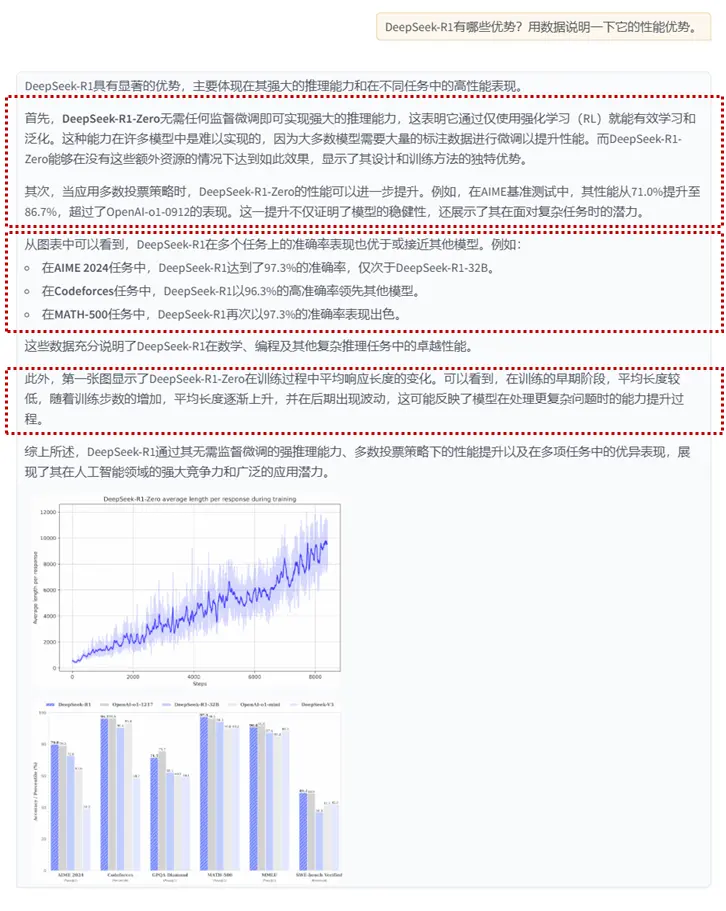
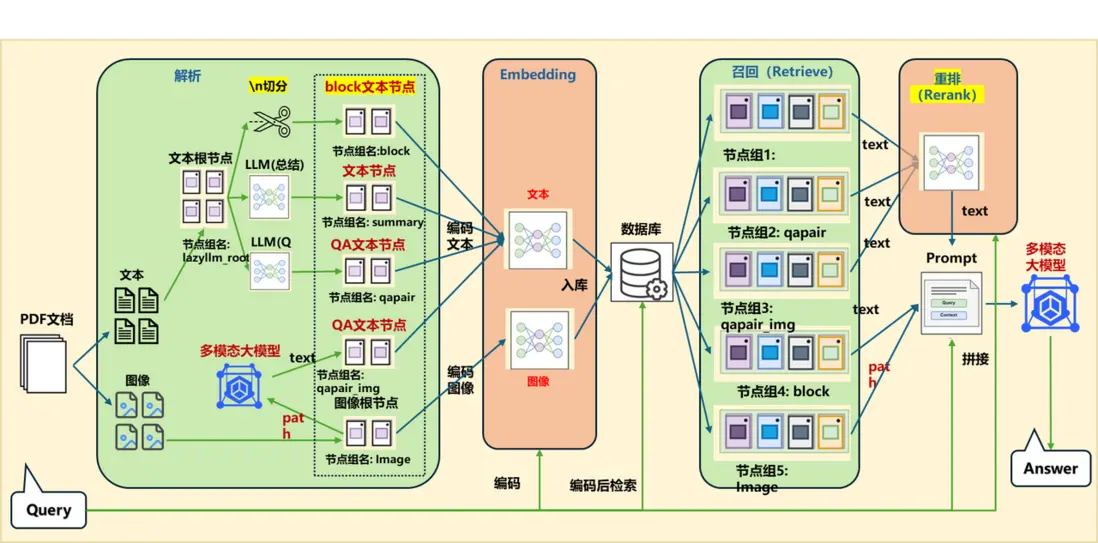
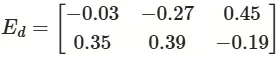在前面的課程中,我們學習了 RAG 相關的知識,以及如何自定義 Reader 組件和在 RAG 任務中處理圖片和表格數據。本節內容將在此基礎上,利用前面學到的知識,搭建一個基於論文的問答系統。
在信息爆炸的時代,科研論文的數量激增,研究人員在查閲文獻時面臨諸多挑戰。論文內容專業性強、邏輯複雜,傳統的關鍵詞檢索方式難以精準提取核心信息,導致獲取有效內容的成本較高。
為了解決這一問題,RAG技術被廣泛應用,RAG不僅能結合了檢索能力,可以精準檢索相關論文,還能結合大語言模型(LLM)的生成能力,對提問進行智能解析,提供深入、清晰的答案,幫助研究人員高效理解論文內容,提高科研效率。
本教程主要介紹如何利用 LazyLLM 搭建一個基於 RAG 的論文問答系統。為了實現該系統,我們需要為RAG準備並接入一個便於處理論文的解析器以及存儲解析結果及向量化結果的數據存儲器。讓我們開始吧!
傳統RAG的論文系統
(一)環境準備
如果您的電腦上安裝了Python,請通過下方命令安裝lazyllm及必要的依賴包。關於 LazyLLM 的環境更詳細的準備可以參考《基礎1-實戰:最基礎的RAG》中對應的內容。
pip install lazyllm
(二)設計方案
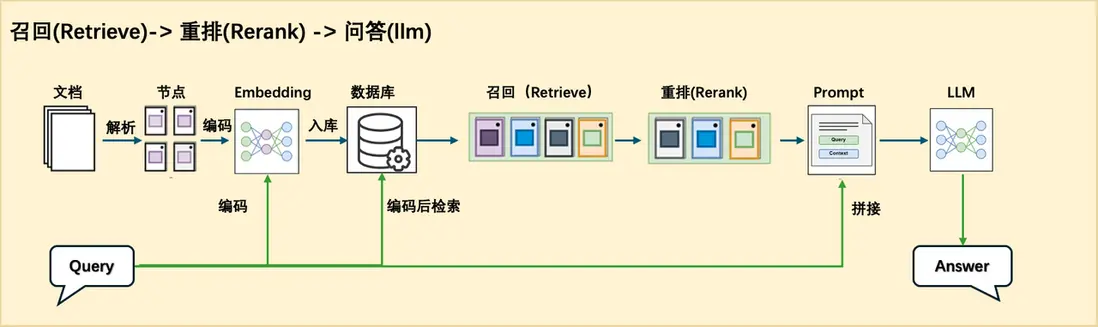
1.整體架構
為了方便我們查閲論文或者快速瞭解相關論文的核心內容,我們可以用 RAG 設計一個論文問答系統。這個問答系統我們採用的是 Retrieve-and-rerank 架構,來保證檢索內容的準確性以及生成結果的合理性。
這個框架中首先把所有需要處理的論文進行預處理,切分成 chunks,然後經過 embedding 模型,把相應的文本和對應的 embedding 存放到數據庫中,這一步屬於離線部分。
這一步處理完成後,就可以進行在線處理了。當提問的 query 來到之後先經過 embedding 模型,生成對應的 embedding 向量,然後使用這個 quey 和對應的 embedding 在數據庫中進行檢索,檢索出相關的文本段出來,用於後面的處理。這一步屬於粗篩,只要檢索出相關的文本段即可,所以這裏可以有基於關鍵字的檢索,也可以有基於語義的檢索方法。
為了使傳給大模型的相關上下文更精準,我們還要對檢索到的這些文本段進行一下精排,即 Rerank。Rerank 可以把多種檢索策略下檢索到的文本段在統一空間中進行比較,然後返回相似度最高 K 個,然後和前面的 query 一起拼接在一個給大模型做最後的結果生成。
2.方案流程
綜上所述,要完成這個系統需要的步驟包括:
- 步驟一:數據準備
- 步驟二:數據處理及組件搭建
- 步驟三:應用的流程編排
- 步驟四:代碼調試
- 步驟五:效果校驗
- 步驟六:體驗效果是否符合要求,不符合要求就返回步驟三進行迭代優化。
(三)實現方案
1.數據準備
首先我們需要準備構建知識庫的數據,這裏我們使用了 arxivQA(https://github.com/taesiri/ArXivQA),這個數據集中的 Papers-2024.md 文件中的前100篇論文,需要把這些論文下載到本地並保存到家目錄下的 ".lazyllm/rag\_for\_qa/rag_master" 目錄下。我們可以再在裏面加一篇《DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs viaReinforcement Learning》文章。
2.組件搭建
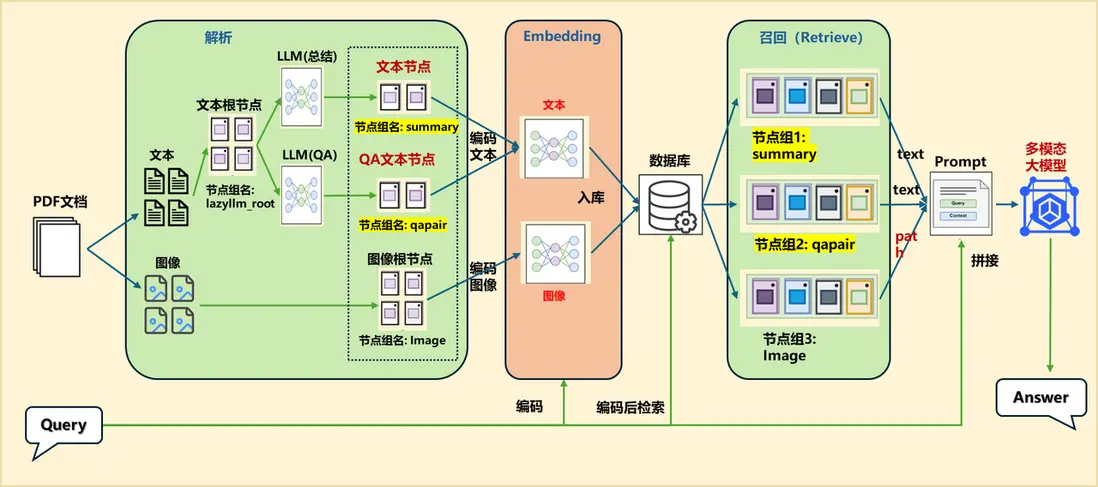
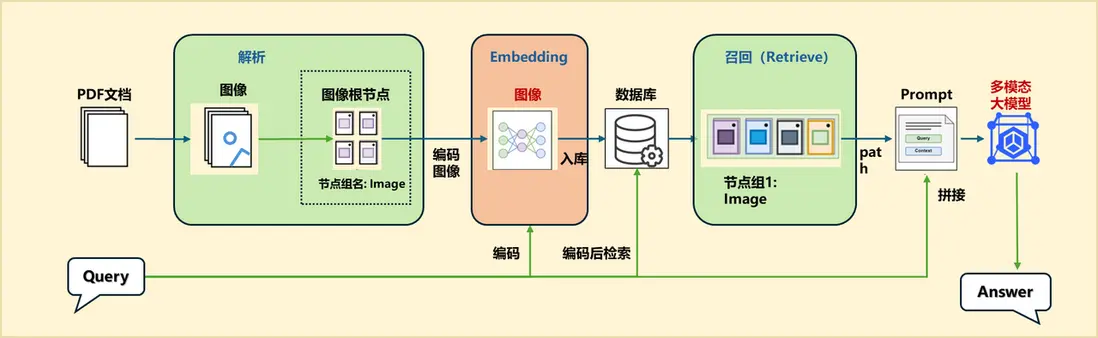
在 LazyLLM 中,我們可以直接使用專門用於提取特定內容的Document解析器類,目前LazyLLM 內置的 Document可以支持 DOCX,PDF,PPT,EXCEL 等常見的富文本內容提取。接下來我們將一起使用LazyLLM 來構建我們的文檔解析流程:
(1)文檔解析器
我們首先需要使用LazyLLM的Document類創建一個基礎的文檔解析器:
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/a09a84cdf0585a5c9d52af6db0e965be95d03123/rag/codes/chapter14/BasciPDFReader.py#L1)
import os
import atexit
import lazyllm
class TmpDir:
def __init__(self):
self.root_dir = os.path.expanduser(os.path.join(lazyllm.config['home'], 'rag_for_qa'))
self.rag_dir = os.path.join(self.root_dir, "rag_master")
os.makedirs(self.rag_dir, exist_ok=True)
self.store_file = os.path.join(self.root_dir, "milvus.db")
self.image_path = "/home/workspace/LazyRAG-Enterprise/images"
tmp_dir = TmpDir()
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir)
documents.create_node_group(name="block", transform=lambda s: s.split("\n") if s else '')
以上代碼使用 LazyLLM 框架的 Document 類來創建一個基礎的文檔解析器,並定義了一個 TmpDir 類來管理本地數據存儲路徑。主要功能包括:
創建並管理數據存儲目錄:
- 通過 TmpDir 類定義數據存儲路徑,包括 RAG 相關目錄和數據庫存儲文件路徑。
- 確保存儲目錄存在(若不存在則創建)。
使用 lazyllm.Document 管理文檔數據:
- 將rag\_master目錄作為dataset\_path傳遞給 Document 類,用於使用LazyLLM內置的文檔解析器加載文檔數據。
- 定義 create\_node\_group 方法,以 "\n" 作為文本切分標識,將文檔分割為多個節點。
(2)創建檢索器
在文檔解析的基礎上,我們可以構建一個檢索器(Retriever),用於高效地從解析後的文本數據中查找相關信息。通過調整數據處理及入庫方式,我們可以觀察這些改動對檢索結果的影響。
現在,讓我們一起使用 LazyLLM 框架中的 Retriever類來構建一個簡單的文檔檢索器:
retriever = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="block", similarity="bm25", topk=3, output_format='content')
以上代碼使用 LazyLLM 框架的Retriever類創建了一個簡單的檢索器,其中我們將之前定義好的文檔解析器作為參數傳入到檢索器中,並選擇對解析器的"block"組,使用BM25 算法查找最匹配的 3 個段落,並返回文本內容。
在這個檢索器中我們提到的BM25(Best Matching 25) 算法是一種用於文本檢索的詞頻(TF)- 逆文檔頻率(IDF) 排序算法,是 Okapi BM25 的簡稱。它廣泛用於搜索引擎、信息檢索(IR)和自然語言處理(NLP)領域,能衡量文檔與查詢的相關性。
現在我們調用一次檢索器,看一下當前文檔解析方法的檢索效果:
print(retriever('deepseek-r1相關論文的Abstract'))
>> ['page_label: 1\n\nresearch@deepseek.com', 'page_label: 13\n\nClaude-3.5- GPT-4o DeepSeek OpenAI OpenAI DeepSeek', 'page_label: 1\n\nDeepSeek-AI']
當前檢索結果的相關性較低,主要問題在於分塊過小,導致信息碎片化,以及 BM25 依賴關鍵詞匹配,難以精準捕捉語義關聯。返回的片段內容過短,且未能直接命中 Abstract 相關信息,影響了查詢效果。
為了提升召回質量,我們需要優化分塊策略,確保每個文本塊包含更完整的語義信息,並結合向量化檢索提高語義匹配的精準度。
在接下來的部分,我們將通過自定義解析器優化分塊方式,並引入向量化檢索,以實現更高效的語義搜索。
(3)定義 PDF Reader
由於論文都是以 pdf 格式保存並且通常排版複雜、圖表豐富,所以我們推薦使用高性能的 PDF 解析工具,來保證提取語義信息的完整性。 我們特別為業界領先的 PDF 文檔解析工具 —— MinerU(https://github.com/opendatalab/MinerU),提供了專門的接入組件,無需額外定製,即可順暢集成。
目前提供一鍵啓動的 MinerU 服務端(server)以及配套的 PDF 客户端。使用流程如下:先在本地啓動 MinerU 解析服務,再通過接入 MineruPDFReader 獲取解析後的文檔內容。
提示:在開始之前,請先確保安裝了 MinerU 依賴哦(lazyllm install mineru 即可一鍵安裝)。 為確保解析結果穩定,當前固定 MinerU 版本為2.5.4。服務運行所需資源請參考 MinerU 官方文檔。
環境準備完畢後,通過以下命令一鍵部署服務:
lazyllm deploy mineru [--port <port>] [--cache_dir <cache_dir>] [--image_save_dir <image_save_dir>] [--model_source <model_source>]
參數説明:
在本地啓動好 MinerU解析服務後,我們只需要為 documents 對象註冊用於PDF文件解析的解析器即可實現 MinerU 接入:
from lazyllm.tools.rag.readers import MineruPDFReader
# 註冊 PDF 解析器,url 替換為已啓動的 MinerU 服務地址
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888"))
tmp_dir = TmpDir()
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir)
# 註冊 PDF 解析器,url 替換為已啓動的 MinerU 服務地址
documents.add_reader("**/*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888"))
documents.create_node_group(name="block", transform=lambda s: s.split("\n") if s else '')
retriever = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="block", similarity="bm25", topk=3, output_format='content')
print(retriever('deepseek-r1相關論文的Abstract'))
>>["title: DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning\ntype: text\nbbox: [264, 179, 330, 192]\nlines: [{'bbox': [264, 179, 331, 194], 'content': 'DeepSeek-AI', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}]\npage: 0\n\nDeepSeek-AI", "title: Abstract\ntype: text\nbbox: [69, 287, 527, 430]\nlines: [{'bbox': [69, 287, 527, 303], 'content': 'We introduce our first-generation reasoning models, DeepSeek-R1-Zero and DeepSeek-R1.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 302, 526, 317], 'content': 'DeepSeek-R1-Zero, a model trained via large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) without super-', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 317, 526, 331], 'content': 'vised fine-tuning (SFT) as a preliminary step, demonstrates remarkable reasoning capabilities.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 329, 526, 347], 'content': 'Through RL, DeepSeek-R1-Zero naturally emerges with numerous powerful and intriguing', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 344, 527, 362], 'content': 'reasoning behaviors. However, it encounters challenges such as poor readability, and language', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 359, 526, 375], 'content': 'mixing. To address these issues and further enhance reasoning performance, we introduce', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 375, 527, 389], 'content': 'DeepSeek-R1, which incorporates multi-stage training and cold-start data before RL. DeepSeek-', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 388, 526, 404], 'content': 'R1 achieves performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on reasoning tasks. To support the', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 403, 526, 417], 'content': 'research community, we open-source DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, and six dense models', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 418, 474, 431], 'content': '(1.5B, 7B, 8B, 14B, 32B, 70B) distilled from DeepSeek-R1 based on Qwen and Llama.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}]\npage: 0\n\nWe introduce our first-generation reasoning models, DeepSeek-R1-Zero and DeepSeek-R1. DeepSeek-R1-Zero, a model trained via large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) without supervised fine-tuning (SFT) as a preliminary step, demonstrates remarkable reasoning capabilities. Through RL, DeepSeek-R1-Zero naturally emerges with numerous powerful and intriguing reasoning behaviors. However, it encounters challenges such as poor readability, and language mixing. To address these issues and further enhance reasoning performance, we introduce DeepSeek-R1, which incorporates multi-stage training and cold-start data before RL. DeepSeekR1 achieves performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on reasoning tasks. To support the research community, we open-source DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, and six dense models (1.5B, 7B, 8B, 14B, 32B, 70B) distilled from DeepSeek-R1 based on Qwen and Llama.", "title: DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning\ntype: text\nbbox: [236, 203, 358, 215]\nlines: [{'bbox': [236, 205, 358, 216], 'content': 'research@deepseek.com', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}]\npage: 0\n\nresearch@deepseek.com"]
通過與加入自定義解析器之前的結果對比,當前雖然分塊質量有所提升,文本塊的完整性比之前更好,但由於檢索仍然依賴 BM25 進行關鍵詞匹配,召回效果依然受到限制。BM25 無法理解語義,僅根據詞頻進行匹配,導致返回的內容仍包含目錄、致謝等無關信息,而 未能精準找到 Abstract。
接下來,我們將引入向量化檢索,提升語義匹配能力,以實現更精準的內容查找。
(4)向量化檢索
4.1 配置數據存儲
LazyLLM 提供了可配置存儲和索引後端的功能,其中milvus可以以在線服務的形式,通過配置url進行調用,同時也支持使用本地臨時文件的形式快速搭建存儲模塊。這裏我們選擇使用本地臨時文件形式的 milvus 來存儲數據。
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/a09a84cdf0585a5c9d52af6db0e965be95d03123/rag/codes/chapter14/MagicPDFReader_Milvus.py#L390)
import lazyllm
from lazyllm.tools.rag import DocField, DataType
import os
import atexit
class TmpDir:
def __init__(self):
self.root_dir = os.path.expanduser(os.path.join(lazyllm.config['home'], 'rag_for_qa'))
self.rag_dir = os.path.join(self.root_dir, "rag_master")
os.makedirs(self.rag_dir, exist_ok=True)
self.store_file = os.path.join(self.root_dir, "milvus.db")
self.image_path = "Stored Images Path"
atexit.register(self.cleanup)
def cleanup(self):
if os.path.isfile(self.store_file):
os.remove(self.store_file)
for filename in os.listdir(self.image_path):
filepath = os.path.join(self.image_path, filename)
if os.path.isfile(filepath):
os.remove(filepath)
tmp_dir = TmpDir()
# 本地存儲
milvus_store_conf = {
"type": "milvus",
"kwargs": {
'uri': tmp_dir.store_file,
'index_kwargs': {
'index_type': 'HNSW',
'metric_type': "COSINE",
}
},
}
# 在線服務
# milvus_store_conf = {
# "type": "milvus",
# "kwargs": {
# 'uri': "http://your-milvus-server",
# 'index_kwargs': {
# 'index_type': 'HNSW',
# 'metric_type': "COSINE",
# }
# },
# }
doc_fields = {
'comment': DocField(data_type=DataType.VARCHAR, max_size=65535, default_value=' '),
'signature': DocField(data_type=DataType.VARCHAR, max_size=32, default_value=' '),
}
在上面的代碼中,首先定義了一個臨時目錄,用來存放數據和數據庫文件。其中裏面定義了一個 cleanup 函數,用於程序結束後清理數據庫文件和圖片文件,並使用 atexit (該模塊的主要功能是註冊回調函數,這些回調函數會在 Python 解釋器即將正常退出時被調用)把自定義的清理函數進行註冊。
然後定義了 milvus 的配置文件,主要包括類型、uri、索引的類型和策略。
這裏就會涉及到milvus 的兩種使用方式了,一種是使用臨時文件的方式,即上面代碼中在 milvus 的配置文件中的 uri 指定為本地數據的路徑。另一種是使用現有的 milvus 服務的方式,我們只要把 milvus 服務的 url 賦給 milvus 的配置文件中的 uri 即可。最後定義了數據的屬性。
4.2 配置文本嵌入
LazyLLM 提供了模型的推理服務,我們可以使用TrainableModule直接將Embedding模型作為服務啓動,並自動接入我們的文檔解析器中。
embed = lazyllm.TrainableModule("bge-large-zh-v1.5")
接下來,我們將前面準備好的 milvus 和 Embedding接入到文檔解析器中,並查看一下效果:
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/a09a84cdf0585a5c9d52af6db0e965be95d03123/rag/codes/chapter14/MagicPDFReader_Milvus.py#L440)
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir,
embed=embed.start(),
manager=True,
store_conf=milvus_store_conf,
doc_fields=doc_fields
)
documents.add_reader("**/*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888"))
documents.create_node_group(name="block", transform=lambda s: s.split("\n") if s else '')
retriever = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="block", topk=3, output_format='content')
print(retriever('deepseek-r1相關論文的Abstract'))
# >>> ["page: 0\ntitle: DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning\nbbox: [264, 179, 330, 192]\ntype: text\nlines: [{'bbox': [264, 179, 331, 194], 'content': 'DeepSeek-AI', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}]\n\nDeepSeek-AI", "page: 0\ntitle: Abstract\nbbox: [69, 287, 527, 430]\ntype: text\nlines: [{'bbox': [69, 287, 527, 303], 'content': 'We introduce our first-generation reasoning models, DeepSeek-R1-Zero and DeepSeek-R1.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 302, 526, 317], 'content': 'DeepSeek-R1-Zero, a model trained via large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) without super-', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 317, 526, 331], 'content': 'vised fine-tuning (SFT) as a preliminary step, demonstrates remarkable reasoning capabilities.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 329, 526, 347], 'content': 'Through RL, DeepSeek-R1-Zero naturally emerges with numerous powerful and intriguing', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 344, 527, 362], 'content': 'reasoning behaviors. However, it encounters challenges such as poor readability, and language', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 359, 526, 375], 'content': 'mixing. To address these issues and further enhance reasoning performance, we introduce', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 375, 527, 389], 'content': 'DeepSeek-R1, which incorporates multi-stage training and cold-start data before RL. DeepSeek-', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 388, 526, 404], 'content': 'R1 achieves performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on reasoning tasks. To support the', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 403, 526, 417], 'content': 'research community, we open-source DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, and six dense models', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 418, 474, 431], 'content': '(1.5B, 7B, 8B, 14B, 32B, 70B) distilled from DeepSeek-R1 based on Qwen and Llama.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}]\n\nWe introduce our first-generation reasoning models, DeepSeek-R1-Zero and DeepSeek-R1. DeepSeek-R1-Zero, a model trained via large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) without supervised fine-tuning (SFT) as a preliminary step, demonstrates remarkable reasoning capabilities. Through RL, DeepSeek-R1-Zero naturally emerges with numerous powerful and intriguing reasoning behaviors. However, it encounters challenges such as poor readability, and language mixing. To address these issues and further enhance reasoning performance, we introduce DeepSeek-R1, which incorporates multi-stage training and cold-start data before RL. DeepSeekR1 achieves performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on reasoning tasks. To support the research community, we open-source DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, and six dense models (1.5B, 7B, 8B, 14B, 32B, 70B) distilled from DeepSeek-R1 based on Qwen and Llama.", "page: 1\ntitle: Abstract\nbbox: [83, 197, 511, 224]\ntype: text\nlines: [{'bbox': [84, 198, 510, 214], 'content': 'Table 2 | Comparison of DeepSeek-R1-Zero and OpenAI o1 models on reasoning-related', 'type': 'text', 'page': 1}, {'bbox': [265, 212, 330, 226], 'content': 'benchmarks.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 1}]\n\nTable 2 | Comparison of DeepSeek-R1-Zero and OpenAI o1 models on reasoning-related benchmarks."]
從結果來看,當前的檢索器已經能夠成功返回與查詢相關的論文摘要內容,並且提取出了正確的Abstract段落。
接下來,為了進一步提升結果的準確性和排序質量,可以考慮引入一個重排模塊(Reranker)。該模塊可以基於文檔的相關性或其他標準對結果進行重新排序,確保最相關的文檔排在最前面。這不僅可以提高用户體驗,還能增強模型對搜索結果排序的精度。
(5)創建重排器
RAG架構中先使用 Retriever 進行候選文檔的快速檢索,然後通過 Reranker 進行精細化排序,這樣的設計能夠在保證檢索效率的同時,提升結果的相關性和排序精度。Reranker 能夠對 Retriever 檢索的結果進行深度理解和優化,是一個提升系統整體性能的關鍵步驟。
LazyLLM 提供了Reranker組件,我們可以像啓動其他模型服務一樣,便捷的將Reranker也作為服務啓動。
reranker = lazyllm.Reranker(name='ModuleReranker',
model="bge-reranker-large",
topk=1,
output_format='content',
join=True).start()通過引入 bge-reranker-large 模型作為 Reranker,可以進一步提高文檔檢索和排序的精度。這對於提高系統的準確性非常重要,尤其是在複雜的查詢任務中。這個過程結合了快速的檢索和精細的重排,能確保用户得到最相關、最有用的結果。
現在我們將Reranker也接入到檢索流程中,在檢索之後通過Reranker對Retriever檢索到的節點進行二次排序
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/a09a84cdf0585a5c9d52af6db0e965be95d03123/rag/codes/chapter14/MagicPDFReader\_Milvus\_Reranker.py#L454)
...
query = "deepseek-r1相關論文的Abstract"
retriever = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="block", topk=3)
ret_nodes = retriever(query)
reranker = lazyllm.Reranker(name='ModuleReranker',
model="/mnt/lustre/share_data/lazyllm/models/bge-reranker-large",
topk=1,
output_format='content',
join=True).start()
context = reranker(nodes=ret_nodes ,query=query)
print(context)
>> '''type: text
page: 0
bbox: [69, 287, 527, 430]
title: Abstract
lines: [{'bbox': [69, 287, 527, 303], 'content': 'We introduce our first-generation reasoning models, DeepSeek-R1-Zero and DeepSeek-R1.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 302, 526, 317], 'content': 'DeepSeek-R1-Zero, a model trained via large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) without super-', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 317, 526, 331], 'content': 'vised fine-tuning (SFT) as a preliminary step, demonstrates remarkable reasoning capabilities.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 329, 526, 347], 'content': 'Through RL, DeepSeek-R1-Zero naturally emerges with numerous powerful and intriguing', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 344, 527, 362], 'content': 'reasoning behaviors. However, it encounters challenges such as poor readability, and language', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 359, 526, 375], 'content': 'mixing. To address these issues and further enhance reasoning performance, we introduce', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 375, 527, 389], 'content': 'DeepSeek-R1, which incorporates multi-stage training and cold-start data before RL. DeepSeek-', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [68, 388, 526, 404], 'content': 'R1 achieves performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on reasoning tasks. To support the', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [69, 403, 526, 417], 'content': 'research community, we open-source DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, and six dense models', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}, {'bbox': [70, 418, 474, 431], 'content': '(1.5B, 7B, 8B, 14B, 32B, 70B) distilled from DeepSeek-R1 based on Qwen and Llama.', 'type': 'text', 'page': 0}]'''
我們將Retriever檢索到的節點和query給到Reranker,並要求Reranker只返回最相關的一個文段後,我們成功的拿到了正確的Abstract段落。
(6)配置大模型
至此,我們已完成數據基礎的解析、入庫以及相關文段的召回。藉助 Retriever 的高效檢索,我們能夠從海量文檔庫中精準提取與查詢高度相關的內容,並通過 Reranker 進一步優化排序,確保最相關的文段位於前列,從而提升檢索質量和結果的精準度。
接下來,我們將進入RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 的最後一步——生成(Generation)。在這一階段,我們會將經過召回與重排的文段與用户的查詢一同傳遞給大語言模型(LLM),讓其基於提供的信息進行深度理解、綜合分析,並最終生成精準、連貫的回答。
LazyLLM 提供了高效的模型推理服務,並支持本地模型推理和在線模型服務兩種形式,分別通過 TrainableModule 和OnlineChatModule 進行配置。
...
prompt = 'You will play the role of an AI Q&A assistant and complete a dialogue task.'\
' In this task, you need to provide your answer based on the given context and question.'\
' If an image can better convey the information being expressed, please include the image reference'\
' in the text in Markdown format. Keep the image path in its original format.'
# 使用本地模型並生成推理服務
llm = lazyllm.TrainableModule('internlm2-chat-7b').start()
# 使用線上模型推理服務
# llm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(api_key="", source="")
# 使用lazyllm.ChatPrompter配置模型推理對話模板
llm = llm.prompt(lazyllm.ChatPrompter(instruction=prompt, extra_keys=['context_str']))
print(llm({"context_str": context, "query":query}))在以上的代碼中,我們定義並啓動了一個LLM服務,並使用lazyllm.ChatPrompter配置了推理模板。至此,我們已完成 LLM 服務的配置,並結合 Retriever + Reranker,完整的構建了一個簡單的RAG,實現高效的檢索增強問答流程。
(四)建知識庫
通過上面各個模塊組件的瞭解,我們需要先利用上面的基於 Mineru 的 Reader 模塊、文檔解析器、文檔檢索器、數據庫配置以及向量化模塊構建知識庫。代碼如下:
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/main/rag/codes/chapter14/BulidMilvus_db.py)
import os
import lazyllm
from lazyllm.tools.rag import DocField, DataType
from lazyllm.tools.rag.readers import MineruPDFReader
def get_cache_path():
return os.path.join(lazyllm.config['home'], 'rag_for_qa')
def get_image_path():
return os.path.join(get_cache_path(), "images")
class TmpDir:
def __init__(self):
self.root_dir = os.path.expanduser(os.path.join(lazyllm.config['home'], 'rag_for_qa'))
self.rag_dir = os.path.join(self.root_dir, "rag_master")
os.makedirs(self.rag_dir, exist_ok=True)
self.store_file = os.path.join(self.root_dir, "milvus.db")
self.image_path = get_image_path()
# atexit.register(self.cleanup)
def cleanup(self):
if os.path.isfile(self.store_file):
os.remove(self.store_file)
for filename in os.listdir(self.image_path):
filepath = os.path.join(self.image_path, filename)
if os.path.isfile(filepath):
os.remove(filepath)
tmp_dir = TmpDir()
# 本地存儲
milvus_store_conf = {
"type": "milvus",
"kwargs": {
'uri': tmp_dir.store_file,
'index_kwargs': {
'index_type': 'HNSW',
'metric_type': "COSINE",
}
},
}
# 在線服務
# milvus_store_conf = {
# "type": "milvus",
# "kwargs": {
# 'uri': "http://your-milvus-server",
# 'index_kwargs': {
# 'index_type': 'HNSW',
# 'metric_type': "COSINE",
# }
# },
# }
doc_fields = {
'comment': DocField(data_type=DataType.VARCHAR, max_size=65535, default_value=' '),
'signature': DocField(data_type=DataType.VARCHAR, max_size=32, default_value=' '),
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
prompt = 'You will play the role of an AI Q&A assistant and complete a dialogue task.'\
' In this task, you need to provide your answer based on the given context and question.'\
' If an image can better present the information being expressed, please include the image reference'\
' in the text in Markdown format. The markdown format of the image must be as follows:'\
' '
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir,
embed=lazyllm.TrainableModule("bge-large-zh-v1.5").start(),
manager=False,
store_conf=milvus_store_conf,
doc_fields=doc_fields)
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888")) # url 需替換為已啓動的 MinerU 服務地址
documents.create_node_group(name="block", transform=lambda s: s.split("\n") if s else '')
retriever = lazyllm.Retriever(doc=documents, group_name="block", topk=3)
retriever("什麼是機器學習")
這裏我們選用的是臨時配置文件的方式使用 milvus 數據庫,這裏需要配置使用的知識庫文檔的路徑,以及構建的數據庫存放路徑。
這裏需要注意一下,在定義臨時配置文件的時候需要把 atexit.register(self.cleanup)這行代碼註釋掉,因為我們的目的是想離線把數據處理完然後放入數據庫中,方便線上使用,所以我們希望運行完代碼之後還要保留數據庫和圖片文件。所以這裏就不能再配置清理函數了。
對於為什麼要在最後定義 Retriever 對象,並且還要調用一下retriever,是因為 LazyLLM 裏面構建知識庫的操作屬於延遲加載,需要在檢索前才會進行加載,所以離線構建知識庫的時候需要調用 Retriever對象檢索來觸發一下。當然如果文檔少的話也可以直接在啓動服務的時候進行加載。
1.編排應用
上面我們已經定義好了 Reader 和存儲配置,下面我們就可以搭建 RAG 的工作流了。
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/a09a84cdf0585a5c9d52af6db0e965be95d03123/rag/codes/chapter14/PaperQA_basic.py#L439)
import lazyllm
prompt = 'You will play the role of an AI Q&A assistant and complete a dialogue task.'\
' In this task, you need to provide your answer based on the given context and question.'\
' If an image can better convey the information being expressed, please include the image reference'\
' in the text in Markdown format. Keep the image path in its original format.'
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir,
embed=lazyllm.TrainableModule("bge-large-zh-v1.5"),
manager=True,
store_conf=milvus_store_conf,
doc_fields=doc_fields)
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888")) # url 需替換為已啓動的 MinerU 服務地址
documents.create_node_group(name="block", transform=lambda s: s.split("\n") if s else '')
with lazyllm.pipeline() as ppl:
ppl.retriever = lazyllm.Retriever(doc=documents, group_name="block", topk=3)
ppl.reranker = lazyllm.Reranker(name='ModuleReranker',
model="bge-reranker-large",
topk=1,
output_format='content',
join=True) | bind(query=ppl.input)
ppl.formatter = (
lambda nodes, query: dict(context_str=nodes, query=query)
) | bind(query=ppl.input)
ppl.llm = lazyllm.TrainableModule('internlm2-chat-7b').prompt(
lazyllm.ChatPrompter(instruction=prompt, extra_keys=['context_str']))
lazyllm.WebModule(ppl, port=23456, static_paths="Stored Images Path").start().wait()
在上面的代碼中,我們先定義了 prompt 和 documents,在定義 documents 時,指定了數據集目錄和embedding 模型,以及管理數據庫用到的存儲配置和字段屬性。然後通過 documents 對象註冊了自定義的 Reader 類,然後定義創建 node group 的名字和轉換規則。
接下來就是工作流的搭建了,在 pipeline 中,依次定義了 Retriever、Reranker、formatter 和 LLM,分別用於檢索召回相關文檔、對召回文檔信息進行重排序、對重排序後的 node 和 query 進行格式化,最後把檢索到的內容輸入給 LLM 來生成相應的答案回覆。
最後通過 WebModule 模塊把上面搭建的 pipeline 啓動成一個 web 服務,這裏需要注意,啓動 WebModule 時,需要傳入圖片的保存路徑,這樣就可以把該目錄設置為靜態目錄,gradio 就可以直接訪問該目錄下的圖片文件了。當 web 服務啓動成功後,則根據生成的 ip 和 port,我們就可以在瀏覽器中進行使用體驗。
2.效果展示
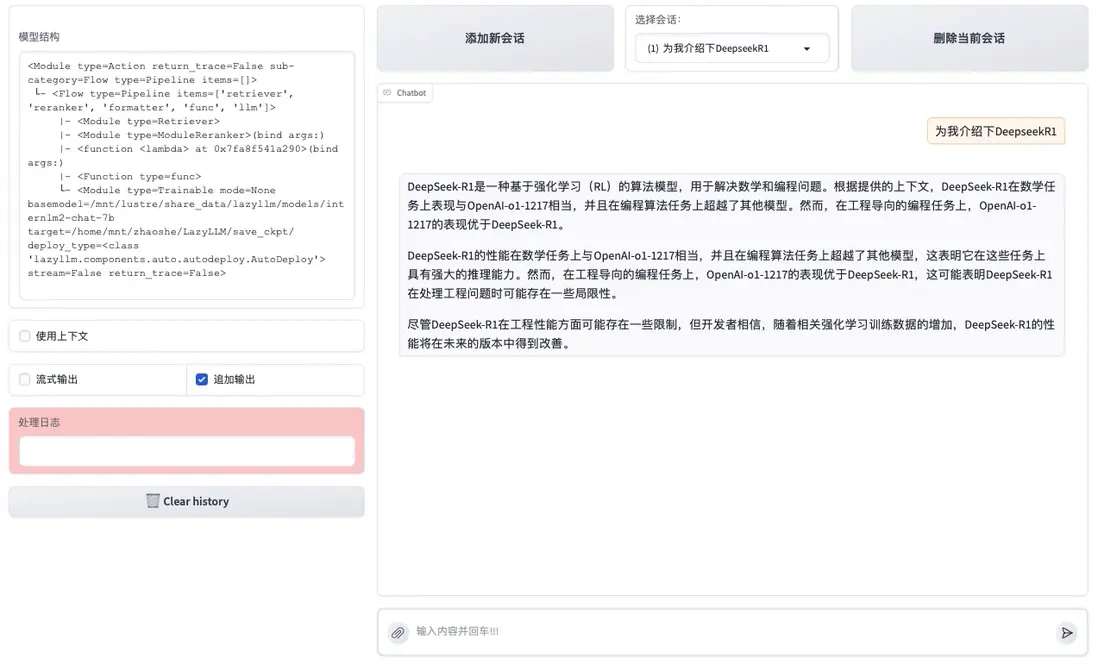
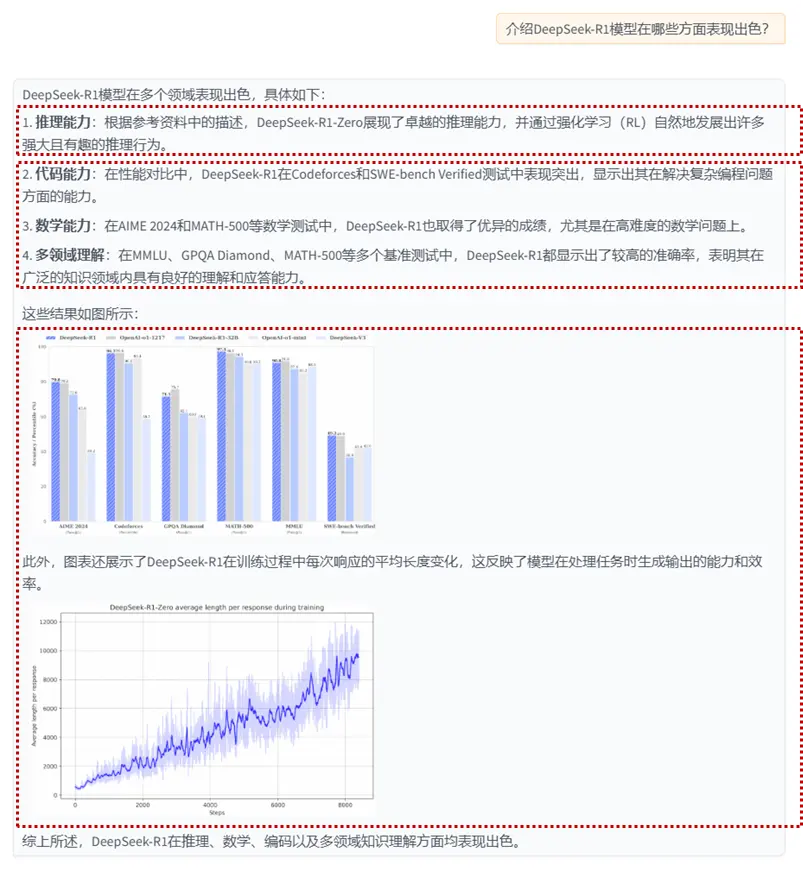
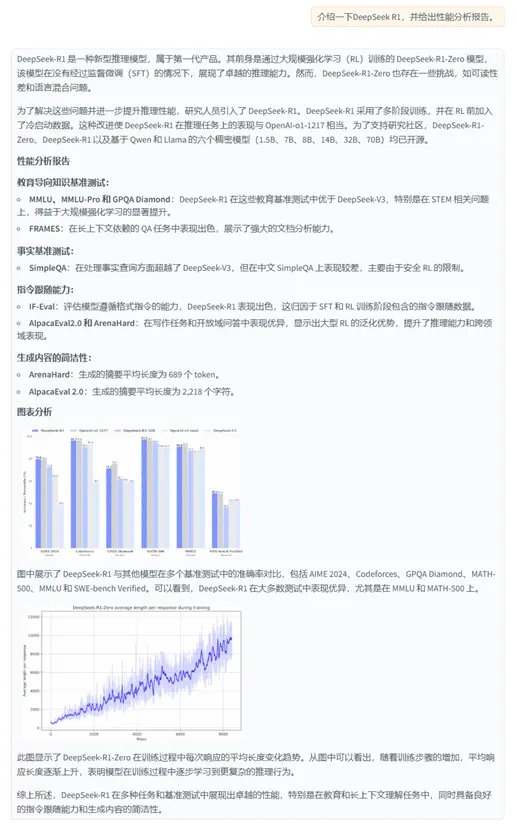
在下圖展示的示例中,用户向系統詢問 論文《DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs viaReinforcement Learning》的相關內容,系統首先檢索到相關段落,並基於其內容生成了精準的回答。同時,系統還能智能提取論文中的圖表信息,並將其檢索與展示,使用户不僅能獲取文本解析,還能直觀查看論文中的關鍵數據與實驗結果。
通過本系統,研究人員可以高效地獲取論文信息,而無需逐字閲讀整篇論文,大大提高了科研工作的便捷性和效率。
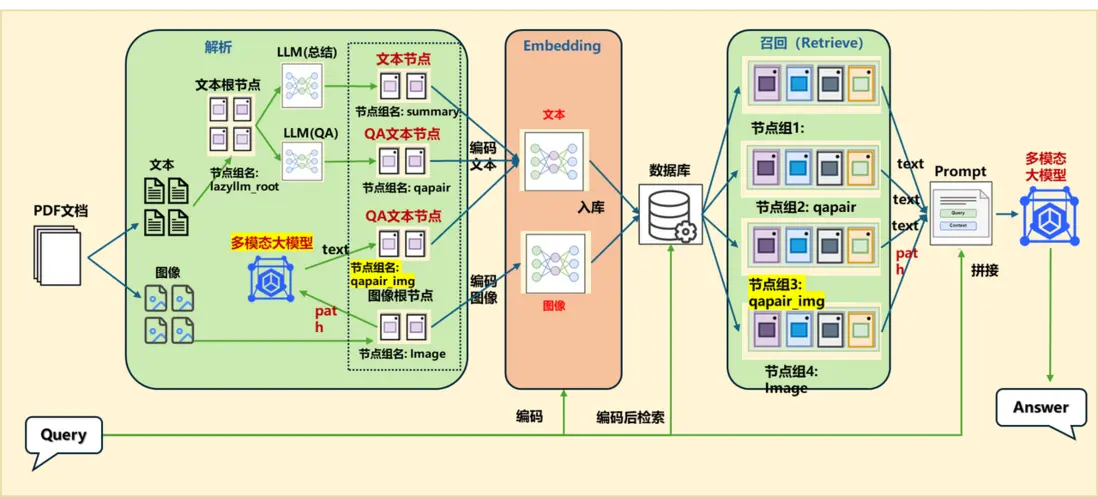
樸素多模態RAG的論文系統
(一)多模態嵌入
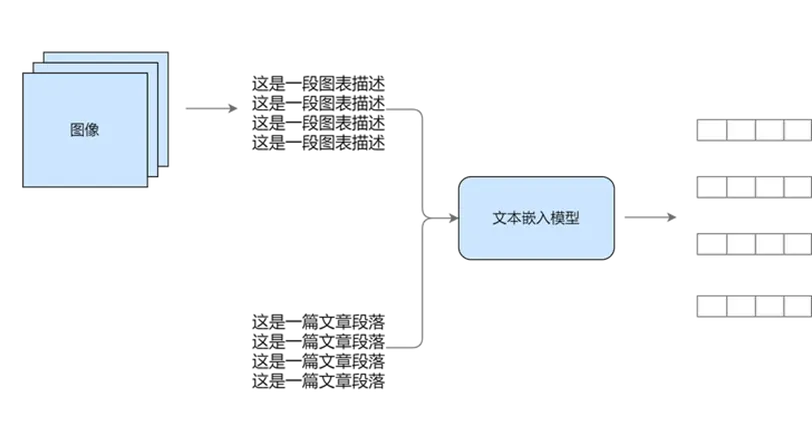
1.方案一
統一到文本模態,然後進行向量嵌入
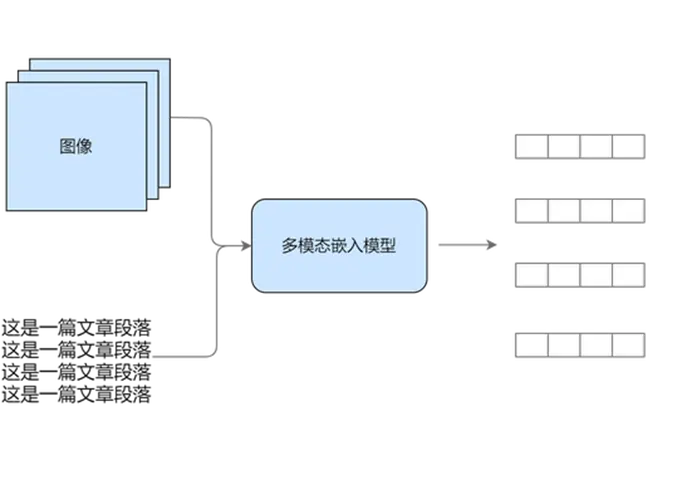
2.方案二
統一到向量空間:利用多模態模型進行映射
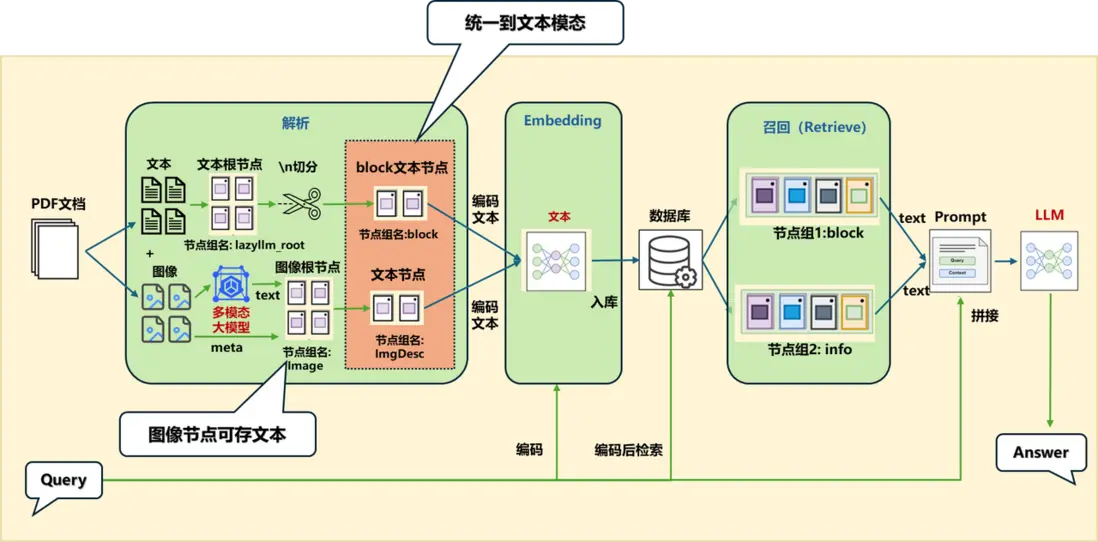
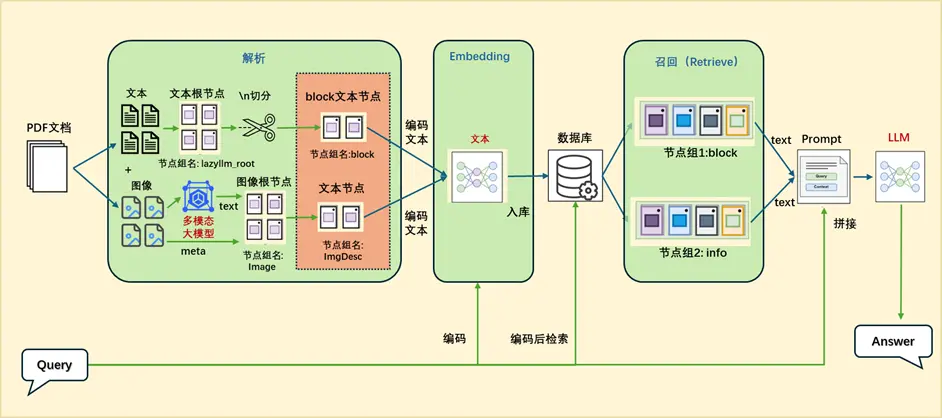
(二)方案一:統一到文本模態
如果在解析的過程單獨為圖片生成描述並構建ImageDocNode節點,可以在原來的 MineruPDFReader 組件傳入一個後處理函數(注意後處理函數的輸入和輸出都應為List[DocNode]):
vlm = lazyllm.TrainableModule(‘internvl-chat-v1-5’).start() # 初始化一個多模態大模型
def build_image_docnode(nodes):
img_nodes = []
for node in nodes:
if node.metadata.get("type", None) == "image" and node.metadata.get("image_path", None):
img_desc = vlm(formatted_query(node.image_path)) # 利用VLM對圖像內容進行解析生成圖像的文本描述
img_nodes.append(ImageDocNode(text=img_desc, image_path=node.metadata.get("image_path"), global_metadata=node.metadata)) # 構建ImageDocNode節點
return nodes + img_nodes
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888", post_func=build_image_docnode)) # 這裏傳入你的後處理函數
1.應用編排實現
documents = lazyllm.Document(
dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir,
embed=lazyllm.TrainableModule("bge-m3"),
manager=False)
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888", post_func=build_image_docnode)) # url 需替換為已啓動的 MinerU 服務地址
documents.create_node_group(name="block", transform=lambda s: s.split("\n") if s else '')
with lazyllm.pipeline() as ppl:
with lazyllm.parallel().sum as ppl.prl:
ppl.prl.retriever1 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="block", similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prl.retriever2 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, lazyllm.Document.ImgDesc, similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prompt = build_vlm_prompt | bind(_0, ppl.input)
ppl.vlm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule()
lazyllm.WebModule(ppl, port=range(23468, 23470), static_paths=get_image_path()).start().wait()
2.效果展示
block節點組召回內容:
We introduce our frst-generation reasoning models, DeepSeek-R1-Zero and DeepSeek-R1. DeepSeek-R1-Zero, a model trained via large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) without supervised fne-tuning (SFT) as a preliminary step, demonstrates remarkable reasoning capabilities. Through RL, DeepSeek-R1-Zero naturally emerges with numerous powerful and intriguing reasoning behaviors. However, it encounters challenges such as poor readability, and language mixing. To address these issues and further enhance reasoning performance, we introduce DeepSeek-R1, which incorporates multi-stage training and cold-start data before RL. DeepSeekR1 achieves performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on reasoning tasks. To support the research community, we open-source DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, and six dense models (1.5B, 7B, 8B, 14B, 32B, 70B) distilled from DeepSeek-R1 based on Qwen and Llama.
info節點組召回內容:
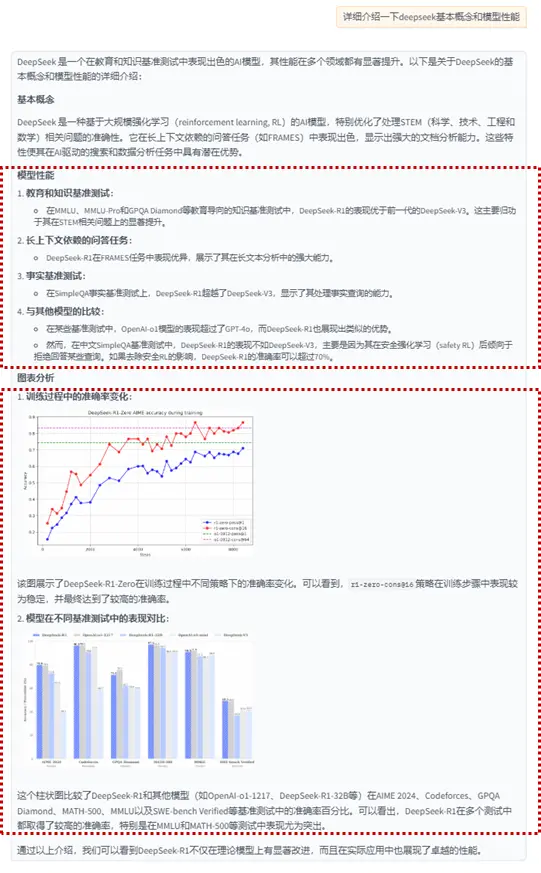
這張圖片是一張柱狀圖,標題為“DeepSeek-R1 OpenAI-01-1217 DeepSeek-R1-32B OpenAI-01-mini DeepSeek-V3”。圖表展示了六種不同模型的性能百分比,每種模型都以不同顏色的條形表示。
從左到右,第一列條形代表“AIMER 2024”模型,第二列代表“Codeforces”模型,第三列代表“GPOA Diamond”模型,第四列代表“MATH-500”模型,第五列代表“MMLU”模型,最後一列代表“SWE-bench Verified”模型。
每組條形都有五條,顏色分別為藍色、灰色、橙色、黃色和紫色,分別對應不同的性能指標。
在圖表下方,有五個百分比數值,分別對應每個模型的性能指標。這些數值以從左到右的順序排列,與條形的顏色相對應。
整個圖表以白色為背景,柱狀圖的顏色與背景形成對比,易於區分。
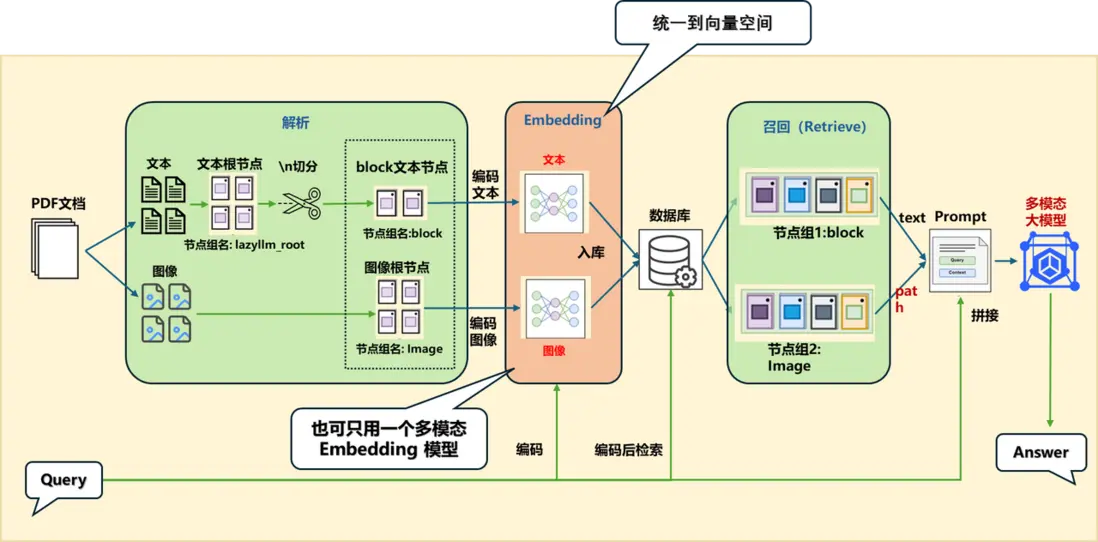
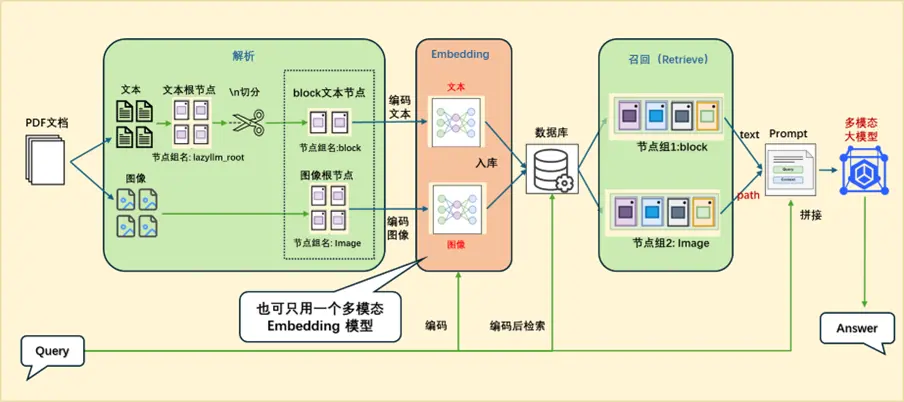
(三)方案二:統一到向量空間
統一到向量空間,兩種方案:
方案A:不同模態用對應的embedding:
- 文本:用文本的embedding
- 圖像:用圖像的embedding
方案B:用多模態embedding:
- 圖文都用同一個embedding
這裏用了方案A,可以展示多embedding的使用。
1.應用編排實現
embed_multimodal = lazyllm.TrainableModule("colqwen2-v0.1")
embed_text = lazyllm.OnlineEmbeddingModule(
source='qwen', embed_model_name='text-embedding-v1')
embeds = {'vec1': embed_text, 'vec2': embed_multimodal}
documents = lazyllm.Document(
dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir, embed=embeds, manager=False)
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888", post_func=build_image_docnode))
documents.create_node_group(name="block", transform=lambda s: s.split("\n") if s else '')
with lazyllm.pipeline() as ppl:
with lazyllm.parallel().sum as ppl.prl:
ppl.prl.retriever1 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="block", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prl.retriever2 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="Image", embed_keys=['vec2'], similarity="maxsim", topk=2)
ppl.prompt = build_vlm_prompt | bind(_0, ppl.input)
ppl.vlm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova", model="SenseNova-V6-Turbo").prompt(lazyllm.ChatPrompter(gen_prompt))
lazyllm.WebModule(ppl, port=range(23468, 23470), static_paths=get_image_path()).start().wait()
2.效果展示
block節點組召回內容:
For education-oriented knowledge benchmarks such as MMLU, MMLU-Pro, and GPQA Diamond, DeepSeek-R1 demonstrates superior performance compared to DeepSeek-V3. This improvement is primarily attributed to enhanced accuracy in STEM-related questions, where significant gains are achieved through large-scale reinforcement learning. Additionally, DeepSeek-R1 excels on FRAMES, a long-context-dependent QA task, showcasing its strong document analysis capabilities. This highlights the potential of reasoning models in AI-driven search and data analysis tasks. On the factual benchmark SimpleQA, DeepSeek-R1 outperforms DeepSeek-V3, demonstrating its capability in handling fact-based queries. A similar trend is observed where OpenAI-o1 surpasses GPT-4o on this benchmark. However, DeepSeek-R1 performs worse than DeepSeek-V3 on the Chinese SimpleQA benchmark, primarily due to its tendency to refuse answering certain queries after safety RL. Without safety RL, DeepSeek-R1 could achieve an accuracy of over 70%.
image節點組召回內容:
/home/mnt/sunxiaoye/.lazyllm/rag_for_qa/images/c357bd57757e4c544fdda3ad32066e64c5d01bb8540066f1a722c8872d664183.jpg
/home/mnt/sunxiaoye/.lazyllm/rag_for_qa/images/2c6271b8cecc68d5b3c22e552f407a5e97d34030f91e15452c595bc8a76e291c.jpg
論文系統的效果優化
(一)改進方案
針對上述論文問答助手,我們還可以從以下幾個角度進行優化:
優化0. 多路召回
- 問題:由於不同類型的文檔結構複雜、信息密度不同,單一的召回策略往往難以適應所有場景。
- 解決方案:並行多路召回
優化1. 文本 QA 對總結提取
- 問題:召回的文檔往往包含大量冗餘信息,直接傳遞給 LLM 可能會影響生成質量,導致回答不夠精準或聚焦。
- 解決方案:預先使用 LLM 對解析後的文段進行處理,讓 LLM 自動生成摘要標題和相關問題,並構造高質量的問答對(QA Pairs)和文檔總結(Summary)。
優化2. 圖像 QA 對提取
- 問題:純文本的回答有時不能很好地解決用户的問題,與文本相比,很多圖表更加清晰。
-
解決方案:
a.利用多模態大模型對圖像內容進行解析,生成圖像的文字描述;
b.將圖像文字描述、路徑等信息存儲在 ImageDocNode 中;
c.利用 Lazyllm 的 LLM_Parse 根據圖像的文字描述生成 QA 對。
優化3. PDF 轉圖化繁為簡
- 問題:PDF 解析過於複雜,代碼功能設計繁瑣。
-
解決方案:
a.將 PDF 直接轉換為圖片;
b.使用專門針對圖文混合版式的多模態嵌入模型對其進行向量化;
c.將和 query 匹配到的圖像與 query 本身送給多模態大模型來做回答。
(二)優化1:+ 文本QA對 & Summary提取 方案
1.應用編排
embed_mltimodal = lazyllm.TrainableModule("colqwen2-v0.1")
embed_text = lazyllm.TrainableModule("bge-m3")
embeds = {'vec1': embed_text, 'vec2': embed_mltimodal}
qapair_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False), language="zh", task_type="qa")
summary_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False), language="zh", task_type="summary")
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir, embed=embeds, manager=False)
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888")) # url 需替換為已啓動的 MinerU 服務地址
documents.create_node_group(name="summary", transform=lambda d: summary_llm(d), trans_node=True)
documents.create_node_group(name='qapair', transform=lambda d: qapair_llm(d), trans_node=True)
with lazyllm.pipeline() as ppl:
with lazyllm.parallel().sum as ppl.prl:
ppl.prl.retriever1 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="qapair", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prl.retriever2 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="summary", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prl.retriever3 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="Image", embed_keys=['vec2'], similarity="maxsim", topk=2)
ppl.prompt = build_vlm_prompt | bind(_0, ppl.input)
ppl.vlm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova", model="SenseNova-V6-Turbo").prompt(lazyllm.ChatPrompter(gen_prompt))
lazyllm.WebModule(ppl, port=range(23468, 23470), static_paths=get_image_path()).start().wait()
2.效果展示
qapair節點組召回內容:
query:
What capabilities does DeepSeek-R1-Zero demonstrate?
answer
DeepSeek-R1-Zero demonstrates remarkable reasoning capabilities and naturally emerges with numerous powerful and intriguing reasoning behaviors through RL.
summary節點組召回內容:
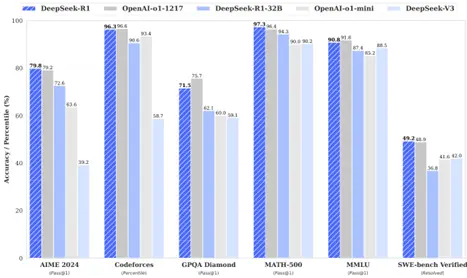
性能對比表格摘要:
- 不同模型在多個基準測試中的表現,包括MMLU、MMLU-Redux、MMLU-Pro、DROP、IF-Eval、GPQA Diamond、SimpleQA、FRAMES、AlpacaEval2.0、ArenaHard等英語理解測試,以及LiveCodeBench、Codeforces、SWE Verified、Aider-Polyglot等代碼能力測試和AIME、MATH-500、CNMO等數學能力測試。
- Claude-3.5-Sonnet-1022 0513、GPT-4o DeepSeek V3、OpenAI OpenAI 01-mini o1-1217、DeepSeek R1等模型在不同測試中各有優劣,例如DeepSeek R1在多數測試中表現優異,尤其在Codeforces和Aider-Polyglot中表現突出。
- 各模型在架構、激活參數、總參數和MMLU (Pass@1)等指標上的差異。
- 中文評估中,各模型在C-Eval和C-SimpleQA上的表現。
image節點組召回內容:
/path/to/images/2c6271b8cecc68d5b3c22e552f407a5e97d34030f91e15452c595bc8a76e291c.jpg
/path/to/ images/b671779ae926ef62c9a0136380a1116f31136c3fd1ed3fedc0e3e05b90925c20.jpg
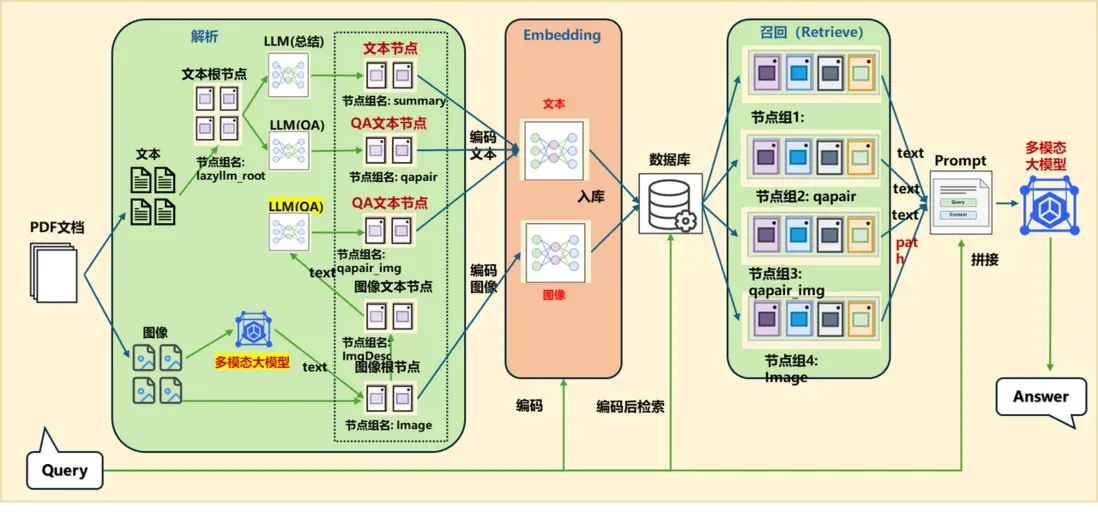
(三)優化2:+ 圖片QA對 方案
1.應用編排
embed_mltimodal = lazyllm.TrainableModule("colqwen2-v0.1")
embed_text = lazyllm.TrainableModule("bge-m3")
embeds = {'vec1': embed_text, 'vec2': embed_mltimodal}
qapair_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False), language="zh", task_type="qa")
qapair_img_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(
lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova", model="SenseNova-V6-Turbo"), language="zh", task_type="qa_img")
summary_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False), language="zh", task_type="summary")
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir, embed=embeds, manager=False)
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:888"))
documents.create_node_group(name="summary", transform=lambda d: summary_llm(d), trans_node=True)
documents.create_node_group(name='qapair', transform=lambda d: qapair_llm(d), trans_node=True)
documents.create_node_group(name='qapair_img', transform=lambda d: qapair_img_llm(d), trans_node=True, parent='Image')
with lazyllm.pipeline() as ppl:
with lazyllm.parallel().sum as ppl.prl:
ppl.prl.retriever1 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="summary", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prl.retriever2 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="Image", embed_keys=['vec2'], similarity="maxsim", topk=2)
ppl.prl.retriever3 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="qapair", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prl.retriever4 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="qapair_img", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prompt = build_vlm_prompt | bind(_0, ppl.input)
ppl.vlm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova", model="SenseNova-V6-Turbo").prompt(lazyllm.ChatPrompter(gen_prompt))
lazyllm.WebModule(ppl, port=range(23468, 23470), static_paths=get_image_path()).start().wait()
2.效果展示
qapair節點組召回內容:
query:
DeepSeek-R1-Zero的性能表現説明了什麼?
answer
DeepSeek-R1-Zero的性能表現突顯了其強大的基礎能力和在推理任務中進一步提升的潛力。
summary節點組召回內容:
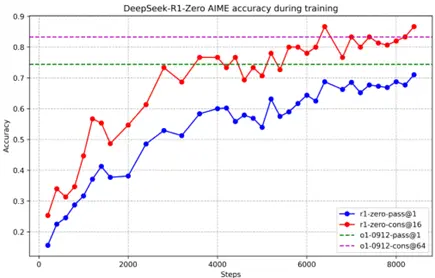
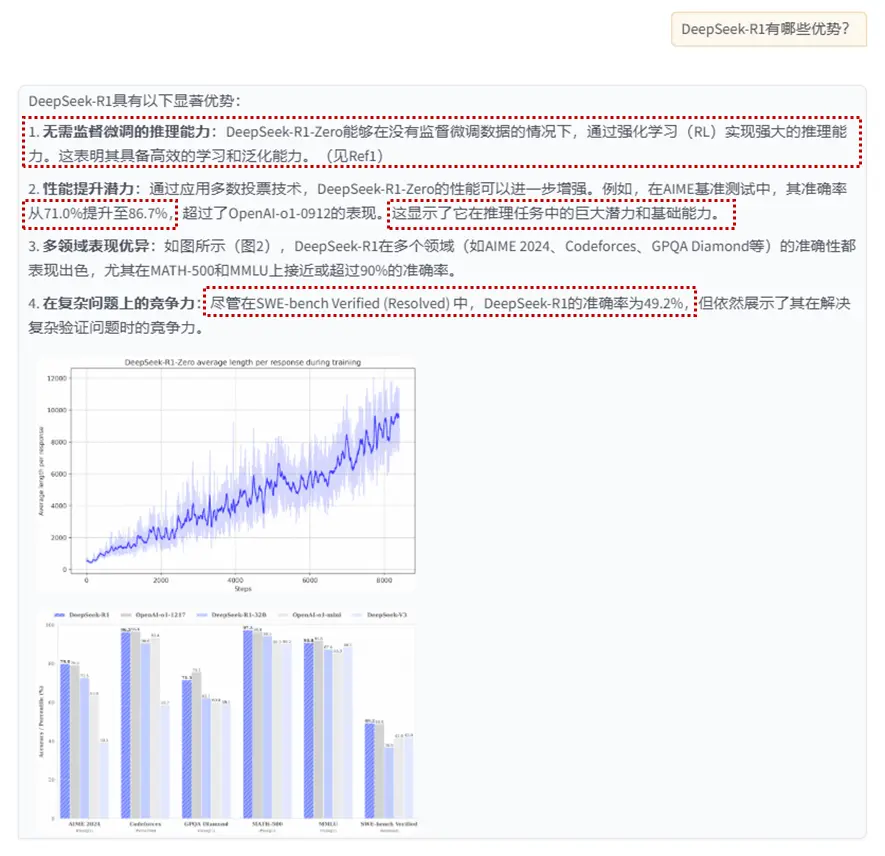
DeepSeek-R1-Zero無需監督微調即可實現強大推理能力,通過僅使用強化學習展現出高效學習和泛化能力。應用多數投票可進一步提升其性能,如在AIME基準測試中,其性能從71.0%提升至86.7%,超越OpenAI-o1-0912。這表明DeepSeek-R1-Zero具備強大的基礎能力,有潛力在推理任務中實現更多進展。
qapair_img 節點組召回內容:
query:
在SWE-bench Verified (Resolved) 中,DeepSeek-R1的準確率是多少?
answer
49.2%
image節點組召回內容:
/path/to/images/b671779ae926ef62c9a0136380a1116f31136c3fd1ed3fedc0e3e05b90925c20.jpg
(2) /path/to/images/2c6271b8cecc68d5b3c22e552f407a5e97d34030f91e15452c595bc8a76e291c.jpg
(四)優化2:+ 圖片QA對(變種) 方案
1.應用編排(變種)
embed_mltimodal = lazyllm.TrainableModule("colqwen2-v0.1")
embed_text = lazyllm.TrainableModule("bge-m3")
embeds = {'vec1': embed_text, 'vec2': embed_mltimodal}
qapair_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False), language="zh", task_type="qa")
summary_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False), language="zh", task_type="summary")
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir, embed=embeds, manager=False)
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888")) # url 需替換為已啓動的 MinerU 服務地址
documents.create_node_group(name="summary", transform=lambda d: summary_llm(d), trans_node=True)
documents.create_node_group(name='qapair', transform=lambda d: qapair_llm(d), trans_node=True)
documents.create_node_group(name='qapair_img', transform=lambda d: qapair_llm(d), trans_node=True, parent='ImgDesc')
with lazyllm.pipeline() as ppl:
with lazyllm.parallel().sum as ppl.prl:
ppl.prl.retriever1 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="summary", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prl.retriever2 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="Image", embed_keys=['vec2'], similarity="maxsim", topk=2)
ppl.prl.retriever3 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="qapair", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prl.retriever4 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="qapair_img", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=1)
ppl.prompt = build_vlm_prompt | bind(_0, ppl.input)
ppl.vlm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova", model="SenseNova-V6-Turbo").prompt(lazyllm.ChatPrompter(gen_prompt))
lazyllm.WebModule(ppl, port=range(23468, 23470), static_paths=get_image_path()).start().wait()
2.效果展示1
qapair節點組召回內容:
query:
DeepSeek-R1-Zero的性能表現説明了什麼?
answer
DeepSeek-R1-Zero的性能表現突顯了其強大的基礎能力和在推理任務中進一步發展的潛力。
summary節點組召回內容:
DeepSeek-R1-Zero無需監督微調即可實現強推理能力,通過僅使用強化學習顯示其有效學習和泛化能力。採用多數投票可進一步提升其性能,如在AIME基準測試中,性能從71.0%提升至86.7%,超過OpenAI-o1-0912。其有競爭力表現展示了強大的基礎能力和在推理任務中進一步發展的潛力。
qapair_img 節點組召回內容:
query:
圖表顯示了DeepSeek-R1-Zero在訓練過程中的平均長度如何變化?
answer
在訓練的早期階段,平均長度相對較低,隨着步數的增加,平均長度逐漸上升,並在後期階段出現波動。
image節點組召回內容:
/path/to/images/b671779ae926ef62c9a0136380a1116f31136c3fd1ed3fedc0e3e05b90925c20.jpg
/path/to/images/2c6271b8cecc68d5b3c22e552f407a5e97d34030f91e15452c595bc8a76e291c.jpg
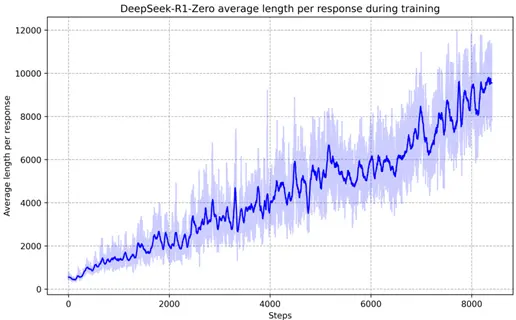
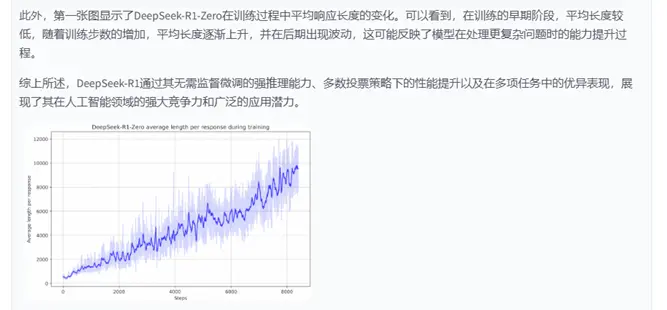
3.效果展示2——圖像QA細節展示
從PDF中解析出的原圖像
多模態大模型生成描述
這張圖片展示了一個圖表,該圖表顯示了DeepSeek-R1-Zero在訓練過程中平均長度隨步數增加而變化的趨勢。圖表中的藍色線表示平均長度,而淺藍色的陰影區域可能表示訓練過程中的不確定性或誤差範圍。
在圖表中,x軸代表步數,從0到大約8000,而y軸表示平均長度,從0到大約12000。圖表顯示,在訓練的早期階段,平均長度相對較低,隨着步數的增加,平均長度逐漸上升,並在後期階段出現波動。圖表中的線條和陰影區域顯示了訓練過程中的變化,可能反映了DeepSeek-R1-Zero在處理數據或任務時所遇到的複雜性和不確定性。
請注意,由於圖表中沒有明確標註x軸和y軸的具體單位,上述描述是基於圖表的視覺呈現,並未提供具體的數值信息。
針對生成的描述利用LLM生成QA對
Q: 這張圖片展示了一個圖表,它顯示了什麼內容?
A: 這張圖片展示了一個圖表,該圖表顯示了DeepSeek-R1-Zero在訓練過程中平均長度隨步數增加而變化的趨勢。
Q: 圖表中的藍色線表示什麼?
A: 圖表中的藍色線表示平均長度。
Q: 圖表中的淺藍色陰影區域可能表示什麼?
A: 淺藍色的陰影區域可能表示訓練過程中的不確定性或誤差範圍。
Q: 圖表的x軸和y軸分別代表什麼?
A: x軸代表步數,從0到大約8000,而y軸表示平均長度,從0到大約12000。
·
Q: 圖表顯示了DeepSeek-R1-Zero在訓練過程中的平均長度如何變化?
A: 在訓練的早期階段,平均長度相對較低,隨着步數的增加,平均長度逐漸上升,並在後期階段出現波動。
Q: 圖表中的線條和陰影區域可能反映了什麼?
A: 線條和陰影區域可能反映了DeepSeek-R1-Zero在處理數據或任務時所遇到的複雜性和不確定性。
Q: 描述中是否提供了具體的數值信息?
A: 沒有,描述中沒有提供具體的數值信息,僅基於圖表的視覺呈現。
最終問答效果
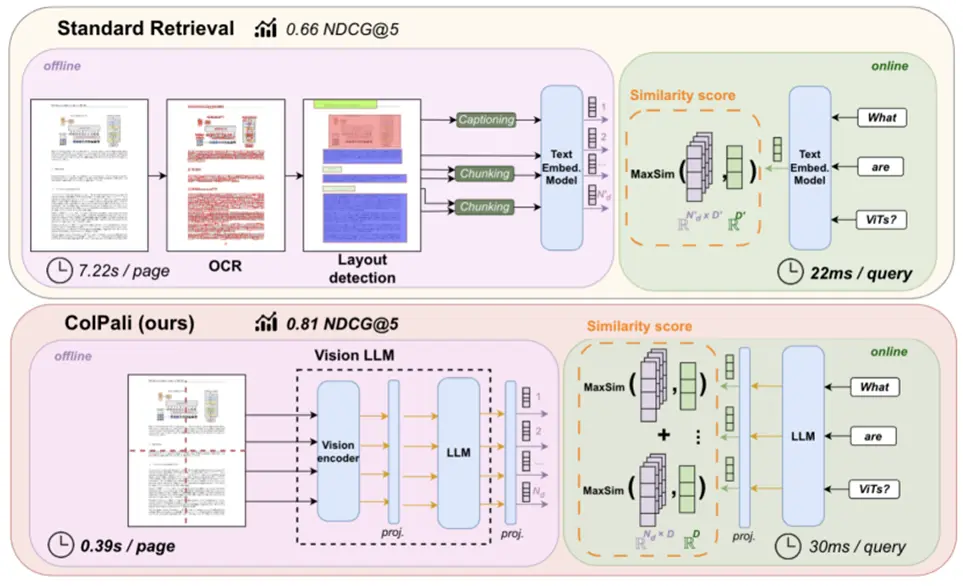
(五)優化3:PDF轉圖化繁為簡
- 傳統方法:將文檔結構化解析 → 圖像 & 文本分別處理
- 新方向:將整頁文檔視為圖像,使用多模態嵌入模型直接編碼
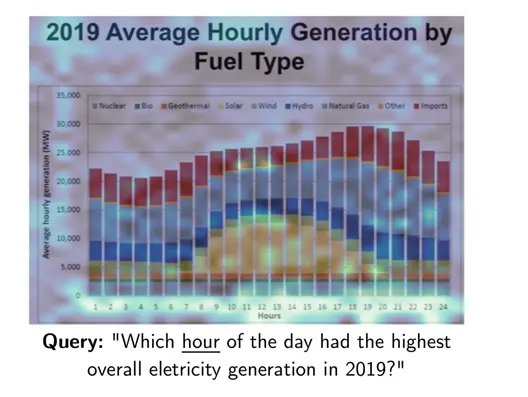
對於用户查詢中的每一項目,ColPali 會識別出最相關的文檔圖像區域(被高亮顯示的區域),並計算查詢與頁面之間的匹配分數。這裏顯示了“hour”和圖像中的“Hours”及其時間高度相關。
(六)優化3:PDF轉圖化繁為簡 LazyLLM方案
代碼實現——PDF轉圖片
之前的方案中,文本解析階段我們採用的是先解析文本、再構建節點的方式,流程相對複雜。這裏直接將PDF解析為圖像。供給後續多模態大模型使用。
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/a09a84cdf0585a5c9d52af6db0e965be95d03123/rag/codes/chapter14/PaperQA_MLM.py#L14C1-L14C35)
# PDF轉圖像閲讀器實現類
class Pdf2ImageReader(ReaderBase):
def __init__(self, image_save_path="pdf_image_path"):
super().__init__(); self.image_save_path = image_save_path
if not os.path.exists(self.image_save_path): os.makedirs(self.image_save_path)
# PDF文件加載和轉換核心方法
def _load_data(self, file: Path, extra_info=None) -> List[ImageDocNode]:
if not isinstance(file, Path): file = Path(file)
docs = fitz.open(file); file_path = []
for page_num in range(docs.page_count):
metadata = extra_info or {}; metadata["file_name"] = file.name; metadata["file_split"] = page_num
page = docs.load_page(page_num); pix = page.get_pixmap(dpi=300)
img = Image.frombytes("RGB", [pix.width, pix.height], pix.samples)
save_path = f"{self.image_save_path}/{file.name[:-4]}_{page_num}.jpg"
img.save(save_path); file_path.append(ImageDocNode(image_path=save_path, global_metadata=metadata))
return file_path
通過上述代碼,就可以通過 ImageDocNode.get\_content()獲取圖像 PIL 對象,也可以通過 ImageDocNode.image\_path 獲取對應的存儲路徑,方便後續進行進一步的操作。
1.優化相似度計算方式——MaxSim相似度計算法
MaxSim函數是一種基於延遲交互的相似度計算方法,它通過將查詢和文檔的每個Token的向量進行逐對相似度計算,並追蹤每對的最大得分來確定整體的相似度。
(1)核心原理
- 延遲交互機制:不直接計算全局相似度,而是逐Token交互後聚合
- 最大匹配策略:每個查詢Token尋找文檔中的最大響應值
下方是MaxSim函數的得分計算函數,我們只需實現相似度計算函數進行註冊即可。MaxSim的具體公式如下:
接下來我們以一個簡單的例子來説明 MaxSim 函數的計算過程。
假設我們有一個查詢 q 和一個文檔 d,它們的嵌入矩陣如下:
(2)計算步驟
步驟1️⃣:通過點積運算(對應元素相乘後求和)
• M11 = 0.5×0.1+(−0.2)×0.4=0.05−0.08=−0.03
• M12 = 0.5×(−0.3)+(−0.2)×0.6=−0.15−0.12=−0.27
• M13 = 0.5×0.7+(−0.2)×(−0.5)=0.35+0.10=0.45
• M21 = 0.3×0.1+0.8×0.4=0.03+0.32=0.35
• M22 = 0.3×(−0.3)+0.8×0.6=−0.09+0.48=0.39
• M23 = 0.3×0.7+0.8×(−0.5)=0.21−0.40=−0.19
步驟2️⃣:取每行最大值
第一行最大值:max(−0.03,−0.27,0.45)=0.45
第二行最大值:max(0.35,0.39,−0.19)=0.39
步驟3️⃣:全局求和
最終相似度:S(q,d)=0.45+0.39=0.84
(3)結果
- 查詢 q 和文檔 d 的最終相似度得分為 0.84。
(4)總結
通過這個例子,我們可以看到 MaxSim 的計算過程:
- 對每個查詢 token,計算它與文檔中所有 token 的點積(相似度)。
- 對每個查詢 token,取它與文檔 token 的最大相似度。
- 將所有查詢 token 的最大相似度相加,得到最終的相似度得分。
其中S為查詢q和文檔d之間的最終相似度得分,Eq表示查詢q的嵌入,Edi表示第i個圖像塊的嵌入。以下為MaxSim函數的代碼實現:
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/a09a84cdf0585a5c9d52af6db0e965be95d03123/rag/codes/chapter14/PaperQA_MLM.py#L43)
import torch
@lazyllm.tools.rag.register_similarity(mode='embedding', batch=True)
def maxsim(query, nodes, **kwargs):
batch_size = 128
scores_list = []
query = torch.Tensor([query for i in range(len(nodes))])
nodes_embed = torch.Tensor(nodes)
for i in range(0, len(query), batch_size):
scores_batch = []
query_batch = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(query[i : i + batch_size], batch_first=True, padding_value=0)
for j in range(0, len(nodes_embed), batch_size):
nodes_batch = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(nodes_embed[j : j + batch_size], batch_first=True, padding_value=0)
scores_batch.append(torch.einsum("bnd,csd->bcns", query_batch, nodes_batch).max(dim=3)[0].sum(dim=2))
scores_batch = torch.cat(scores_batch, dim=1).cpu()
scores_list.append(scores_batch)
scores = scores_list[0][0].tolist()
return scores
2.應用編排
(代碼GitHub鏈接:https://github.com/LazyAGI/Tutorial/blob/a09a84cdf0585a5c9d52af6db0e965be95d03123/rag/codes/chapter14/PaperQA_MLM.py#L64C1-L64C33)
# 定義將圖像路徑轉換為markdown格式的函數
def format_markdown_image(text):
json_part = text[text.index("{"):]; data = json.loads(json_part)
image_paths = data.get("files", []); return f'\n\n'
# 初始化文檔處理模塊並添加PDF閲讀器
image_file_path = "/content/images"
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path="/content/doc",
embed=lazyllm.TrainableModule("colqwen2-v0.1"))
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", Pdf2ImageReader(image_file_path))
# 構建圖像檢索和處理流水線
with pipeline() as ppl:
ppl.retriever = Retriever(doc=documents, group_name="Image", similarity="maxsim", topk=1)
ppl.formatter1 = lambda nodes : [node.image_path for node in nodes]
ppl.formatter2 = encode_query_with_filepaths | bind(ppl.input, _0)
with parallel().sum as ppl.prl:
ppl.prl.vlm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova", model="SenseChat-Vision")
ppl.prl.post_action = format_markdown_image# 啓動Web服務
lazyllm.WebModule(ppl, static_paths=image_file_path).start().wait()
3.效果展示
論文系統綜合方案
(一)應用編排
embed_mltimodal = lazyllm.TrainableModule("colqwen2-v0.1")
embed_text = lazyllm.TrainableModule("bge-m3")
embeds = {'vec1': embed_text, 'vec2': embed_mltimodal}
qapair_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False), language="zh", task_type="qa")
qapair_img_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(
lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova", model="SenseNova-V6-Turbo"), language="zh", task_type="qa_img")
summary_llm = lazyllm.LLMParser(lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(stream=False), language="zh", task_type="summary")
documents = lazyllm.Document(dataset_path=tmp_dir.rag_dir, embed=embeds, manager=False)
documents.add_reader("*.pdf", MineruPDFReader(url="http://127.0.0.1:8888"))
documents.create_node_group(name="block", transform=lambda s: s.split("\n") if s else '')
documents.create_node_group(name="summary", transform=lambda d: summary_llm(d), trans_node=True)
documents.create_node_group(name='qapair', transform=lambda d: qapair_llm(d), trans_node=True)
documents.create_node_group(name='qapair_img', transform=lambda d: qapair_img_llm(d), trans_node=True, parent='Image')
with lazyllm.pipeline() as ppl:
with lazyllm.parallel().sum as ppl.mix:
with lazyllm.pipeline() as ppl.mix.rank:
with lazyllm.parallel().sum as ppl.mix.rank.short:
ppl.mix.rank.short.retriever1 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="summary", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=4)
ppl.mix.rank.short.retriever2 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="qapair", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=4)
ppl.mix.rank.short.retriever3 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="qapair_img", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=4)
ppl.mix.rank.reranker = lazyllm.Reranker("ModuleReranker", model="bge-reranker-large", topk=3) | bind(query=ppl.mix.rank.input)
ppl.mix.retriever4 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="block", embed_keys=['vec1'], similarity="cosine", topk=2)
ppl.mix.retriever5 = lazyllm.Retriever(documents, group_name="Image", embed_keys=['vec2'], similarity="maxsim", topk=2)
ppl.prompt = build_vlm_prompt | bind(_0, ppl.input)
ppl.vlm = lazyllm.OnlineChatModule(source="sensenova", model="SenseNova-V6-Turbo").prompt(lazyllm.ChatPrompter(gen_prompt))
lazyllm.WebModule(ppl, port=range(23468, 23470), static_paths=get_image_path()).start().wait()
(二)效果展示
召回內容:
內容1:DeepSeek-R1 outperforms DeepSeek-V3 on education benchmarks and long-context QA, excelling in STEM and factual queries via reinforcement learning. However, it underperforms on Chinese SimpleQA due to safety RL restrictions.
內容2:DeepSeek-R1在IF-Eval、AlpacaEval2.0和ArenaHard上表現出色,得益於SFT和RL訓練中包含的指令跟隨數據。其優於DeepSeek-V3,展示了大型RL的泛化優勢,提升推理能力和跨領域表現。生成的摘要長度平均為689個token(ArenaHard)和2218個字符(AlpacaEval2.0),表明其簡潔性。
內容3:各模型在多種基準測試中的性能對比,包括MMLU、Codeforces、AIME等,顯示不同模型在英語、代碼和數學等領域的差異化表現。
內容4: We introduce our frst-generation reasoning models, DeepSeek-R1-Zero and DeepSeek-R1. DeepSeek-R1-Zero, a model trained via large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) without supervised fne-tuning (SFT) as a preliminary step, demonstrates remarkable reasoning capabilities. Through RL, DeepSeek-R1-Zero naturally emerges with numerous powerful and intriguing reasoning behaviors. However, it encounters challenges such as poor readability, and language mixing. To address these issues and further enhance reasoning performance, we introduce DeepSeek-R1, which incorporates multi-stage training and cold-start data before RL. DeepSeekR1 achieves performance comparable to OpenAI-o1-1217 on reasoning tasks. To support the research community, we open-source DeepSeek-R1-Zero, DeepSeek-R1, and six dense models (1.5B, 7B, 8B, 14B, 32B, 70B) distilled from DeepSeek-R1 based on Qwen and Llama.
內容5:| | Benchmark (Metric) | Claude-3.5- Sonnet-1022 0513 | GPT-4o DeepSeek V3 | | OpenAI OpenAI 01-mini o1-1217 | DeepSeek R1 |
Image 節點組召回內容:
/path/to/images/2c6271b8cecc68d5b3c22e552f407a5e97d34030f91e15452c595bc8a76e291c.jpg
/path/to/images/b671779ae926ef62c9a0136380a1116f31136c3fd1ed3fedc0e3e05b90925c20.jpg
總結拓展
在本節課程中,我們詳細探討了如何利用RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation)技術構建一個基於論文的問答系統。通過結合檢索能力和大語言模型的生成能力,該系統能夠幫助研究人員高效地從海量論文中提取核心信息,極大地提升了科研工作的效率。以下是本節內容的總結與拓展:
(一)系統架構與流程
- 數據準備:我們使用了arxivQA數據集中的論文,並通過自定義的PDF解析器(基於mineru)對論文進行解析,提取文本、圖片和表格等內容。
- 數據處理與組件搭建:通過LazyLLM框架,我們構建了文檔解析器、檢索器、重排器(Reranker)和大模型(LLM)等核心組件,逐步實現了從文檔解析到問答生成的完整流程。
- 效果展示與優化:通過引入向量化檢索和重排器,系統能夠更精準地檢索到與查詢相關的論文段落,並結合大模型生成清晰、準確的回答。我們還通過QA文本對提取和多路召回等優化策略,進一步提升了系統的召回質量和生成效果。
(二)關鍵技術點
- 自定義PDF解析器:通過mineru工具,我們實現了對PDF文檔的深度解析,能夠提取文本、圖片和表格等結構化信息,並將其存儲為DocNode對象,便於後續的檢索和處理。
- 向量化檢索與重排:我們使用了BGE模型進行文本嵌入,並結合Milvus數據庫進行向量化檢索。通過引入重排器(Reranker),系統能夠對檢索結果進行精細化排序,確保最相關的內容排在最前面。
- 多模態整合:在進階優化中,我們探討了如何將多模態大模型(如視覺模型)整合到RAG系統中,進一步提升系統對圖表等非文本信息的理解能力。
(三)優化策略
- 多路召回:通過並行多路召回策略,系統能夠結合多種檢索方法(如基於關鍵詞的稀疏檢索和基於語義的密集檢索),提高召回的全面性和魯棒性。
- QA文本對提取:通過LLM生成高質量的問答對(QA Pairs),系統能夠在召回階段更精準地匹配用户查詢,提升生成結果的相關性和準確性。
- 多模態協同處理:通過整合多模態大模型,系統能夠更好地處理論文中的圖表信息,提供更全面的問答服務。
- PDF轉圖化繁為簡:使用專門針對圖文混合版式的多模態嵌入模型對轉換為圖的PDF文檔進行向量化,省去了對PDF文檔進行復雜解析和處理的邏輯,大大簡化了開發工作。
(四)未來拓展方向
- 多語言支持:當前的系統主要針對中文和英文論文,未來可以擴展到支持更多語言的論文解析和問答。
- 更復雜的文檔結構處理:隨着論文結構的多樣化,系統可以進一步優化對複雜文檔(如多級標題、交叉引用等)的處理能力。
- 實時更新與增量學習:為了應對科研領域的快速變化,系統可以引入實時更新機制,支持對新論文的快速解析和知識庫的增量更新。
- 用户個性化推薦:通過分析用户的查詢歷史和研究興趣,系統可以提供個性化的論文推薦和問答服務,進一步提升用户體驗。
(五)總結
通過本節課程的學習,我們不僅掌握瞭如何利用RAG技術構建一個高效的論文問答系統,還深入瞭解瞭如何通過優化策略提升系統的召回質量和生成效果。未來,隨着多模態技術和增量學習等技術的進一步發展,RAG系統在科研領域的應用前景將更加廣闊。
希望本節內容能夠幫助大家更好地理解和應用RAG技術,期待大家在未來的科研工作中能夠利用這些技術提升工作效率,取得更多的研究成果!
更多技術討論,歡迎移步 "lazyllm"gzh!