本文介紹GraphQL中的Authenication和Authorication
參考:
- https://graphql.org/learn/authorization/
- https://www.apollographql.com/docs/apollo-server/security/authentication/
Authenication和Authorication的區別
Authenication 和 Authorication 的概念十分容易混淆,兩者的定義如下:
- Authenication 指用户認證,即是否有用户登錄,哪個用户登錄
- Authorication 指用户權限認證,再具體的操作中決定用户是否有權利使用查看數據或調用方法
Authenication
提供用户的authenication有多種方式,包括HTTP header和JSON web token。
下面給出一個創建Authenication的示例
創建用户組的schema
分別創建一個用户信息的type,並定義創建用户和登錄的方法
type AuthPayload {
token: String!
name: String!
}
input UserCreateInput {
name: String!
password: String!
}
type Mutation {
createUser(data: UserCreateInput): String
login(data: UserCreateInput): AuthPayload
logout(data: UserCreateInput, param: Int!): Int
}
定義本地CreateUser和Login的Resolver
通常情況下,用户在用前端創建用户時,會傳入用户名和密碼,後端不會直接保存用户密碼,而是將用户信息加密為webtoken儲存起來,而login的情況下,也是會將用户用户名和密碼的信息與weebtoken進行比對。
可以在context中,設置一個用户組緩存來儲存數據,同樣適用於將用户信息儲存於數據庫或雲端。
const resolver = {
Mutation: {
createUser: async (parent: any, args: any, ctx: any, info: any) => {
if (args.data.password.length < 8) {
throw new Error('Password must be 8 characters or longer.')
}
const password = await bcrypt.hash(args.data.password, 10);
const id = uuidv4();
const token = jwt.sign({ userId: id }, 'password');
ctx.users.push({
id,
name: args.data.name,
password,
token
});
return token;
},
login: async (parent: any, args: any, ctx: any, info: any) => {
const user = ctx.users.find(u => u.name === args.data.name);
if (!user) throw Error('User not exist');
const isMatch = await bcrypt.compare(args.data.password, user.password);
if (!isMatch) throw new Error('Password mismatch');
return {
name: user.name,
token: user.token ? user.token : jwt.sign({ userId: user.id }, 'password'),
}
},
}
}
Authorization
用上述步驟執行完Authentication的操作以後,需要驗證用户操作函數是否有權限只需要在相應方法的Resolver中進行驗證即可,調用Query或Mutation可以在Header中添加一個由後端返回給前端的token,示例如下:
後端:
const getUserId = (request) => {
const token = request.headers.authorization;
if (!token) {
throw new Error('Authentication required')
}
const decoded = jwt.verify(token, 'password')
return decoded.userId
}
const resolver = {
Mutation: {
callFunction: async (parent: any, args: any, ctx: any, info: any) => {
const id = getUserId(ctx.request);
if (!id) throw Error('ID not exist');
// Do operation
}
}
}
在Apollo GraphQL中可以在前端的header加一個authorication的字段,輸入token:
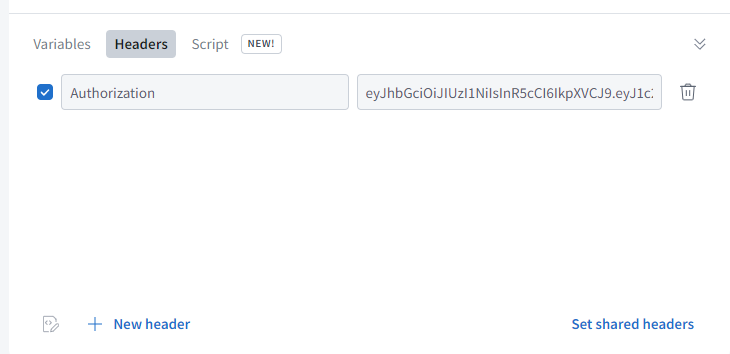
前端可以在創建Apollo GraohQL Module時,創建一個MidWare包含我們的header:
const authMiddleware = new ApolloLink((operation: any, forward: any) => {
operation.setContext({
headers: new HttpHeaders().set(
"Authorization",
"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..." //Token
),
});
return forward(operation);
});
export function createApollo(httpLink: HttpLink): ApolloClientOptions<any> {
return {
link: httpLink.create({uri}),
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
};
}
export function createApolloWithAuth(httpLink: HttpLink): ApolloClientOptions<any> {
return {
link: from([
authMiddleware,
httpLink.create({
uri,
}),
]),
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
};
}










