class DistributedBankTransferService {
@Autowired
private AccountServiceA accountServiceA; // 銀行A的賬户服務
@Autowired
private AccountServiceB accountServiceB; // 銀行B的賬户服務
/**
* 跨銀行轉賬 - 分佈式事務場景
* 挑戰:如何保證兩個不同銀行系統的數據一致性
*/
public void crossBankTransfer(String fromAccount, String toAccount, BigDecimal amount) {
try {
// 步驟1:從銀行A扣款
accountServiceA.debit(fromAccount, amount);
// 網絡可能在這裏出現問題...
// 步驟2:向銀行B轉賬
accountServiceB.credit(toAccount, amount);
// 問題:如果步驟2失敗,步驟1已經執行,如何回滾?
// 問題:如何保證兩個操作的原子性?
// 問題:如何處理網絡分區和節點故障?
} catch (Exception e) {
// 分佈式環境下的異常處理變得複雜
// 需要考慮補償操作
handleDistributedTransactionFailure(fromAccount, toAccount, amount, e);
}
}
private void handleDistributedTransactionFailure(String fromAccount, String toAccount,
BigDecimal amount, Exception e) {
// 實現補償邏輯
// 這裏需要複雜的狀態管理和重試機制
}
}1.3 CAP定理與BASE理論
1.3.1 CAP定理詳解
CAP定理指出,在分佈式系統中,一致性(Consistency)、可用性(Availability)和分區容錯性(Partition tolerance)三者不可兼得,最多隻能同時保證其中兩個。
/**
* CAP定理在分佈式事務中的體現
*/
public class CAPTheoryExample {
/**
* CP系統:保證一致性和分區容錯性,犧牲可用性
* 例如:傳統的2PC協議
*/
public class CPSystem {
public void processTransaction() {
// 在網絡分區時,系統會阻塞等待
// 保證數據一致性,但犧牲了可用性
waitForAllNodesResponse(); // 可能長時間阻塞
}
}
/**
* AP系統:保證可用性和分區容錯性,犧牲強一致性
* 例如:最終一致性系統
*/
public class APSystem {
public void processTransaction() {
// 即使在網絡分區時也能繼續服務
// 但可能出現數據不一致的情況
processWithEventualConsistency();
}
private void processWithEventualConsistency() {
// 立即響應用户請求
// 通過異步方式最終達到一致性
}
}
}1.3.2 BASE理論
BASE理論是對CAP定理的延伸,提出了基本可用(Basically Available)、軟狀態(Soft state)和最終一致性(Eventually consistent)的概念。
/**
* BASE理論的實現示例
*/
@Service
public class BaseTheoryExample {
@Autowired
private MessageQueue messageQueue;
/**
* 基於BASE理論的訂單處理
* BA: 基本可用 - 系統在出現故障時仍能提供基本功能
* S: 軟狀態 - 系統狀態可以有一段時間的不一致
* E: 最終一致性 - 系統最終會達到一致狀態
*/
public OrderResult processOrder(OrderRequest request) {
try {
// 1. 立即創建訂單(基本可用)
Order order = createOrderImmediately(request);
// 2. 異步處理其他操作(軟狀態)
sendAsyncMessage(new InventoryDeductionMessage(request));
sendAsyncMessage(new PaymentProcessMessage(request));
sendAsyncMessage(new NotificationMessage(request));
// 3. 返回處理中狀態(軟狀態)
return OrderResult.builder()
.orderId(order.getId())
.status(OrderStatus.PROCESSING)
.message("訂單創建成功,正在處理中...")
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 即使部分功能失敗,仍提供基本服務
return OrderResult.builder()
.status(OrderStatus.FAILED)
.message("訂單創建失敗,請稍後重試")
.build();
}
}
/**
* 異步消息處理器 - 實現最終一致性
*/
@EventListener
public void handleInventoryDeduction(InventoryDeductionMessage message) {
try {
inventoryService.deductStock(message.getProductId(), message.getQuantity());
// 成功後發送確認消息
messageQueue.send(new InventoryDeductionConfirmMessage(message.getOrderId()));
} catch (Exception e) {
// 失敗後發送補償消息
messageQueue.send(new OrderCancellationMessage(message.getOrderId()));
}
}
private Order createOrderImmediately(OrderRequest request) {
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(request.getUserId());
order.setProductId(request.getProductId());
order.setQuantity(request.getQuantity());
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.PROCESSING);
return orderRepository.save(order);
}
private void sendAsyncMessage(Object message) {
messageQueue.send(message);
}
}1.4 分佈式事務的分類
1.4.1 剛性事務 vs 柔性事務
/**
* 剛性事務:嚴格遵循ACID特性
* 適用場景:對數據一致性要求極高的場景,如金融交易
*/
@Service
public class RigidTransactionExample {
/**
* 使用2PC協議實現的剛性事務
*/
@GlobalTransactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void rigidTransaction(TransferRequest request) {
// 階段1:準備階段
// 所有參與者都必須準備好才能提交
// 階段2:提交階段
// 要麼全部提交,要麼全部回滾
accountService.debit(request.getFromAccount(), request.getAmount());
accountService.credit(request.getToAccount(), request.getAmount());
// 如果任何操作失敗,整個事務回滾
// 保證強一致性,但可能影響性能和可用性
}
}
/**
* 柔性事務:放寬一致性要求,追求最終一致性
* 適用場景:對性能和可用性要求較高的場景
*/
@Service
public class FlexibleTransactionExample {
/**
* 使用Saga模式實現的柔性事務
*/
public void flexibleTransaction(OrderRequest request) {
// 將大事務拆分為多個小事務
// 每個小事務都有對應的補償操作
SagaTransaction saga = SagaTransaction.builder()
.addStep(new DeductInventoryStep(request), new CompensateInventoryStep(request))
.addStep(new DeductAccountStep(request), new CompensateAccountStep(request))
.addStep(new CreateOrderStep(request), new CancelOrderStep(request))
.build();
saga.execute();
// 如果某個步驟失敗,執行補償操作
// 最終達到一致性,但過程中可能存在不一致狀態
}
}第二章:分佈式事務核心算法與協議
2.1 兩階段提交協議(2PC)
2.1.1 2PC協議原理
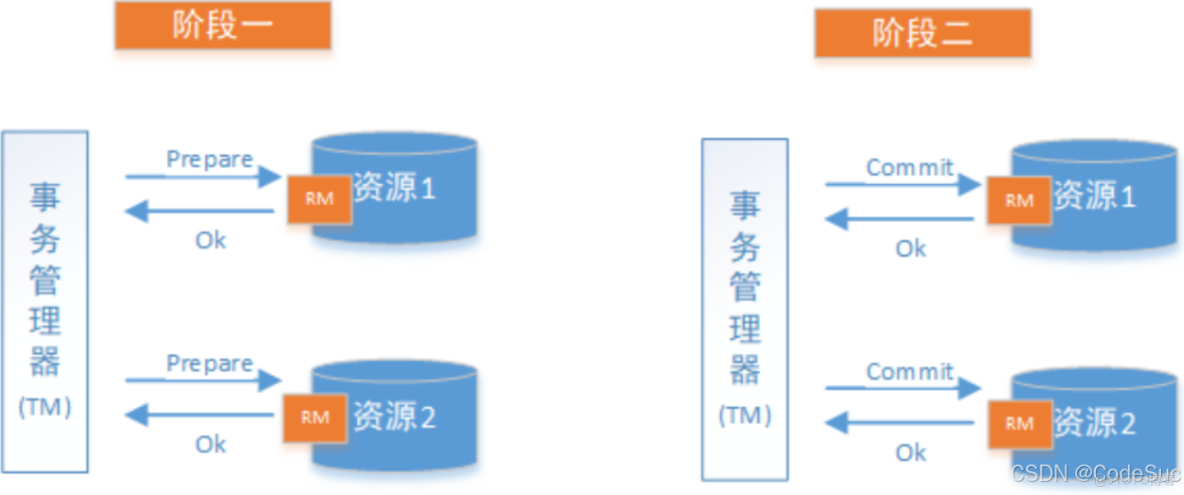
兩階段提交協議是最經典的分佈式事務解決方案,分為準備階段和提交階段。
/**
* 2PC協議的協調者實現
*/
@Component
public class TwoPhaseCommitCoordinator {
private List<TransactionParticipant> participants;
private TransactionLog transactionLog;
/**
* 執行兩階段提交
*/
public boolean executeTransaction(String transactionId, TransactionContext context) {
// 階段1:準備階段(Prepare Phase)
boolean prepareResult = preparePhase(transactionId, context);
if (prepareResult) {
// 階段2:提交階段(Commit Phase)
return commitPhase(transactionId);
} else {
// 如果準備階段失敗,執行回滾
return abortPhase(transactionId);
}
}
/**
* 準備階段:詢問所有參與者是否可以提交
*/
private boolean preparePhase(String transactionId, TransactionContext context) {
log.info("開始準備階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
// 記錄事務開始日誌
transactionLog.logTransactionStart(transactionId, participants);
List<CompletableFuture<Boolean>> prepareFutures = new ArrayList<>();
// 並行向所有參與者發送準備請求
for (TransactionParticipant participant : participants) {
CompletableFuture<Boolean> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
// 發送準備請求
PrepareRequest request = new PrepareRequest(transactionId, context);
PrepareResponse response = participant.prepare(request);
if (response.isSuccess()) {
log.info("參與者 {} 準備成功", participant.getId());
return true;
} else {
log.warn("參與者 {} 準備失敗: {}", participant.getId(), response.getErrorMessage());
return false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} 準備階段異常", participant.getId(), e);
return false;
}
});
prepareFutures.add(future);
}
// 等待所有參與者響應
try {
List<Boolean> results = prepareFutures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 只有所有參與者都準備成功才能進入提交階段
boolean allPrepared = results.stream().allMatch(Boolean::booleanValue);
if (allPrepared) {
transactionLog.logPrepareSuccess(transactionId);
log.info("所有參與者準備成功,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
} else {
transactionLog.logPrepareFailure(transactionId);
log.warn("部分參與者準備失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
}
return allPrepared;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("準備階段異常,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
transactionLog.logPrepareFailure(transactionId);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 提交階段:通知所有參與者提交事務
*/
private boolean commitPhase(String transactionId) {
log.info("開始提交階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
transactionLog.logCommitStart(transactionId);
List<CompletableFuture<Boolean>> commitFutures = new ArrayList<>();
// 並行向所有參與者發送提交請求
for (TransactionParticipant participant : participants) {
CompletableFuture<Boolean> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
CommitRequest request = new CommitRequest(transactionId);
CommitResponse response = participant.commit(request);
if (response.isSuccess()) {
log.info("參與者 {} 提交成功", participant.getId());
return true;
} else {
log.error("參與者 {} 提交失敗: {}", participant.getId(), response.getErrorMessage());
// 注意:在2PC中,如果準備階段成功但提交階段失敗,
// 這是一個嚴重問題,需要人工干預
return false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} 提交階段異常", participant.getId(), e);
return false;
}
});
commitFutures.add(future);
}
// 等待所有參與者提交完成
try {
List<Boolean> results = commitFutures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
boolean allCommitted = results.stream().allMatch(Boolean::booleanValue);
if (allCommitted) {
transactionLog.logCommitSuccess(transactionId);
log.info("所有參與者提交成功,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
} else {
transactionLog.logCommitFailure(transactionId);
log.error("部分參與者提交失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
// 這種情況下需要人工干預或重試機制
}
return allCommitted;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("提交階段異常,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
transactionLog.logCommitFailure(transactionId);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 回滾階段:通知所有參與者回滾事務
*/
private boolean abortPhase(String transactionId) {
log.info("開始回滾階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
transactionLog.logAbortStart(transactionId);
// 向所有參與者發送回滾請求
for (TransactionParticipant participant : participants) {
try {
AbortRequest request = new AbortRequest(transactionId);
participant.abort(request);
log.info("參與者 {} 回滾成功", participant.getId());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} 回滾失敗", participant.getId(), e);
// 回滾失敗也需要記錄,可能需要人工處理
}
}
transactionLog.logAbortComplete(transactionId);
return true;
}
}2.1.2 2PC參與者實現
/**
* 2PC協議的參與者實現
*/
@Component
public class TwoPhaseCommitParticipant implements TransactionParticipant {
private String participantId;
private DataSource dataSource;
private Map<String, Connection> transactionConnections = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public PrepareResponse prepare(PrepareRequest request) {
String transactionId = request.getTransactionId();
try {
log.info("參與者 {} 收到準備請求,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId);
// 1. 開啓本地事務
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
// 2. 執行業務邏輯
boolean businessResult = executeBusinessLogic(connection, request.getContext());
if (businessResult) {
// 3. 業務邏輯執行成功,保存連接等待提交指令
transactionConnections.put(transactionId, connection);
log.info("參與者 {} 準備成功,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId);
return PrepareResponse.success();
} else {
// 4. 業務邏輯執行失敗,回滾並關閉連接
connection.rollback();
connection.close();
log.warn("參與者 {} 準備失敗,業務邏輯執行失敗,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId);
return PrepareResponse.failure("業務邏輯執行失敗");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} 準備階段異常,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId, e);
return PrepareResponse.failure("準備階段異常: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Override
public CommitResponse commit(CommitRequest request) {
String transactionId = request.getTransactionId();
Connection connection = transactionConnections.get(transactionId);
if (connection == null) {
log.error("參與者 {} 未找到事務連接,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId);
return CommitResponse.failure("未找到事務連接");
}
try {
log.info("參與者 {} 開始提交,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId);
// 提交本地事務
connection.commit();
connection.close();
// 清理事務連接
transactionConnections.remove(transactionId);
log.info("參與者 {} 提交成功,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId);
return CommitResponse.success();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} 提交失敗,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId, e);
try {
connection.rollback();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException rollbackException) {
log.error("回滾失敗", rollbackException);
}
transactionConnections.remove(transactionId);
return CommitResponse.failure("提交失敗: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Override
public void abort(AbortRequest request) {
String transactionId = request.getTransactionId();
Connection connection = transactionConnections.get(transactionId);
if (connection != null) {
try {
log.info("參與者 {} 開始回滾,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId);
connection.rollback();
connection.close();
transactionConnections.remove(transactionId);
log.info("參與者 {} 回滾成功,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} 回滾失敗,事務ID: {}", participantId, transactionId, e);
}
}
}
/**
* 執行具體的業務邏輯
*/
private boolean executeBusinessLogic(Connection connection, TransactionContext context) {
try {
// 這裏實現具體的業務邏輯
// 例如:扣減庫存、扣減餘額等
if (context.getOperation().equals("DEDUCT_INVENTORY")) {
return deductInventory(connection, context);
} else if (context.getOperation().equals("DEDUCT_BALANCE")) {
return deductBalance(connection, context);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("業務邏輯執行異常", e);
return false;
}
}
private boolean deductInventory(Connection connection, TransactionContext context) throws SQLException {
String sql = "UPDATE inventory SET quantity = quantity - ? WHERE product_id = ? AND quantity >= ?";
try (PreparedStatement stmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql)) {
stmt.setInt(1, context.getQuantity());
stmt.setString(2, context.getProductId());
stmt.setInt(3, context.getQuantity());
int affectedRows = stmt.executeUpdate();
return affectedRows > 0;
}
}
private boolean deductBalance(Connection connection, TransactionContext context) throws SQLException {
String sql = "UPDATE account SET balance = balance - ? WHERE user_id = ? AND balance >= ?";
try (PreparedStatement stmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql)) {
stmt.setBigDecimal(1, context.getAmount());
stmt.setString(2, context.getUserId());
stmt.setBigDecimal(3, context.getAmount());
int affectedRows = stmt.executeUpdate();
return affectedRows > 0;
}
}
}2.1.3 2PC協議的優缺點
優點:
- 強一致性保證
- 實現相對簡單
- 廣泛支持
缺點:
- 同步阻塞:所有參與者都需要等待協調者的指令
- 單點故障:協調者故障會導致整個系統阻塞
- 數據不一致:在某些異常情況下可能出現數據不一致
2.2 三階段提交協議(3PC)
2.2.1 3PC協議改進
三階段提交協議是對2PC的改進,增加了CanCommit階段,並引入了超時機制。
/**
* 3PC協議的協調者實現
*/
@Component
public class ThreePhaseCommitCoordinator {
private List<TransactionParticipant> participants;
private TransactionLog transactionLog;
private final int TIMEOUT_SECONDS = 30;
/**
* 執行三階段提交
*/
public boolean executeTransaction(String transactionId, TransactionContext context) {
// 階段1:CanCommit階段
boolean canCommitResult = canCommitPhase(transactionId, context);
if (!canCommitResult) {
return false;
}
// 階段2:PreCommit階段
boolean preCommitResult = preCommitPhase(transactionId, context);
if (preCommitResult) {
// 階段3:DoCommit階段
return doCommitPhase(transactionId);
} else {
// 如果PreCommit失敗,執行回滾
return abortPhase(transactionId);
}
}
/**
* 階段1:CanCommit - 詢問參與者是否可以執行事務
*/
private boolean canCommitPhase(String transactionId, TransactionContext context) {
log.info("開始CanCommit階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
List<CompletableFuture<Boolean>> canCommitFutures = new ArrayList<>();
for (TransactionParticipant participant : participants) {
CompletableFuture<Boolean> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
CanCommitRequest request = new CanCommitRequest(transactionId, context);
CanCommitResponse response = participant.canCommit(request);
return response.isCanCommit();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} CanCommit階段異常", participant.getId(), e);
return false;
}
});
canCommitFutures.add(future);
}
try {
// 設置超時時間
List<Boolean> results = canCommitFutures.stream()
.map(future -> {
try {
return future.get(TIMEOUT_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
log.warn("CanCommit階段超時");
return false;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("CanCommit階段異常", e);
return false;
}
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
boolean allCanCommit = results.stream().allMatch(Boolean::booleanValue);
if (allCanCommit) {
log.info("所有參與者CanCommit成功,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
} else {
log.warn("部分參與者CanCommit失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
}
return allCanCommit;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("CanCommit階段異常,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 階段2:PreCommit - 執行事務但不提交
*/
private boolean preCommitPhase(String transactionId, TransactionContext context) {
log.info("開始PreCommit階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
List<CompletableFuture<Boolean>> preCommitFutures = new ArrayList<>();
for (TransactionParticipant participant : participants) {
CompletableFuture<Boolean> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
PreCommitRequest request = new PreCommitRequest(transactionId, context);
PreCommitResponse response = participant.preCommit(request);
return response.isSuccess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} PreCommit階段異常", participant.getId(), e);
return false;
}
});
preCommitFutures.add(future);
}
try {
List<Boolean> results = preCommitFutures.stream()
.map(future -> {
try {
return future.get(TIMEOUT_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
log.warn("PreCommit階段超時");
return false;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("PreCommit階段異常", e);
return false;
}
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
boolean allPreCommitted = results.stream().allMatch(Boolean::booleanValue);
if (allPreCommitted) {
transactionLog.logPreCommitSuccess(transactionId);
log.info("所有參與者PreCommit成功,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
} else {
transactionLog.logPreCommitFailure(transactionId);
log.warn("部分參與者PreCommit失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
}
return allPreCommitted;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("PreCommit階段異常,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 階段3:DoCommit - 正式提交事務
*/
private boolean doCommitPhase(String transactionId) {
log.info("開始DoCommit階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
// 3PC的改進:即使協調者故障,參與者也會在超時後自動提交
// 因為能到達DoCommit階段説明所有參與者都已經PreCommit成功
for (TransactionParticipant participant : participants) {
// 異步發送DoCommit請求,不等待響應
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
DoCommitRequest request = new DoCommitRequest(transactionId);
participant.doCommit(request);
log.info("參與者 {} DoCommit成功", participant.getId());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} DoCommit失敗", participant.getId(), e);
// 在3PC中,DoCommit失敗的影響較小,因為參與者會自動提交
}
});
}
transactionLog.logDoCommitComplete(transactionId);
return true;
}
private boolean abortPhase(String transactionId) {
log.info("開始Abort階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
for (TransactionParticipant participant : participants) {
try {
AbortRequest request = new AbortRequest(transactionId);
participant.abort(request);
log.info("參與者 {} Abort成功", participant.getId());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("參與者 {} Abort失敗", participant.getId(), e);
}
}
return true;
}
}2.3 TCC(Try-Confirm-Cancel)模式
2.3.1 TCC模式原理與實現
TCC是一種柔性事務解決方案,將業務邏輯分為Try、Confirm、Cancel三個階段。
/**
* TCC模式的業務接口定義
*/
public interface TccTransactionService {
/**
* Try階段:嘗試執行業務邏輯,預留資源
* @param context 事務上下文
* @return 是否成功
*/
boolean tryExecute(TccTransactionContext context);
/**
* Confirm階段:確認執行,提交業務邏輯
* @param context 事務上下文
* @return 是否成功
*/
boolean confirmExecute(TccTransactionContext context);
/**
* Cancel階段:取消執行,回滾業務邏輯
* @param context 事務上下文
* @return 是否成功
*/
boolean cancelExecute(TccTransactionContext context);
}
/**
* 庫存服務的TCC實現
*/
@Service
public class InventoryTccService implements TccTransactionService {
@Autowired
private InventoryRepository inventoryRepository;
@Autowired
private InventoryFreezeRepository freezeRepository;
/**
* Try階段:凍結庫存
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean tryExecute(TccTransactionContext context) {
String productId = context.getProductId();
int quantity = context.getQuantity();
String transactionId = context.getTransactionId();
try {
// 1. 檢查庫存是否充足
Inventory inventory = inventoryRepository.findByProductId(productId);
if (inventory == null || inventory.getAvailableQuantity() < quantity) {
log.warn("庫存不足,產品ID: {}, 需要數量: {}, 可用數量: {}",
productId, quantity, inventory != null ? inventory.getAvailableQuantity() : 0);
return false;
}
// 2. 凍結庫存
inventory.setAvailableQuantity(inventory.getAvailableQuantity() - quantity);
inventory.setFrozenQuantity(inventory.getFrozenQuantity() + quantity);
inventoryRepository.save(inventory);
// 3. 記錄凍結記錄
InventoryFreeze freeze = new InventoryFreeze();
freeze.setTransactionId(transactionId);
freeze.setProductId(productId);
freeze.setQuantity(quantity);
freeze.setStatus(FreezeStatus.FROZEN);
freeze.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
freezeRepository.save(freeze);
log.info("庫存凍結成功,事務ID: {}, 產品ID: {}, 數量: {}", transactionId, productId, quantity);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("庫存凍結失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
return false;
}
}
/**
* Confirm階段:確認扣減庫存
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean confirmExecute(TccTransactionContext context) {
String transactionId = context.getTransactionId();
String productId = context.getProductId();
int quantity = context.getQuantity();
try {
// 1. 查找凍結記錄
InventoryFreeze freeze = freezeRepository.findByTransactionId(transactionId);
if (freeze == null) {
log.warn("未找到凍結記錄,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
return false;
}
if (freeze.getStatus() == FreezeStatus.CONFIRMED) {
log.info("庫存已確認扣減,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
return true; // 冪等性處理
}
// 2. 確認扣減庫存
Inventory inventory = inventoryRepository.findByProductId(productId);
inventory.setFrozenQuantity(inventory.getFrozenQuantity() - quantity);
// 注意:這裏不需要再減少totalQuantity,因為在Try階段已經從available轉移到frozen
inventoryRepository.save(inventory);
// 3. 更新凍結記錄狀態
freeze.setStatus(FreezeStatus.CONFIRMED);
freeze.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
freezeRepository.save(freeze);
log.info("庫存確認扣減成功,事務ID: {}, 產品ID: {}, 數量: {}", transactionId, productId, quantity);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("庫存確認扣減失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
return false;
}
}
/**
* Cancel階段:取消凍結,恢復庫存
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean cancelExecute(TccTransactionContext context) {
String transactionId = context.getTransactionId();
String productId = context.getProductId();
int quantity = context.getQuantity();
try {
// 1. 查找凍結記錄
InventoryFreeze freeze = freezeRepository.findByTransactionId(transactionId);
if (freeze == null) {
log.info("未找到凍結記錄,可能已經取消,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
return true; // 冪等性處理
}
if (freeze.getStatus() == FreezeStatus.CANCELLED) {
log.info("庫存已取消凍結,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
return true; // 冪等性處理
}
// 2. 恢復庫存
Inventory inventory = inventoryRepository.findByProductId(productId);
inventory.setAvailableQuantity(inventory.getAvailableQuantity() + quantity);
inventory.setFrozenQuantity(inventory.getFrozenQuantity() - quantity);
inventoryRepository.save(inventory);
// 3. 更新凍結記錄狀態
freeze.setStatus(FreezeStatus.CANCELLED);
freeze.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
freezeRepository.save(freeze);
log.info("庫存取消凍結成功,事務ID: {}, 產品ID: {}, 數量: {}", transactionId, productId, quantity);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("庫存取消凍結失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
return false;
}
}
}2.3.2 TCC事務管理器
/**
* TCC事務管理器
*/
@Component
public class TccTransactionManager {
private Map<String, List<TccTransactionService>> transactionServices = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private TccTransactionLog transactionLog;
/**
* 執行TCC事務
*/
public boolean executeTransaction(String transactionId, List<TccTransactionContext> contexts) {
log.info("開始執行TCC事務,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
List<TccTransactionService> services = new ArrayList<>();
// Try階段:嘗試執行所有業務邏輯
boolean tryResult = tryPhase(transactionId, contexts, services);
if (tryResult) {
// Confirm階段:確認執行
return confirmPhase(transactionId, contexts, services);
} else {
// Cancel階段:取消執行
return cancelPhase(transactionId, contexts, services);
}
}
/**
* Try階段
*/
private boolean tryPhase(String transactionId, List<TccTransactionContext> contexts,
List<TccTransactionService> services) {
log.info("開始Try階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
transactionLog.logTryStart(transactionId);
for (TccTransactionContext context : contexts) {
try {
TccTransactionService service = getServiceByType(context.getServiceType());
services.add(service);
boolean result = service.tryExecute(context);
if (!result) {
log.warn("Try階段失敗,服務類型: {}, 事務ID: {}", context.getServiceType(), transactionId);
transactionLog.logTryFailure(transactionId, context.getServiceType());
return false;
}
log.info("Try階段成功,服務類型: {}, 事務ID: {}", context.getServiceType(), transactionId);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Try階段異常,服務類型: {}, 事務ID: {}", context.getServiceType(), transactionId, e);
transactionLog.logTryFailure(transactionId, context.getServiceType());
return false;
}
}
transactionLog.logTrySuccess(transactionId);
transactionServices.put(transactionId, services);
return true;
}
/**
* Confirm階段
*/
private boolean confirmPhase(String transactionId, List<TccTransactionContext> contexts,
List<TccTransactionService> services) {
log.info("開始Confirm階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
transactionLog.logConfirmStart(transactionId);
boolean allConfirmed = true;
for (int i = 0; i < contexts.size(); i++) {
TccTransactionContext context = contexts.get(i);
TccTransactionService service = services.get(i);
try {
boolean result = service.confirmExecute(context);
if (!result) {
log.error("Confirm階段失敗,服務類型: {}, 事務ID: {}", context.getServiceType(), transactionId);
allConfirmed = false;
// 注意:即使某個服務Confirm失敗,也要繼續嘗試其他服務
// 因為Try階段已經成功,需要盡力保證最終一致性
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Confirm階段異常,服務類型: {}, 事務ID: {}", context.getServiceType(), transactionId, e);
allConfirmed = false;
}
}
if (allConfirmed) {
transactionLog.logConfirmSuccess(transactionId);
log.info("Confirm階段全部成功,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
} else {
transactionLog.logConfirmFailure(transactionId);
log.error("Confirm階段部分失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
// 啓動重試機制
scheduleRetryConfirm(transactionId, contexts, services);
}
return allConfirmed;
}
/**
* Cancel階段
*/
private boolean cancelPhase(String transactionId, List<TccTransactionContext> contexts,
List<TccTransactionService> services) {
log.info("開始Cancel階段,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
transactionLog.logCancelStart(transactionId);
// 逆序執行Cancel操作
Collections.reverse(contexts);
Collections.reverse(services);
boolean allCancelled = true;
for (int i = 0; i < contexts.size(); i++) {
TccTransactionContext context = contexts.get(i);
TccTransactionService service = services.get(i);
try {
boolean result = service.cancelExecute(context);
if (!result) {
log.error("Cancel階段失敗,服務類型: {}, 事務ID: {}", context.getServiceType(), transactionId);
allCancelled = false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Cancel階段異常,服務類型: {}, 事務ID: {}", context.getServiceType(), transactionId, e);
allCancelled = false;
}
}
if (allCancelled) {
transactionLog.logCancelSuccess(transactionId);
log.info("Cancel階段全部成功,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
} else {
transactionLog.logCancelFailure(transactionId);
log.error("Cancel階段部分失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
// 啓動重試機制
scheduleRetryCancel(transactionId, contexts, services);
}
return allCancelled;
}
/**
* 重試Confirm操作
*/
private void scheduleRetryConfirm(String transactionId, List<TccTransactionContext> contexts,
List<TccTransactionService> services) {
// 實現重試邏輯,可以使用定時任務或消息隊列
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
int maxRetries = 3;
int retryCount = 0;
while (retryCount < maxRetries) {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000 * (retryCount + 1)); // 指數退避
boolean result = confirmPhase(transactionId, contexts, services);
if (result) {
log.info("重試Confirm成功,事務ID: {}, 重試次數: {}", transactionId, retryCount + 1);
return;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("重試Confirm異常,事務ID: {}, 重試次數: {}", transactionId, retryCount + 1, e);
}
retryCount++;
}
log.error("重試Confirm最終失敗,事務ID: {}, 需要人工干預", transactionId);
// 發送告警或記錄到死信隊列
});
}
private void scheduleRetryCancel(String transactionId, List<TccTransactionContext> contexts,
List<TccTransactionService> services) {
// 類似的重試Cancel邏輯
// ...
}
private TccTransactionService getServiceByType(String serviceType) {
// 根據服務類型獲取對應的TCC服務實現
// 可以使用Spring的ApplicationContext或服務註冊表
return null;
}
}第三章:分佈式事務實現方案詳解
3.1 基於消息隊列的最終一致性
3.1.1 本地消息表模式
本地消息表是一種常用的分佈式事務解決方案,通過將業務操作和消息發送放在同一個本地事務中來保證一致性。
/**
* 本地消息表實現
*/
@Service
@Transactional
public class LocalMessageTableService {
@Autowired
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Autowired
private LocalMessageRepository messageRepository;
@Autowired
private MessagePublisher messagePublisher;
/**
* 創建訂單併發送消息
* 使用本地事務保證訂單創建和消息記錄的一致性
*/
public void createOrderWithMessage(OrderRequest request) {
String transactionId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
try {
// 1. 創建訂單
Order order = createOrder(request, transactionId);
// 2. 在同一個事務中記錄待發送的消息
recordLocalMessage(transactionId, "INVENTORY_DEDUCTION",
createInventoryDeductionMessage(order));
recordLocalMessage(transactionId, "PAYMENT_PROCESS",
createPaymentMessage(order));
recordLocalMessage(transactionId, "NOTIFICATION_SEND",
createNotificationMessage(order));
log.info("訂單創建成功,事務ID: {}, 訂單ID: {}", transactionId, order.getId());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("訂單創建失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
throw e;
}
}
private Order createOrder(OrderRequest request, String transactionId) {
Order order = new Order();
order.setTransactionId(transactionId);
order.setUserId(request.getUserId());
order.setProductId(request.getProductId());
order.setQuantity(request.getQuantity());
order.setAmount(request.getAmount());
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.CREATED);
order.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
return orderRepository.save(order);
}
private void recordLocalMessage(String transactionId, String messageType, Object messageContent) {
LocalMessage message = new LocalMessage();
message.setTransactionId(transactionId);
message.setMessageType(messageType);
message.setMessageContent(JSON.toJSONString(messageContent));
message.setStatus(MessageStatus.PENDING);
message.setRetryCount(0);
message.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
message.setNextRetryTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(5));
messageRepository.save(message);
}
private InventoryDeductionMessage createInventoryDeductionMessage(Order order) {
return InventoryDeductionMessage.builder()
.transactionId(order.getTransactionId())
.orderId(order.getId())
.productId(order.getProductId())
.quantity(order.getQuantity())
.build();
}
private PaymentMessage createPaymentMessage(Order order) {
return PaymentMessage.builder()
.transactionId(order.getTransactionId())
.orderId(order.getId())
.userId(order.getUserId())
.amount(order.getAmount())
.build();
}
private NotificationMessage createNotificationMessage(Order order) {
return NotificationMessage.builder()
.transactionId(order.getTransactionId())
.orderId(order.getId())
.userId(order.getUserId())
.messageType("ORDER_CREATED")
.build();
}
}
/**
* 消息發送定時任務
*/
@Component
public class MessagePublishScheduler {
@Autowired
private LocalMessageRepository messageRepository;
@Autowired
private MessagePublisher messagePublisher;
private final int MAX_RETRY_COUNT = 5;
/**
* 定時掃描併發送待發送的消息
*/
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000) // 每5秒執行一次
public void publishPendingMessages() {
List<LocalMessage> pendingMessages = messageRepository.findPendingMessages(
LocalDateTime.now(), PageRequest.of(0, 100));
for (LocalMessage message : pendingMessages) {
try {
publishMessage(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("消息發送失敗,消息ID: {}", message.getId(), e);
handlePublishFailure(message);
}
}
}
private void publishMessage(LocalMessage message) {
log.info("開始發送消息,消息ID: {}, 類型: {}", message.getId(), message.getMessageType());
// 根據消息類型發送到不同的隊列
switch (message.getMessageType()) {
case "INVENTORY_DEDUCTION":
messagePublisher.publishToInventoryQueue(message.getMessageContent());
break;
case "PAYMENT_PROCESS":
messagePublisher.publishToPaymentQueue(message.getMessageContent());
break;
case "NOTIFICATION_SEND":
messagePublisher.publishToNotificationQueue(message.getMessageContent());
break;
default:
log.warn("未知的消息類型: {}", message.getMessageType());
return;
}
// 更新消息狀態為已發送
message.setStatus(MessageStatus.SENT);
message.setSentTime(LocalDateTime.now());
messageRepository.save(message);
log.info("消息發送成功,消息ID: {}", message.getId());
}
private void handlePublishFailure(LocalMessage message) {
message.setRetryCount(message.getRetryCount() + 1);
if (message.getRetryCount() >= MAX_RETRY_COUNT) {
// 超過最大重試次數,標記為失敗
message.setStatus(MessageStatus.FAILED);
log.error("消息發送最終失敗,消息ID: {}, 重試次數: {}", message.getId(), message.getRetryCount());
// 可以發送告警或記錄到死信隊列
sendFailureAlert(message);
} else {
// 計算下次重試時間(指數退避)
long delaySeconds = (long) Math.pow(2, message.getRetryCount()) * 5;
message.setNextRetryTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(delaySeconds));
log.warn("消息發送失敗,將在{}秒後重試,消息ID: {}, 重試次數: {}",
delaySeconds, message.getId(), message.getRetryCount());
}
messageRepository.save(message);
}
private void sendFailureAlert(LocalMessage message) {
// 發送告警通知
AlertMessage alert = AlertMessage.builder()
.level(AlertLevel.ERROR)
.title("分佈式事務消息發送失敗")
.content(String.format("消息ID: %s, 事務ID: %s, 消息類型: %s",
message.getId(), message.getTransactionId(), message.getMessageType()))
.build();
// 發送告警(郵件、短信、釘釘等)
alertService.sendAlert(alert);
}
}3.1.2 消息消費者實現
/**
* 庫存扣減消息消費者
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "inventory.deduction.queue")
public class InventoryDeductionConsumer {
@Autowired
private InventoryService inventoryService;
@Autowired
private MessagePublisher messagePublisher;
@RabbitHandler
public void handleInventoryDeduction(String messageContent,
@Header Map<String, Object> headers,
Channel channel,
@Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long deliveryTag) {
InventoryDeductionMessage message = JSON.parseObject(messageContent, InventoryDeductionMessage.class);
String transactionId = message.getTransactionId();
try {
log.info("開始處理庫存扣減,事務ID: {}, 訂單ID: {}", transactionId, message.getOrderId());
// 執行庫存扣減
boolean success = inventoryService.deductStock(message.getProductId(), message.getQuantity());
if (success) {
// 庫存扣減成功,發送成功消息
messagePublisher.publishInventoryDeductionResult(transactionId, true, "庫存扣減成功");
// 手動確認消息
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag, false);
log.info("庫存扣減成功,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
} else {
// 庫存不足,發送失敗消息
messagePublisher.publishInventoryDeductionResult(transactionId, false, "庫存不足");
// 拒絕消息並重新入隊
channel.basicNack(deliveryTag, false, true);
log.warn("庫存不足,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("庫存扣減處理異常,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
try {
// 發送異常消息
messagePublisher.publishInventoryDeductionResult(transactionId, false, "系統異常: " + e.getMessage());
// 拒絕消息並重新入隊
channel.basicNack(deliveryTag, false, true);
} catch (IOException ioException) {
log.error("消息確認失敗", ioException);
}
}
}
}通過本地消息表模式,我們實現了最終一致性的分佈式事務。這種模式的優點是實現簡單、性能較好,缺點是需要額外的存儲空間和定時任務來處理消息發送。
第四章:主流分佈式事務框架實戰
4.1 Spring Cloud Alibaba Seata實戰
4.1.1 Seata架構與核心組件
Seata是阿里巴巴開源的分佈式事務解決方案,致力於在微服務架構下提供高性能和簡單易用的分佈式事務服務。
/**
* Seata配置類
*/
@Configuration
public class SeataConfiguration {
/**
* 配置數據源代理,支持分佈式事務
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
return new DataSourceProxy(druidDataSource);
}
/**
* 配置事務管理器
*/
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
/**
* 配置全局事務掃描器
*/
@Bean
public GlobalTransactionScanner globalTransactionScanner() {
return new GlobalTransactionScanner("order-service", "my_test_tx_group");
}
}
/**
* 訂單服務 - 事務發起者
*/
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
@Autowired
private StorageService storageService;
/**
* 創建訂單的全局事務
* @GlobalTransactional 註解開啓全局事務
*/
@GlobalTransactional(name = "create-order", rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void createOrder(OrderRequest request) {
log.info("開始創建訂單,用户ID: {}, 商品ID: {}, 數量: {}, 金額: {}",
request.getUserId(), request.getProductId(), request.getCount(), request.getMoney());
// 1. 創建訂單記錄
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(request.getUserId());
order.setProductId(request.getProductId());
order.setCount(request.getCount());
order.setMoney(request.getMoney());
order.setStatus(0); // 0: 創建中
orderMapper.create(order);
log.info("訂單創建成功,訂單ID: {}", order.getId());
// 2. 扣減庫存 - 遠程調用
log.info("開始扣減庫存");
storageService.decrease(request.getProductId(), request.getCount());
log.info("庫存扣減成功");
// 3. 扣減賬户餘額 - 遠程調用
log.info("開始扣減賬户餘額");
accountService.decrease(request.getUserId(), request.getMoney());
log.info("賬户餘額扣減成功");
// 4. 更新訂單狀態
log.info("開始更新訂單狀態");
orderMapper.update(order.getId(), 1); // 1: 已完成
log.info("訂單狀態更新成功");
log.info("訂單創建完成,訂單ID: {}", order.getId());
}
}
/**
* 賬户服務 - 事務參與者
*/
@Service
public class AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper accountMapper;
/**
* 扣減賬户餘額
* 使用 @Transactional 註解,會自動加入全局事務
*/
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void decrease(Long userId, BigDecimal money) {
log.info("開始扣減賬户餘額,用户ID: {}, 扣減金額: {}", userId, money);
// 檢查賬户餘額
Account account = accountMapper.selectByUserId(userId);
if (account == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("賬户不存在,用户ID: " + userId);
}
if (account.getResidue().compareTo(money) < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("賬户餘額不足,當前餘額: " + account.getResidue() + ", 需要扣減: " + money);
}
// 扣減餘額
accountMapper.decrease(userId, money);
log.info("賬户餘額扣減成功,用户ID: {}, 扣減金額: {}", userId, money);
// 模擬業務異常
if (money.compareTo(new BigDecimal("1000")) > 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("單筆交易金額不能超過1000元");
}
}
}
/**
* 庫存服務 - 事務參與者
*/
@Service
public class StorageService {
@Autowired
private StorageMapper storageMapper;
/**
* 扣減庫存
*/
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void decrease(Long productId, Integer count) {
log.info("開始扣減庫存,商品ID: {}, 扣減數量: {}", productId, count);
// 檢查庫存
Storage storage = storageMapper.selectByProductId(productId);
if (storage == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("商品不存在,商品ID: " + productId);
}
if (storage.getResidue() < count) {
throw new RuntimeException("庫存不足,當前庫存: " + storage.getResidue() + ", 需要扣減: " + count);
}
// 扣減庫存
storageMapper.decrease(productId, count);
log.info("庫存扣減成功,商品ID: {}, 扣減數量: {}", productId, count);
}
}4.1.2 Seata事務模式詳解
Seata支持四種事務模式:AT、TCC、SAGA、XA。
/**
* TCC模式實現示例
*/
@LocalTCC
public interface AccountTccService {
/**
* Try階段:嘗試執行業務
* 預留資源,但不提交
*/
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(name = "accountTcc", commitMethod = "commit", rollbackMethod = "rollback")
boolean prepare(@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "userId") Long userId,
@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "money") BigDecimal money);
/**
* Confirm階段:確認執行業務
* 真正執行業務邏輯
*/
boolean commit(BusinessActionContext context);
/**
* Cancel階段:取消執行業務
* 釋放預留資源
*/
boolean rollback(BusinessActionContext context);
}
@Service
public class AccountTccServiceImpl implements AccountTccService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Autowired
private AccountFreezeMapper freezeMapper;
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean prepare(Long userId, BigDecimal money) {
log.info("TCC Try階段 - 凍結賬户餘額,用户ID: {}, 金額: {}", userId, money);
// 1. 檢查賬户餘額
Account account = accountMapper.selectByUserId(userId);
if (account == null || account.getResidue().compareTo(money) < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("賬户餘額不足");
}
// 2. 凍結金額
AccountFreeze freeze = new AccountFreeze();
freeze.setUserId(userId);
freeze.setFreezeMoney(money);
freeze.setState(AccountFreeze.State.TRY);
freezeMapper.insert(freeze);
// 3. 扣減可用餘額
accountMapper.deduct(userId, money);
return true;
}
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean commit(BusinessActionContext context) {
Long userId = Long.valueOf(context.getActionContext("userId").toString());
BigDecimal money = new BigDecimal(context.getActionContext("money").toString());
log.info("TCC Confirm階段 - 確認扣減,用户ID: {}, 金額: {}", userId, money);
// 1. 查找凍結記錄
AccountFreeze freeze = freezeMapper.selectByUserIdAndMoney(userId, money);
if (freeze == null) {
return true; // 冪等處理
}
// 2. 刪除凍結記錄
freezeMapper.deleteById(freeze.getId());
return true;
}
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean rollback(BusinessActionContext context) {
Long userId = Long.valueOf(context.getActionContext("userId").toString());
BigDecimal money = new BigDecimal(context.getActionContext("money").toString());
log.info("TCC Cancel階段 - 回滾操作,用户ID: {}, 金額: {}", userId, money);
// 1. 查找凍結記錄
AccountFreeze freeze = freezeMapper.selectByUserIdAndMoney(userId, money);
if (freeze == null) {
return true; // 冪等處理
}
// 2. 恢復可用餘額
accountMapper.restore(userId, money);
// 3. 刪除凍結記錄
freezeMapper.deleteById(freeze.getId());
return true;
}
}4.2 Apache ShardingSphere分佈式事務
4.2.1 ShardingSphere-Transaction集成
/**
* ShardingSphere分佈式事務配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class ShardingSphereTransactionConfiguration {
/**
* 配置分片數據源
*/
@Bean
public DataSource shardingDataSource() throws SQLException {
// 配置真實數據源
Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>();
dataSourceMap.put("ds0", createDataSource("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo_ds_0"));
dataSourceMap.put("ds1", createDataSource("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo_ds_1"));
// 配置分片規則
ShardingRuleConfiguration shardingRuleConfig = new ShardingRuleConfiguration();
shardingRuleConfig.getTableRuleConfigs().add(getOrderTableRuleConfiguration());
shardingRuleConfig.getTableRuleConfigs().add(getOrderItemTableRuleConfiguration());
// 配置分佈式事務
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("sql-show", "true");
return ShardingDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(dataSourceMap, shardingRuleConfig, props);
}
private DataSource createDataSource(String url) {
HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("password");
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
return dataSource;
}
private TableRuleConfiguration getOrderTableRuleConfiguration() {
TableRuleConfiguration result = new TableRuleConfiguration("t_order", "ds${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}");
result.setDatabaseShardingStrategyConfig(new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("user_id", "ds${user_id % 2}"));
result.setTableShardingStrategyConfig(new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("order_id", "t_order_${order_id % 2}"));
return result;
}
private TableRuleConfiguration getOrderItemTableRuleConfiguration() {
TableRuleConfiguration result = new TableRuleConfiguration("t_order_item", "ds${0..1}.t_order_item_${0..1}");
result.setDatabaseShardingStrategyConfig(new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("user_id", "ds${user_id % 2}"));
result.setTableShardingStrategyConfig(new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("order_id", "t_order_item_${order_id % 2}"));
return result;
}
}
/**
* 使用ShardingSphere分佈式事務的服務
*/
@Service
public class ShardingOrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Autowired
private OrderItemRepository orderItemRepository;
/**
* 創建訂單 - 跨分片事務
* 使用XA事務保證強一致性
*/
@ShardingTransactionType(TransactionType.XA)
@Transactional
public void createOrder(CreateOrderRequest request) {
log.info("開始創建分片訂單,用户ID: {}", request.getUserId());
// 1. 創建主訂單
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(request.getUserId());
order.setOrderId(generateOrderId());
order.setStatus("CREATED");
order.setTotalAmount(request.getTotalAmount());
order.setCreateTime(new Date());
orderRepository.save(order);
log.info("主訂單創建成功,訂單ID: {}", order.getOrderId());
// 2. 創建訂單明細(可能分佈在不同分片)
for (OrderItemRequest itemRequest : request.getItems()) {
OrderItem item = new OrderItem();
item.setOrderId(order.getOrderId());
item.setUserId(request.getUserId());
item.setProductId(itemRequest.getProductId());
item.setQuantity(itemRequest.getQuantity());
item.setPrice(itemRequest.getPrice());
item.setCreateTime(new Date());
orderItemRepository.save(item);
log.info("訂單明細創建成功,商品ID: {}", itemRequest.getProductId());
}
// 3. 模擬業務異常測試事務回滾
if (request.getTotalAmount().compareTo(new BigDecimal("10000")) > 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("訂單金額超過限制");
}
log.info("分片訂單創建完成,訂單ID: {}", order.getOrderId());
}
/**
* 使用BASE事務處理最終一致性場景
*/
@ShardingTransactionType(TransactionType.BASE)
@Transactional
public void createOrderWithEventualConsistency(CreateOrderRequest request) {
log.info("開始創建訂單(最終一致性),用户ID: {}", request.getUserId());
try {
// 業務邏輯處理
createOrderInternal(request);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("訂單創建失敗,將進行補償處理", e);
// 在BASE模式下,異常會觸發補償邏輯
throw e;
}
}
private void createOrderInternal(CreateOrderRequest request) {
// 具體的訂單創建邏輯
// ...
}
private Long generateOrderId() {
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}4.3 RocketMQ事務消息實踐
4.3.1 RocketMQ事務消息機制
/**
* RocketMQ事務消息配置
*/
@Configuration
public class RocketMQTransactionConfiguration {
@Bean
public TransactionMQProducer transactionMQProducer() {
TransactionMQProducer producer = new TransactionMQProducer("order_transaction_group");
producer.setNamesrvAddr("localhost:9876");
// 設置事務監聽器
producer.setTransactionListener(new OrderTransactionListener());
// 設置線程池
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, 5, 100, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2000),
r -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setName("client-transaction-msg-check-thread");
return thread;
});
producer.setExecutorService(executorService);
return producer;
}
}
/**
* 事務消息監聽器
*/
@Component
public class OrderTransactionListener implements TransactionListener {
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@Autowired
private TransactionLogService transactionLogService;
/**
* 執行本地事務
*/
@Override
public LocalTransactionState executeLocalTransaction(Message msg, Object arg) {
String transactionId = msg.getTransactionId();
log.info("執行本地事務,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
try {
// 執行本地業務邏輯
OrderTransactionContext context = (OrderTransactionContext) arg;
orderService.createOrderLocal(context.getOrderRequest());
// 記錄事務日誌
transactionLogService.recordTransaction(transactionId, "COMMIT", context);
log.info("本地事務執行成功,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
return LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("本地事務執行失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
// 記錄失敗日誌
transactionLogService.recordTransaction(transactionId, "ROLLBACK", arg);
return LocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK_MESSAGE;
}
}
/**
* 檢查本地事務狀態(消息回查)
*/
@Override
public LocalTransactionState checkLocalTransaction(MessageExt msg) {
String transactionId = msg.getTransactionId();
log.info("檢查本地事務狀態,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
// 查詢事務日誌
TransactionLog transactionLog = transactionLogService.getByTransactionId(transactionId);
if (transactionLog == null) {
log.warn("未找到事務日誌,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
return LocalTransactionState.UNKNOW;
}
switch (transactionLog.getStatus()) {
case "COMMIT":
return LocalTransactionState.COMMIT_MESSAGE;
case "ROLLBACK":
return LocalTransactionState.ROLLBACK_MESSAGE;
default:
return LocalTransactionState.UNKNOW;
}
}
}
/**
* 訂單事務消息服務
*/
@Service
public class OrderTransactionMessageService {
@Autowired
private TransactionMQProducer transactionMQProducer;
/**
* 發送事務消息
*/
public void sendTransactionMessage(OrderRequest orderRequest) {
String transactionId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 構造消息
Message message = new Message();
message.setTopic("ORDER_TOPIC");
message.setTags("CREATE_ORDER");
message.setKeys(orderRequest.getUserId().toString());
message.setBody(JSON.toJSONString(orderRequest).getBytes());
message.setTransactionId(transactionId);
// 構造事務上下文
OrderTransactionContext context = new OrderTransactionContext();
context.setTransactionId(transactionId);
context.setOrderRequest(orderRequest);
try {
log.info("開始發送事務消息,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
// 發送事務消息
SendResult sendResult = transactionMQProducer.sendMessageInTransaction(message, context);
log.info("事務消息發送結果,事務ID: {}, 結果: {}", transactionId, sendResult.getSendStatus());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("事務消息發送失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
throw new RuntimeException("事務消息發送失敗", e);
}
}
}
/**
* 訂單消息消費者
*/
@Component
@RocketMQMessageListener(
topic = "ORDER_TOPIC",
consumerGroup = "order_consumer_group",
messageModel = MessageModel.CLUSTERING
)
public class OrderMessageConsumer implements RocketMQListener<String> {
@Autowired
private InventoryService inventoryService;
@Autowired
private PaymentService paymentService;
@Override
public void onMessage(String message) {
log.info("收到訂單消息: {}", message);
try {
OrderRequest orderRequest = JSON.parseObject(message, OrderRequest.class);
// 處理下游業務
processDownstreamBusiness(orderRequest);
log.info("訂單消息處理成功,訂單ID: {}", orderRequest.getOrderId());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("訂單消息處理失敗: {}", message, e);
throw e; // 拋出異常觸發重試
}
}
private void processDownstreamBusiness(OrderRequest orderRequest) {
// 1. 扣減庫存
inventoryService.deductStock(orderRequest.getProductId(), orderRequest.getQuantity());
// 2. 處理支付
paymentService.processPayment(orderRequest.getUserId(), orderRequest.getAmount());
// 3. 發送通知
// notificationService.sendOrderNotification(orderRequest);
}
}4.4 框架選型對比分析
4.4.1 各框架特性對比
/**
* 分佈式事務框架選型決策器
*/
@Component
public class TransactionFrameworkSelector {
/**
* 根據業務場景選擇合適的分佈式事務方案
*/
public TransactionSolution selectSolution(BusinessScenario scenario) {
// 高一致性要求場景
if (scenario.getConsistencyLevel() == ConsistencyLevel.STRONG) {
if (scenario.getPerformanceRequirement() == PerformanceLevel.HIGH) {
return TransactionSolution.SEATA_AT;
} else {
return TransactionSolution.SEATA_XA;
}
}
// 最終一致性場景
if (scenario.getConsistencyLevel() == ConsistencyLevel.EVENTUAL) {
if (scenario.hasComplexCompensation()) {
return TransactionSolution.SEATA_SAGA;
} else {
return TransactionSolution.ROCKETMQ_TRANSACTION;
}
}
// 分庫分表場景
if (scenario.hasSharding()) {
return TransactionSolution.SHARDING_SPHERE_XA;
}
// 默認推薦
return TransactionSolution.SEATA_AT;
}
/**
* 框架特性對比
*/
public void compareFrameworks() {
log.info("=== 分佈式事務框架對比 ===");
// Seata AT模式
log.info("Seata AT模式:");
log.info("- 優點: 無侵入、性能好、使用簡單");
log.info("- 缺點: 依賴數據庫行鎖、不支持跨數據庫類型");
log.info("- 適用場景: 關係型數據庫、高性能要求");
// Seata TCC模式
log.info("Seata TCC模式:");
log.info("- 優點: 性能最好、支持跨數據庫");
log.info("- 缺點: 代碼侵入性強、開發複雜");
log.info("- 適用場景: 對性能要求極高、業務邏輯複雜");
// RocketMQ事務消息
log.info("RocketMQ事務消息:");
log.info("- 優點: 最終一致性、高可用、解耦");
log.info("- 缺點: 不支持強一致性、消息可能重複");
log.info("- 適用場景: 異步處理、最終一致性要求");
// ShardingSphere
log.info("ShardingSphere分佈式事務:");
log.info("- 優點: 與分庫分表完美結合");
log.info("- 缺點: 主要針對分片場景");
log.info("- 適用場景: 分庫分表環境");
}
}
/**
* 業務場景枚舉
*/
public class BusinessScenario {
private ConsistencyLevel consistencyLevel;
private PerformanceLevel performanceRequirement;
private boolean hasSharding;
private boolean hasComplexCompensation;
// getters and setters...
}
enum ConsistencyLevel {
STRONG, // 強一致性
EVENTUAL // 最終一致性
}
enum PerformanceLevel {
HIGH, // 高性能要求
MEDIUM, // 中等性能要求
LOW // 低性能要求
}
enum TransactionSolution {
SEATA_AT,
SEATA_TCC,
SEATA_SAGA,
SEATA_XA,
ROCKETMQ_TRANSACTION,
SHARDING_SPHERE_XA,
LOCAL_MESSAGE_TABLE
}第五章:分佈式事務性能優化與最佳實踐
5.1 性能瓶頸分析與優化策略
5.1.1 常見性能瓶頸識別
/**
* 分佈式事務性能監控器
*/
@Component
public class TransactionPerformanceMonitor {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final Timer transactionTimer;
private final Counter successCounter;
private final Counter failureCounter;
public TransactionPerformanceMonitor(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.transactionTimer = Timer.builder("distributed.transaction.duration")
.description("分佈式事務執行時間")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.successCounter = Counter.builder("distributed.transaction.success")
.description("分佈式事務成功次數")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.failureCounter = Counter.builder("distributed.transaction.failure")
.description("分佈式事務失敗次數")
.register(meterRegistry);
}
/**
* 監控事務執行性能
*/
public <T> T monitorTransaction(String transactionName, Supplier<T> transactionLogic) {
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start(meterRegistry);
try {
log.info("開始執行分佈式事務: {}", transactionName);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
T result = transactionLogic.get();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
// 記錄成功指標
successCounter.increment();
sample.stop(transactionTimer);
log.info("分佈式事務執行成功: {}, 耗時: {}ms", transactionName, duration);
// 性能告警
if (duration > 5000) {
log.warn("分佈式事務執行時間過長: {}, 耗時: {}ms", transactionName, duration);
sendPerformanceAlert(transactionName, duration);
}
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 記錄失敗指標
failureCounter.increment();
sample.stop(transactionTimer);
log.error("分佈式事務執行失敗: {}", transactionName, e);
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 分析性能瓶頸
*/
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) // 每分鐘執行一次
public void analyzePerformanceBottlenecks() {
// 獲取事務執行統計
Timer.Snapshot snapshot = transactionTimer.takeSnapshot();
double avgDuration = snapshot.mean(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
double maxDuration = snapshot.max(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
double p95Duration = snapshot.percentile(0.95, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
log.info("分佈式事務性能統計 - 平均耗時: {}ms, 最大耗時: {}ms, P95耗時: {}ms",
avgDuration, maxDuration, p95Duration);
// 性能瓶頸分析
if (p95Duration > 3000) {
log.warn("檢測到性能瓶頸 - P95耗時超過3秒: {}ms", p95Duration);
analyzeBottleneckCauses();
}
}
private void analyzeBottleneckCauses() {
log.info("開始分析性能瓶頸原因:");
log.info("1. 檢查數據庫連接池配置");
log.info("2. 檢查網絡延遲");
log.info("3. 檢查事務參與者數量");
log.info("4. 檢查業務邏輯複雜度");
log.info("5. 檢查鎖競爭情況");
}
private void sendPerformanceAlert(String transactionName, long duration) {
// 發送性能告警
// alertService.sendAlert(...);
}
}
/**
* 分佈式事務優化器
*/
@Component
public class TransactionOptimizer {
/**
* 連接池優化配置
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.hikari")
public HikariConfig hikariConfig() {
HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig();
// 優化連接池配置
config.setMaximumPoolSize(20); // 最大連接數
config.setMinimumIdle(5); // 最小空閒連接數
config.setConnectionTimeout(30000); // 連接超時時間
config.setIdleTimeout(600000); // 空閒超時時間
config.setMaxLifetime(1800000); // 連接最大生命週期
config.setLeakDetectionThreshold(60000); // 連接泄漏檢測閾值
// 優化SQL執行
config.addDataSourceProperty("cachePrepStmts", "true");
config.addDataSourceProperty("prepStmtCacheSize", "250");
config.addDataSourceProperty("prepStmtCacheSqlLimit", "2048");
config.addDataSourceProperty("useServerPrepStmts", "true");
return config;
}
/**
* Seata客户端優化配置
*/
@Bean
public GlobalTransactionScanner optimizedGlobalTransactionScanner() {
GlobalTransactionScanner scanner = new GlobalTransactionScanner("order-service", "my_test_tx_group");
// 優化配置
System.setProperty("client.tm.commitRetryCount", "3");
System.setProperty("client.tm.rollbackRetryCount", "3");
System.setProperty("client.rm.asyncCommitBufferLimit", "10000");
System.setProperty("client.rm.reportRetryCount", "5");
System.setProperty("client.rm.tableMetaCheckEnable", "false");
return scanner;
}
/**
* 批量操作優化
*/
@Service
public static class BatchTransactionService {
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
/**
* 批量創建訂單 - 優化版本
*/
@GlobalTransactional
public void createOrdersBatch(List<OrderRequest> requests) {
log.info("開始批量創建訂單,數量: {}", requests.size());
// 1. 批量插入訂單
List<Order> orders = requests.stream()
.map(this::convertToOrder)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
orderMapper.batchInsert(orders);
// 2. 批量處理庫存扣減
Map<Long, Integer> productStockMap = requests.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
OrderRequest::getProductId,
Collectors.summingInt(OrderRequest::getCount)
));
for (Map.Entry<Long, Integer> entry : productStockMap.entrySet()) {
storageService.decrease(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
// 3. 批量處理賬户扣減
Map<Long, BigDecimal> userAmountMap = requests.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
OrderRequest::getUserId,
Collectors.reducing(BigDecimal.ZERO, OrderRequest::getMoney, BigDecimal::add)
));
for (Map.Entry<Long, BigDecimal> entry : userAmountMap.entrySet()) {
accountService.decrease(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
log.info("批量訂單創建完成,數量: {}", requests.size());
}
private Order convertToOrder(OrderRequest request) {
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(request.getUserId());
order.setProductId(request.getProductId());
order.setCount(request.getCount());
order.setMoney(request.getMoney());
order.setStatus(0);
return order;
}
}
}5.1.2 緩存策略優化
/**
* 分佈式事務緩存優化
*/
@Component
public class TransactionCacheOptimizer {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
private static final String ACCOUNT_CACHE_PREFIX = "account:";
private static final String INVENTORY_CACHE_PREFIX = "inventory:";
private static final int CACHE_EXPIRE_SECONDS = 300;
/**
* 賬户信息緩存
*/
public Account getAccountWithCache(Long userId) {
String cacheKey = ACCOUNT_CACHE_PREFIX + userId;
// 先從緩存獲取
Account account = (Account) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(cacheKey);
if (account != null) {
log.debug("從緩存獲取賬户信息,用户ID: {}", userId);
return account;
}
// 緩存未命中,從數據庫獲取
account = accountMapper.selectByUserId(userId);
if (account != null) {
// 寫入緩存
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(cacheKey, account, CACHE_EXPIRE_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.debug("賬户信息寫入緩存,用户ID: {}", userId);
}
return account;
}
/**
* 庫存信息緩存
*/
public Storage getStorageWithCache(Long productId) {
String cacheKey = INVENTORY_CACHE_PREFIX + productId;
Storage storage = (Storage) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(cacheKey);
if (storage != null) {
return storage;
}
storage = storageMapper.selectByProductId(productId);
if (storage != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(cacheKey, storage, CACHE_EXPIRE_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
return storage;
}
/**
* 緩存失效策略
*/
public void invalidateAccountCache(Long userId) {
String cacheKey = ACCOUNT_CACHE_PREFIX + userId;
redisTemplate.delete(cacheKey);
log.debug("清除賬户緩存,用户ID: {}", userId);
}
public void invalidateStorageCache(Long productId) {
String cacheKey = INVENTORY_CACHE_PREFIX + productId;
redisTemplate.delete(cacheKey);
log.debug("清除庫存緩存,商品ID: {}", productId);
}
/**
* 預熱緩存
*/
@PostConstruct
public void warmUpCache() {
log.info("開始預熱緩存");
// 預熱熱點賬户數據
List<Long> hotUserIds = getHotUserIds();
for (Long userId : hotUserIds) {
getAccountWithCache(userId);
}
// 預熱熱點商品庫存數據
List<Long> hotProductIds = getHotProductIds();
for (Long productId : hotProductIds) {
getStorageWithCache(productId);
}
log.info("緩存預熱完成");
}
private List<Long> getHotUserIds() {
// 獲取熱點用户ID列表
return Arrays.asList(1L, 2L, 3L, 4L, 5L);
}
private List<Long> getHotProductIds() {
// 獲取熱點商品ID列表
return Arrays.asList(1L, 2L, 3L, 4L, 5L);
}
}5.2 監控與故障排查
5.2.1 全鏈路監控實現
/**
* 分佈式事務鏈路追蹤
*/
@Component
public class TransactionTracing {
private final Tracer tracer;
public TransactionTracing(Tracer tracer) {
this.tracer = tracer;
}
/**
* 創建事務追蹤Span
*/
public Span createTransactionSpan(String transactionName, String xid) {
Span span = tracer.nextSpan()
.name("distributed-transaction")
.tag("transaction.name", transactionName)
.tag("transaction.xid", xid)
.tag("service.name", "order-service")
.start();
return span;
}
/**
* 記錄事務階段
*/
public void recordTransactionPhase(Span span, String phase, String status) {
span.tag("transaction.phase", phase)
.tag("transaction.status", status)
.event("phase." + phase + "." + status);
}
/**
* 記錄事務異常
*/
public void recordTransactionError(Span span, Throwable error) {
span.tag("error", "true")
.tag("error.message", error.getMessage())
.tag("error.class", error.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
/**
* 事務健康檢查
*/
@Component
public class TransactionHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
@Autowired
private TransactionStatisticsService statisticsService;
@Override
public Health health() {
try {
// 檢查事務成功率
TransactionStatistics stats = statisticsService.getRecentStatistics(Duration.ofMinutes(5));
double successRate = stats.getSuccessRate();
long avgDuration = stats.getAverageDuration();
Health.Builder builder = new Health.Builder();
if (successRate >= 0.95 && avgDuration <= 3000) {
builder.up();
} else if (successRate >= 0.90 && avgDuration <= 5000) {
builder.status("WARNING");
} else {
builder.down();
}
return builder
.withDetail("successRate", successRate)
.withDetail("averageDuration", avgDuration + "ms")
.withDetail("totalTransactions", stats.getTotalCount())
.withDetail("failedTransactions", stats.getFailedCount())
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
return Health.down()
.withDetail("error", e.getMessage())
.build();
}
}
}
/**
* 事務統計服務
*/
@Service
public class TransactionStatisticsService {
@Autowired
private MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public TransactionStatistics getRecentStatistics(Duration duration) {
// 獲取指定時間段內的事務統計
Timer transactionTimer = meterRegistry.get("distributed.transaction.duration").timer();
Counter successCounter = meterRegistry.get("distributed.transaction.success").counter();
Counter failureCounter = meterRegistry.get("distributed.transaction.failure").counter();
long totalCount = (long) (successCounter.count() + failureCounter.count());
long failedCount = (long) failureCounter.count();
double successRate = totalCount > 0 ? (double) (totalCount - failedCount) / totalCount : 0;
long avgDuration = (long) transactionTimer.mean(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return TransactionStatistics.builder()
.totalCount(totalCount)
.failedCount(failedCount)
.successRate(successRate)
.averageDuration(avgDuration)
.build();
}
}5.2.2 故障診斷工具
/**
* 分佈式事務故障診斷器
*/
@Component
public class TransactionDiagnostics {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 診斷數據庫連接狀態
*/
public DiagnosticResult diagnoseDatabaseConnection() {
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
boolean isValid = connection.isValid(5);
if (isValid) {
return DiagnosticResult.success("數據庫連接正常");
} else {
return DiagnosticResult.failure("數據庫連接異常");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
return DiagnosticResult.failure("數據庫連接失敗: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 診斷Redis連接狀態
*/
public DiagnosticResult diagnoseRedisConnection() {
try {
String pong = redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory()
.getConnection()
.ping();
if ("PONG".equals(pong)) {
return DiagnosticResult.success("Redis連接正常");
} else {
return DiagnosticResult.failure("Redis連接異常");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return DiagnosticResult.failure("Redis連接失敗: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 診斷Seata連接狀態
*/
public DiagnosticResult diagnoseSeataConnection() {
try {
// 檢查TM連接
boolean tmConnected = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrentOrCreate().getXid() != null;
if (tmConnected) {
return DiagnosticResult.success("Seata連接正常");
} else {
return DiagnosticResult.failure("Seata連接異常");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return DiagnosticResult.failure("Seata連接失敗: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 診斷事務鎖狀態
*/
public DiagnosticResult diagnoseTransactionLocks() {
try {
// 查詢當前鎖信息
String sql = "SELECT * FROM lock_table WHERE xid IS NOT NULL";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery()) {
int lockCount = 0;
while (resultSet.next()) {
lockCount++;
}
if (lockCount == 0) {
return DiagnosticResult.success("無事務鎖");
} else if (lockCount < 100) {
return DiagnosticResult.warning("存在 " + lockCount + " 個事務鎖");
} else {
return DiagnosticResult.failure("事務鎖過多: " + lockCount);
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
return DiagnosticResult.failure("查詢事務鎖失敗: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 綜合診斷報告
*/
public ComprehensiveDiagnosticReport generateDiagnosticReport() {
ComprehensiveDiagnosticReport report = new ComprehensiveDiagnosticReport();
report.setDatabaseResult(diagnoseDatabaseConnection());
report.setRedisResult(diagnoseRedisConnection());
report.setSeataResult(diagnoseSeataConnection());
report.setLockResult(diagnoseTransactionLocks());
report.setTimestamp(LocalDateTime.now());
// 計算整體健康狀態
report.calculateOverallHealth();
return report;
}
}
/**
* 診斷結果
*/
@Data
@Builder
public class DiagnosticResult {
private String status; // SUCCESS, WARNING, FAILURE
private String message;
private LocalDateTime timestamp;
public static DiagnosticResult success(String message) {
return DiagnosticResult.builder()
.status("SUCCESS")
.message(message)
.timestamp(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
}
public static DiagnosticResult warning(String message) {
return DiagnosticResult.builder()
.status("WARNING")
.message(message)
.timestamp(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
}
public static DiagnosticResult failure(String message) {
return DiagnosticResult.builder()
.status("FAILURE")
.message(message)
.timestamp(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
}
}5.3 生產環境部署最佳實踐
5.3.1 部署架構設計
# docker-compose.yml - 生產環境部署配置
version: '3.8'
services:
# Seata Server
seata-server:
image: seataio/seata-server:1.5.2
hostname: seata-server
ports:
- "8091:8091"
environment:
- SEATA_PORT=8091
- STORE_MODE=db
- SEATA_CONFIG_NAME=file:/root/seata-config/registry
volumes:
- ./seata-config:/root/seata-config
networks:
- seata-network
restart: always
# MySQL主庫
mysql-master:
image: mysql:8.0
hostname: mysql-master
ports:
- "3306:3306"
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root123
- MYSQL_DATABASE=seata
volumes:
- mysql-master-data:/var/lib/mysql
- ./mysql-config/master.cnf:/etc/mysql/conf.d/master.cnf
networks:
- seata-network
restart: always
# MySQL從庫
mysql-slave:
image: mysql:8.0
hostname: mysql-slave
ports:
- "3307:3306"
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root123
- MYSQL_DATABASE=seata
volumes:
- mysql-slave-data:/var/lib/mysql
- ./mysql-config/slave.cnf:/etc/mysql/conf.d/slave.cnf
networks:
- seata-network
restart: always
depends_on:
- mysql-master
# Redis集羣
redis-master:
image: redis:7.0
hostname: redis-master
ports:
- "6379:6379"
command: redis-server --appendonly yes --cluster-enabled yes
volumes:
- redis-master-data:/data
networks:
- seata-network
restart: always
# 訂單服務
order-service:
image: order-service:latest
hostname: order-service
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=prod
- SEATA_SERVER_ADDR=seata-server:8091
- MYSQL_HOST=mysql-master:3306
- REDIS_HOST=redis-master:6379
networks:
- seata-network
restart: always
depends_on:
- seata-server
- mysql-master
- redis-master
# 庫存服務
inventory-service:
image: inventory-service:latest
hostname: inventory-service
ports:
- "8081:8081"
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=prod
- SEATA_SERVER_ADDR=seata-server:8091
- MYSQL_HOST=mysql-master:3306
- REDIS_HOST=redis-master:6379
networks:
- seata-network
restart: always
depends_on:
- seata-server
- mysql-master
- redis-master
volumes:
mysql-master-data:
mysql-slave-data:
redis-master-data:
networks:
seata-network:
driver: bridge5.3.2 配置管理最佳實踐
/**
* 生產環境配置
*/
@Configuration
@Profile("prod")
public class ProductionTransactionConfiguration {
/**
* 生產環境數據源配置
*/
@Bean
@Primary
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource() {
HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig();
// 生產環境優化配置
config.setMaximumPoolSize(50);
config.setMinimumIdle(10);
config.setConnectionTimeout(30000);
config.setIdleTimeout(300000);
config.setMaxLifetime(1800000);
config.setLeakDetectionThreshold(60000);
// 連接池監控
config.setRegisterMbeans(true);
return new HikariDataSource(config);
}
/**
* 只讀數據源配置
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.slave")
public DataSource slaveDataSource() {
HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig();
config.setMaximumPoolSize(30);
config.setMinimumIdle(5);
config.setReadOnly(true);
return new HikariDataSource(config);
}
/**
* 讀寫分離配置
*/
@Bean
public DataSource routingDataSource() {
Map<Object, Object> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>();
dataSourceMap.put("master", masterDataSource());
dataSourceMap.put("slave", slaveDataSource());
DynamicDataSource routingDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
routingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(dataSourceMap);
routingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(masterDataSource());
return routingDataSource;
}
/**
* Seata生產環境配置
*/
@Bean
public GlobalTransactionScanner productionGlobalTransactionScanner() {
GlobalTransactionScanner scanner = new GlobalTransactionScanner("order-service", "default_tx_group");
// 生產環境優化配置
System.setProperty("seata.server.addr", "seata-server:8091");
System.setProperty("client.tm.commitRetryCount", "5");
System.setProperty("client.tm.rollbackRetryCount", "5");
System.setProperty("client.rm.asyncCommitBufferLimit", "10000");
System.setProperty("client.rm.reportRetryCount", "5");
System.setProperty("client.rm.tableMetaCheckEnable", "true");
System.setProperty("client.rm.reportSuccessEnable", "false");
System.setProperty("client.rm.sagaBranchRegisterEnable", "false");
System.setProperty("client.tm.degradeCheck", "false");
System.setProperty("client.tm.degradeCheckAllowTimes", "10");
System.setProperty("client.tm.degradeCheckPeriod", "2000");
return scanner;
}
}
/**
* 動態數據源
*/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceType();
}
}
/**
* 數據源上下文持有者
*/
public class DataSourceContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setDataSourceType(String dataSourceType) {
contextHolder.set(dataSourceType);
}
public static String getDataSourceType() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void clearDataSourceType() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}5.4 常見問題與解決方案
5.4.1 事務超時處理
/**
* 事務超時處理器
*/
@Component
public class TransactionTimeoutHandler {
private static final int DEFAULT_TIMEOUT = 30000; // 30秒
private static final int MAX_TIMEOUT = 300000; // 5分鐘
/**
* 動態調整事務超時時間
*/
public int calculateTimeout(TransactionContext context) {
int participantCount = context.getParticipantCount();
int businessComplexity = context.getBusinessComplexity();
// 基礎超時時間
int timeout = DEFAULT_TIMEOUT;
// 根據參與者數量調整
timeout += participantCount * 5000;
// 根據業務複雜度調整
timeout += businessComplexity * 10000;
// 限制最大超時時間
return Math.min(timeout, MAX_TIMEOUT);
}
/**
* 超時重試策略
*/
@Retryable(value = {TransactionTimeoutException.class},
maxAttempts = 3,
backoff = @Backoff(delay = 1000, multiplier = 2))
public void handleTimeoutWithRetry(Runnable transactionLogic) {
try {
transactionLogic.run();
} catch (TransactionTimeoutException e) {
log.warn("事務超時,準備重試: {}", e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 超時降級處理
*/
public void handleTimeoutDegradation(String transactionId) {
log.warn("事務超時,執行降級處理,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
// 1. 記錄超時事務
recordTimeoutTransaction(transactionId);
// 2. 發送告警
sendTimeoutAlert(transactionId);
// 3. 執行補償邏輯
executeCompensation(transactionId);
}
private void recordTimeoutTransaction(String transactionId) {
// 記錄超時事務到數據庫
}
private void sendTimeoutAlert(String transactionId) {
// 發送超時告警
}
private void executeCompensation(String transactionId) {
// 執行補償邏輯
}
}5.4.2 死鎖檢測與處理
/**
* 死鎖檢測器
*/
@Component
public class DeadlockDetector {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
/**
* 檢測數據庫死鎖
*/
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000) // 每30秒檢測一次
public void detectDeadlocks() {
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
// MySQL死鎖檢測SQL
String sql = "SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_LOCKS";
try (PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery()) {
List<LockInfo> locks = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
LockInfo lockInfo = new LockInfo();
lockInfo.setLockId(resultSet.getString("lock_id"));
lockInfo.setLockTrxId(resultSet.getString("lock_trx_id"));
lockInfo.setLockMode(resultSet.getString("lock_mode"));
lockInfo.setLockType(resultSet.getString("lock_type"));
lockInfo.setLockTable(resultSet.getString("lock_table"));
locks.add(lockInfo);
}
if (!locks.isEmpty()) {
analyzeDeadlock(locks);
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("死鎖檢測失敗", e);
}
}
/**
* 分析死鎖情況
*/
private void analyzeDeadlock(List<LockInfo> locks) {
log.warn("檢測到潛在死鎖,鎖數量: {}", locks.size());
// 按事務ID分組
Map<String, List<LockInfo>> locksByTrx = locks.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(LockInfo::getLockTrxId));
// 檢測循環等待
for (Map.Entry<String, List<LockInfo>> entry : locksByTrx.entrySet()) {
String trxId = entry.getKey();
List<LockInfo> trxLocks = entry.getValue();
log.warn("事務 {} 持有鎖: {}", trxId, trxLocks.size());
}
// 發送死鎖告警
sendDeadlockAlert(locks);
}
/**
* 死鎖解決策略
*/
public void resolveDeadlock(String transactionId) {
log.info("開始解決死鎖,事務ID: {}", transactionId);
try {
// 1. 回滾優先級較低的事務
rollbackLowerPriorityTransaction(transactionId);
// 2. 記錄死鎖事件
recordDeadlockEvent(transactionId);
// 3. 優化鎖獲取順序
optimizeLockOrder();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("死鎖解決失敗,事務ID: {}", transactionId, e);
}
}
private void rollbackLowerPriorityTransaction(String transactionId) {
// 回滾優先級較低的事務
}
private void recordDeadlockEvent(String transactionId) {
// 記錄死鎖事件
}
private void optimizeLockOrder() {
// 優化鎖獲取順序
}
private void sendDeadlockAlert(List<LockInfo> locks) {
// 發送死鎖告警
}
}
/**
* 鎖信息
*/
@Data
public class LockInfo {
private String lockId;
private String lockTrxId;
private String lockMode;
private String lockType;
private String lockTable;
}第六章:總結與展望
6.1 知識點總結回顧
6.1.1 分佈式事務核心概念
通過前面章節的深入學習,我們全面掌握了分佈式事務的核心概念和實現原理:
ACID特性在分佈式環境下的挑戰:
- 原子性(Atomicity):在分佈式系統中,需要確保跨多個服務的操作要麼全部成功,要麼全部失敗
- 一致性(Consistency):數據在分佈式節點間保持一致狀態,避免數據不一致問題
- 隔離性(Isolation):併發事務之間不會相互影響,防止髒讀、幻讀等問題
- 持久性(Durability):事務提交後的數據變更必須持久化保存
CAP理論與BASE理論:
- CAP理論:一致性(Consistency)、可用性(Availability)、分區容錯性(Partition tolerance)不可能同時滿足
- BASE理論:基本可用(Basically Available)、軟狀態(Soft state)、最終一致性(Eventually consistent)
6.1.2 分佈式事務解決方案對比
我們深入學習了多種分佈式事務解決方案,每種方案都有其適用場景:
/**
* 分佈式事務解決方案總結
*/
public class TransactionSolutionSummary {
/**
* 兩階段提交(2PC)
* 優點:強一致性,實現簡單
* 缺點:性能較差,存在單點故障風險
* 適用場景:對一致性要求極高的金融場景
*/
public void twoPhaseCommitSummary() {
log.info("2PC特點:");
log.info("- 強一致性保證");
log.info("- 阻塞式協議,性能較差");
log.info("- 協調者單點故障風險");
log.info("- 適用於金融、支付等強一致性場景");
}
/**
* TCC(Try-Confirm-Cancel)
* 優點:性能好,無鎖設計
* 缺點:業務侵入性強,開發複雜度高
* 適用場景:高併發、對性能要求高的場景
*/
public void tccSummary() {
log.info("TCC特點:");
log.info("- 三階段提交,性能優秀");
log.info("- 無鎖設計,支持高併發");
log.info("- 業務侵入性強,需要實現三個方法");
log.info("- 適用於電商、秒殺等高併發場景");
}
/**
* 本地消息表
* 優點:實現簡單,可靠性高
* 缺點:需要額外存儲,有一定延遲
* 適用場景:對實時性要求不高的異步場景
*/
public void localMessageTableSummary() {
log.info("本地消息表特點:");
log.info("- 實現簡單,易於理解");
log.info("- 最終一致性保證");
log.info("- 需要定時任務處理消息");
log.info("- 適用於訂單處理、數據同步等場景");
}
/**
* 消息事務
* 優點:解耦性好,擴展性強
* 缺點:依賴消息中間件,複雜度較高
* 適用場景:微服務架構下的異步處理
*/
public void messageTransactionSummary() {
log.info("消息事務特點:");
log.info("- 基於消息中間件實現");
log.info("- 服務間解耦,擴展性好");
log.info("- 支持異步處理");
log.info("- 適用於微服務架構");
}
/**
* Saga模式
* 優點:長事務支持,補償機制靈活
* 缺點:補償邏輯複雜,一致性較弱
* 適用場景:長流程業務,如旅遊預訂
*/
public void sagaSummary() {
log.info("Saga模式特點:");
log.info("- 支持長事務處理");
log.info("- 靈活的補償機制");
log.info("- 最終一致性");
log.info("- 適用於複雜業務流程");
}
}6.1.3 主流框架實戰經驗
通過實際代碼示例,我們掌握了主流分佈式事務框架的使用:
Seata框架:
- AT模式:自動代理數據源,無業務侵入
- TCC模式:手動實現三階段方法,性能優秀
- Saga模式:狀態機編排,適合複雜流程
- XA模式:標準兩階段提交實現
Apache ShardingSphere:
- XA事務:強一致性保證
- BASE事務:最終一致性,性能更好
RocketMQ事務消息:
- 半消息機制確保消息可靠性
- 本地事務與消息發送解耦
6.2 技術發展趨勢
6.2.1 雲原生分佈式事務
隨着雲原生技術的發展,分佈式事務也在向雲原生方向演進:
/**
* 雲原生分佈式事務趨勢
*/
@Component
public class CloudNativeTransactionTrends {
/**
* Kubernetes環境下的分佈式事務
*/
public void kubernetesTransactionPattern() {
log.info("Kubernetes環境下分佈式事務特點:");
log.info("1. 服務發現與負載均衡自動化");
log.info("2. 容器化部署,彈性伸縮");
log.info("3. 配置管理雲原生化");
log.info("4. 監控與日誌統一收集");
// 示例:Kubernetes配置
String k8sConfig = """
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: seata-server
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: seata-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: seata-server
spec:
containers:
- name: seata-server
image: seataio/seata-server:1.5.2
ports:
- containerPort: 8091
env:
- name: SEATA_PORT
value: "8091"
- name: STORE_MODE
value: "db"
""";
log.info("Kubernetes部署配置示例:\n{}", k8sConfig);
}
/**
* 服務網格中的分佈式事務
*/
public void serviceMeshTransaction() {
log.info("服務網格(Service Mesh)中的分佈式事務:");
log.info("1. Istio/Envoy代理層事務管理");
log.info("2. 分佈式追蹤自動化");
log.info("3. 流量管理與故障注入");
log.info("4. 安全策略統一管理");
}
/**
* Serverless環境下的事務處理
*/
public void serverlessTransaction() {
log.info("Serverless環境下的分佈式事務:");
log.info("1. 函數計算的事務協調");
log.info("2. 事件驅動的事務模式");
log.info("3. 冷啓動對事務性能的影響");
log.info("4. 狀態管理的挑戰與解決方案");
}
}6.2.2 新興技術融合
分佈式事務技術正在與其他新興技術深度融合:
/**
* 新興技術與分佈式事務融合
*/
@Component
public class EmergingTechnologyIntegration {
/**
* 區塊鏈與分佈式事務
*/
public void blockchainTransaction() {
log.info("區塊鏈技術在分佈式事務中的應用:");
log.info("1. 智能合約實現自動化事務執行");
log.info("2. 不可篡改的事務記錄");
log.info("3. 去中心化的事務協調");
log.info("4. 跨鏈事務處理");
// 示例:智能合約事務
String smartContract = """
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract DistributedTransaction {
enum TransactionStatus { PENDING, COMMITTED, ABORTED }
struct Transaction {
address coordinator;
TransactionStatus status;
mapping(address => bool) participants;
}
mapping(bytes32 => Transaction) public transactions;
function createTransaction(bytes32 txId) public {
transactions[txId].coordinator = msg.sender;
transactions[txId].status = TransactionStatus.PENDING;
}
function commitTransaction(bytes32 txId) public {
require(transactions[txId].coordinator == msg.sender);
transactions[txId].status = TransactionStatus.COMMITTED;
}
}
""";
log.info("智能合約示例:\n{}", smartContract);
}
/**
* AI/ML在分佈式事務中的應用
*/
public void aiMlTransaction() {
log.info("AI/ML在分佈式事務中的應用:");
log.info("1. 智能事務路由與負載均衡");
log.info("2. 異常檢測與自動恢復");
log.info("3. 性能預測與優化建議");
log.info("4. 智能補償策略選擇");
}
/**
* 邊緣計算環境下的分佈式事務
*/
public void edgeComputingTransaction() {
log.info("邊緣計算環境下的分佈式事務:");
log.info("1. 網絡延遲與帶寬限制");
log.info("2. 離線場景下的事務處理");
log.info("3. 邊緣節點間的協調機制");
log.info("4. 雲邊協同的事務模式");
}
}6.3 擴展閲讀推薦
6.3.1 經典論文與書籍
為了更深入地理解分佈式事務,推薦以下經典資料:
/**
* 擴展閲讀資源推薦
*/
@Component
public class ExtendedReadingRecommendations {
/**
* 經典論文推薦
*/
public void recommendPapers() {
List<Paper> papers = Arrays.asList(
new Paper("Consensus in the Presence of Partial Synchrony",
"Dwork, Lynch, Stockmeyer", 1988,
"分佈式共識算法的奠基性論文"),
new Paper("Impossibility of Distributed Consensus with One Faulty Process",
"Fischer, Lynch, Paterson", 1985,
"FLP不可能性定理,分佈式系統理論基礎"),
new Paper("The Part-Time Parliament",
"Leslie Lamport", 1998,
"Paxos算法的原始論文"),
new Paper("In Search of an Understandable Consensus Algorithm",
"Diego Ongaro, John Ousterhout", 2014,
"Raft算法論文,更易理解的共識算法"),
new Paper("Sagas",
"Hector Garcia-Molina, Kenneth Salem", 1987,
"Saga模式的原始論文")
);
papers.forEach(paper -> {
log.info("論文:{}", paper.getTitle());
log.info("作者:{}", paper.getAuthors());
log.info("年份:{}", paper.getYear());
log.info("簡介:{}", paper.getDescription());
log.info("---");
});
}
/**
* 技術書籍推薦
*/
public void recommendBooks() {
List<Book> books = Arrays.asList(
new Book("設計數據密集型應用",
"Martin Kleppmann",
"深入講解分佈式系統設計原理"),
new Book("分佈式系統概念與設計",
"George Coulouris等",
"分佈式系統的經典教材"),
new Book("微服務架構設計模式",
"Chris Richardson",
"微服務架構下的事務處理模式"),
new Book("高性能MySQL",
"Baron Schwartz等",
"MySQL事務處理與優化"),
new Book("Redis設計與實現",
"黃健宏",
"Redis事務機制深度解析")
);
books.forEach(book -> {
log.info("書籍:{}", book.getTitle());
log.info("作者:{}", book.getAuthor());
log.info("簡介:{}", book.getDescription());
log.info("---");
});
}
/**
* 在線資源推薦
*/
public void recommendOnlineResources() {
List<OnlineResource> resources = Arrays.asList(
new OnlineResource("Apache Seata官方文檔",
"https://seata.io/zh-cn/docs/overview/what-is-seata.html",
"Seata框架的官方文檔和最佳實踐"),
new OnlineResource("分佈式事務系列博客",
"",
"深入淺出的分佈式事務系列文章"),
new OnlineResource("MIT 6.824分佈式系統課程",
"https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.824/",
"MIT的分佈式系統經典課程"),
new OnlineResource("Raft算法可視化",
"http://thesecretlivesofdata.com/raft/",
"Raft算法的可視化演示")
);
resources.forEach(resource -> {
log.info("資源:{}", resource.getTitle());
log.info("鏈接:{}", resource.getUrl());
log.info("描述:{}", resource.getDescription());
log.info("---");
});
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class Paper {
private String title;
private String authors;
private int year;
private String description;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
private String description;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class OnlineResource {
private String title;
private String url;
private String description;
}6.3.2 開源項目與工具
/**
* 開源項目推薦
*/
@Component
public class OpenSourceProjectRecommendations {
/**
* 分佈式事務框架
*/
public void recommendTransactionFrameworks() {
List<OpenSourceProject> frameworks = Arrays.asList(
new OpenSourceProject("Seata",
"https://github.com/seata/seata",
"阿里巴巴開源的分佈式事務解決方案",
"Java"),
new OpenSourceProject("Apache ShardingSphere",
"https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere",
"分佈式數據庫中間件,支持分佈式事務",
"Java"),
new OpenSourceProject("TCC-Transaction",
"https://github.com/changmingxie/tcc-transaction",
"TCC型分佈式事務框架",
"Java"),
new OpenSourceProject("Hmily",
"https://github.com/dromara/hmily",
"高性能異步分佈式事務TCC框架",
"Java"),
new OpenSourceProject("ByteTCC",
"https://github.com/liuyangming/ByteTCC",
"基於TCC機制的分佈式事務管理器",
"Java")
);
frameworks.forEach(project -> {
log.info("項目:{}", project.getName());
log.info("地址:{}", project.getUrl());
log.info("描述:{}", project.getDescription());
log.info("語言:{}", project.getLanguage());
log.info("---");
});
}
/**
* 監控與診斷工具
*/
public void recommendMonitoringTools() {
List<OpenSourceProject> tools = Arrays.asList(
new OpenSourceProject("Zipkin",
"https://github.com/openzipkin/zipkin",
"分佈式追蹤系統",
"Java"),
new OpenSourceProject("Jaeger",
"https://github.com/jaegertracing/jaeger",
"CNCF分佈式追蹤項目",
"Go"),
new OpenSourceProject("SkyWalking",
"https://github.com/apache/skywalking",
"應用性能監控系統",
"Java"),
new OpenSourceProject("Prometheus",
"https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus",
"監控和告警工具包",
"Go")
);
tools.forEach(tool -> {
log.info("工具:{}", tool.getName());
log.info("地址:{}", tool.getUrl());
log.info("描述:{}", tool.getDescription());
log.info("語言:{}", tool.getLanguage());
log.info("---");
});
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class OpenSourceProject {
private String name;
private String url;
private String description;
private String language;
}6.4 思考問題與討論
6.4.1 深度思考題
為了加深對分佈式事務的理解,以下是一些值得深入思考的問題:
/**
* 深度思考題
*/
@Component
public class DeepThinkingQuestions {
/**
* 理論層面的思考題
*/
public void theoreticalQuestions() {
List<String> questions = Arrays.asList(
"1. 在CAP定理的約束下,如何在一致性和可用性之間找到最佳平衡點?",
"2. 為什麼説FLP不可能性定理並不意味着分佈式共識無法實現?實際系統是如何繞過這個限制的?",
"3. BASE理論中的'最終一致性'在實際業務中可以接受多長的不一致時間窗口?",
"4. 分佈式事務的性能瓶頸主要來自哪裏?網絡延遲、鎖競爭還是協調開銷?",
"5. 在微服務架構中,是否應該完全避免分佈式事務?有哪些替代方案?"
);
questions.forEach(question -> {
log.info("思考題:{}", question);
log.info("---");
});
}
/**
* 實踐層面的思考題
*/
public void practicalQuestions() {
List<String> questions = Arrays.asList(
"1. 在電商系統中,訂單、庫存、支付服務如何設計分佈式事務?考慮性能和一致性要求。",
"2. 如何設計一個支持百萬級TPS的分佈式事務系統?需要考慮哪些關鍵因素?",
"3. 在跨國部署的系統中,網絡延遲很高,如何優化分佈式事務的性能?",
"4. 如何設計分佈式事務的監控體系?需要監控哪些關鍵指標?",
"5. 在容器化環境中部署分佈式事務系統時,需要注意哪些問題?"
);
questions.forEach(question -> {
log.info("實踐題:{}", question);
log.info("---");
});
}
/**
* 架構設計思考題
*/
public void architecturalQuestions() {
List<String> questions = Arrays.asList(
"1. 如何設計一個既支持強一致性又支持最終一致性的混合事務系統?",
"2. 在多雲環境下,如何實現跨雲的分佈式事務?需要考慮哪些技術挑戰?",
"3. 如何設計分佈式事務的降級策略?在系統壓力過大時如何保證核心功能?",
"4. 邊緣計算場景下,如何處理網絡分區時的分佈式事務?",
"5. 如何設計支持動態擴縮容的分佈式事務協調器?"
);
questions.forEach(question -> {
log.info("架構題:{}", question);
log.info("---");
});
}
}6.4.2 實戰練習建議
/**
* 實戰練習建議
*/
@Component
public class PracticalExercises {
/**
* 初級練習
*/
public void beginnerExercises() {
log.info("初級練習建議:");
log.info("1. 搭建Seata環境,實現簡單的訂單-庫存-賬户事務");
log.info("2. 使用本地消息表模式實現異步事務處理");
log.info("3. 編寫TCC模式的Try-Confirm-Cancel方法");
log.info("4. 實現基於RocketMQ的事務消息");
log.info("5. 配置Seata的AT模式自動代理");
}
/**
* 中級練習
*/
public void intermediateExercises() {
log.info("中級練習建議:");
log.info("1. 設計並實現一個完整的電商下單流程分佈式事務");
log.info("2. 實現分佈式事務的性能監控和告警系統");
log.info("3. 編寫分佈式事務的壓力測試工具");
log.info("4. 實現事務的自動重試和補償機制");
log.info("5. 設計分佈式事務的故障注入和恢復測試");
}
/**
* 高級練習
*/
public void advancedExercises() {
log.info("高級練習建議:");
log.info("1. 設計支持多種事務模式的統一事務框架");
log.info("2. 實現分佈式事務的智能路由和負載均衡");
log.info("3. 開發分佈式事務的可視化管理平台");
log.info("4. 實現跨數據中心的分佈式事務協調");
log.info("5. 設計基於機器學習的事務性能優化系統");
}
}6.5 結語
通過本文的深入學習,我們全面掌握了分佈式事務的理論基礎、實現原理、主流框架使用以及性能優化等核心知識。分佈式事務作為分佈式系統中的關鍵技術,其重要性不言而喻。
核心收穫:
- 理論基礎紮實:深入理解了ACID特性、CAP定理、BASE理論等分佈式事務的理論基礎
- 方案選擇清晰:掌握了2PC、TCC、Saga、本地消息表等多種解決方案的適用場景
- 框架使用熟練:通過大量代碼示例,熟練掌握了Seata、ShardingSphere、RocketMQ等主流框架
- 性能優化深入:學會了分佈式事務的性能瓶頸分析、監控診斷、部署優化等實戰技能
- 最佳實踐豐富:積累了生產環境部署、故障處理、架構設計等寶貴經驗
技術發展展望:
分佈式事務技術正在向更加智能化、雲原生化的方向發展。未來我們將看到:
- 與AI/ML技術的深度融合,實現智能化的事務管理
- 雲原生環境下的事務處理模式創新
- 邊緣計算場景下的分佈式事務解決方案
- 區塊鏈技術在分佈式事務中的應用探索
持續學習建議:
技術發展日新月異,建議大家:
- 關注開源社區的最新動態,參與項目貢獻
- 深入研讀經典論文,夯實理論基礎
- 在實際項目中應用所學知識,積累實戰經驗
- 參與技術交流,分享經驗心得
- 保持對新技術的敏感度,及時學習新的解決方案
分佈式事務是一個複雜而又充滿挑戰的技術領域,希望本文能夠為大家的學習和實踐提供有價值的參考。讓我們在分佈式系統的道路上繼續探索,共同推動技術的發展與進步!