11. Spring AI + ELT
@
- 11. Spring AI + ELT
- ELT
- Document Loaders
- 讀取Text
- 讀取markdown
- pdf
- B站:
- DocumentSplitter
- TokenTextSplitter
- 自定分割器:
- 分隔經驗:
- 分塊五種策略
- 1)固定大小分塊
- 2)語義分塊
- 3)遞歸分塊
- 4)基於文檔結構的分塊
- 5)基於LLM的分塊
- ContentFormatTransformer
- KeywordMetadataEnriching
- SummaryMetadataEnricher
- 文本向量化
- 存儲向量
- 向量數據庫檢索
- 對話階段
- 提升檢索精度—rerank(重排序)
- 為什麼需要 rerank
- 重排序:
- 代碼
- Document Loaders
- ELT
- 最後:
ELT
在之前,我們主要完成了數據檢索階段, 但是完整的RAG流程還需要有emedding階段, 即:
提取(讀取)、轉換(分隔)和加載(寫入)
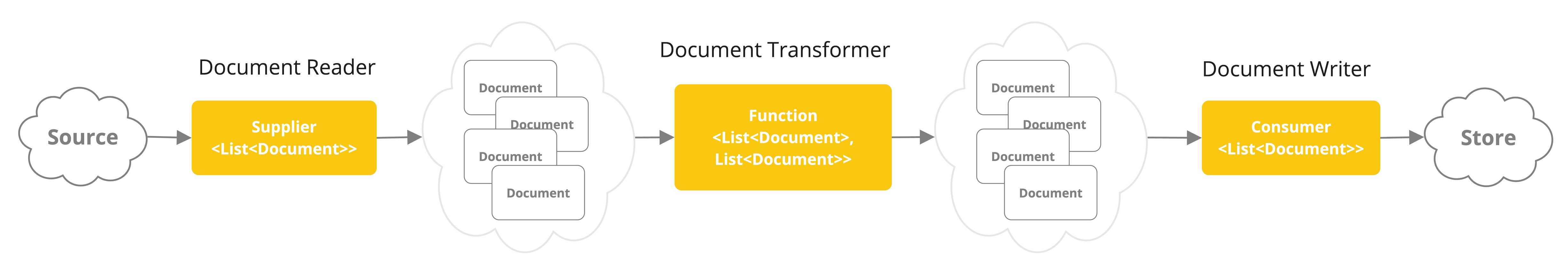
Document Loaders
Document Loaders 文檔讀取器
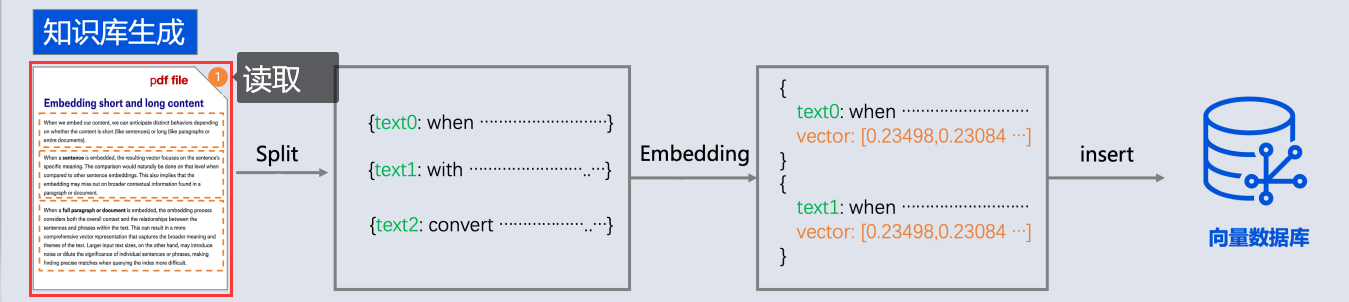
springai提供了以下文檔閲讀器
- JSON
- 文本
- HTML(JSoup)
- Markdown
- PDF頁面
- PDF段落
- Tika(DOCX、PPTX、HTML……)
alibaba ai也提供了很多閲讀器
https://github.com/alibaba/spring-ai-alibaba/tree/main/community/document-parsers
- document-parser-apache-pdfbox:用於解析 PDF 格式文檔。
- document-parser-bshtml:用於解析基於 BSHTML 格式的文檔。
- document-parser-pdf-tables:專門用於從 PDF 文檔中提取表格數據。
- document-parser-bibtex:用於解析 BibTeX 格式的參考文獻數據。
- document-parser-markdown:用於解析 Markdown 格式的文檔。
- document-parser-tika:一個多功能文檔解析器,支持多種文檔格式。
以及網絡來源文檔讀取器:
https://github.com/alibaba/spring-ai-alibaba/tree/main/community/document-readers

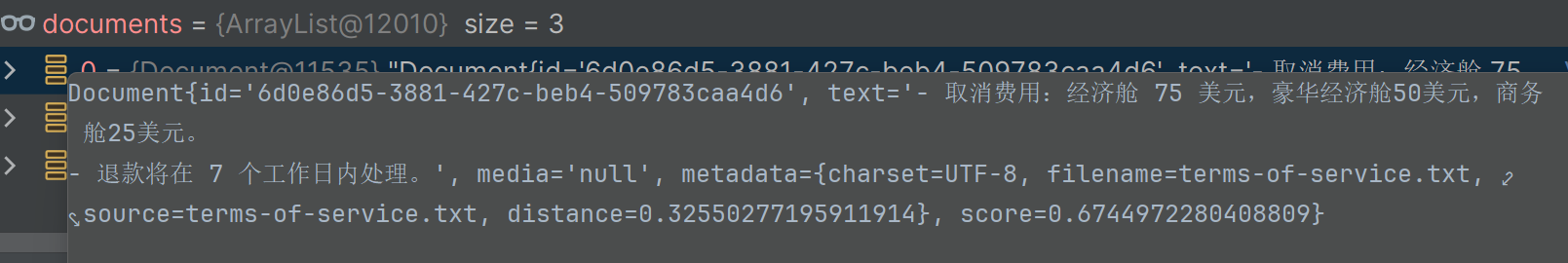
讀取Text
@Test
public void testReaderText(@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
for (Document document : documents) {
System.out.println(document.getText());
}
}
讀取markdown
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-markdown-document-reader</artifactId>
</dependency>
@Test
public void testReaderMD(@Value("classpath:rag/9_橫店影視股份有限公司_0.md") Resource resource) {
MarkdownDocumentReaderConfig config = MarkdownDocumentReaderConfig.builder()
.withHorizontalRuleCreateDocument(true) // 分割線創建新document
.withIncludeCodeBlock(false) // 代碼創建新document false 會創建
.withIncludeBlockquote(false) // 引用創建新document false 會創建
.withAdditionalMetadata("filename", resource.getFilename()) // 每個document添加的元數據
.build();
MarkdownDocumentReader markdownDocumentReader = new MarkdownDocumentReader(resource, config);
List<Document> documents = markdownDocumentReader.read();
for (Document document : documents) {
System.out.println(document.getText());
}
}
● PagePdfDocumentReader一頁1個document
● ParagraphPdfDocumentReader 按pdf目錄分成一個個document
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-markdown-document-reader</artifactId>
</dependency>
@Test
public void testReaderPdf(@Value("classpath:rag/平安銀行2023年半年度報告摘要.pdf") Resource resource) {
PagePdfDocumentReader pdfReader = new PagePdfDocumentReader(resource,
PdfDocumentReaderConfig.builder()
.withPageTopMargin(0)
.withPageExtractedTextFormatter(ExtractedTextFormatter.builder()
.withNumberOfTopTextLinesToDelete(0)
.build())
.withPagesPerDocument(1)
.build());
List<Document> documents = pdfReader.read();
for (Document document : documents) {
System.out.println(document.getText());
}
}
// 必需要帶目錄, 按pdf的目錄分document
@Test
public void testReaderParagraphPdf(@Value("classpath:rag/平安銀行2023年半年度報告.pdf") Resource resource) {
ParagraphPdfDocumentReader pdfReader = new ParagraphPdfDocumentReader(resource,
PdfDocumentReaderConfig.builder()
// 不同的PDF生成工具可能使用不同的座標系 , 如果內容識別有問題, 可以設置該屬性為true
.withReversedParagraphPosition(true)
.withPageTopMargin(0) // 上邊距
.withPageExtractedTextFormatter(ExtractedTextFormatter.builder()
// 從頁面文本中刪除前 N 行
.withNumberOfTopTextLinesToDelete(0)
.build())
.build());
List<Document> documents = pdfReader.read();
for (Document document : documents) {
System.out.println(document.getText());
}
}
B站:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-alibaba-starter-document-reader-bilibili</artifactId>
</dependency>
@Test
void bilibiliDocumentReaderTest() {
BilibiliDocumentReader bilibiliDocumentReader = new BilibiliDocumentReader(
"https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1C5UxYuEc2/?spm_id_from=333.1387.upload.video_card.click&vd_source=fa810d8b8d6765676cb343ada918d6eb");
List<Document> documents = bilibiliDocumentReader.get();
System.out.println(documents);
}
DocumentSplitter
DocumentSplitter文檔拆分器(轉換器)
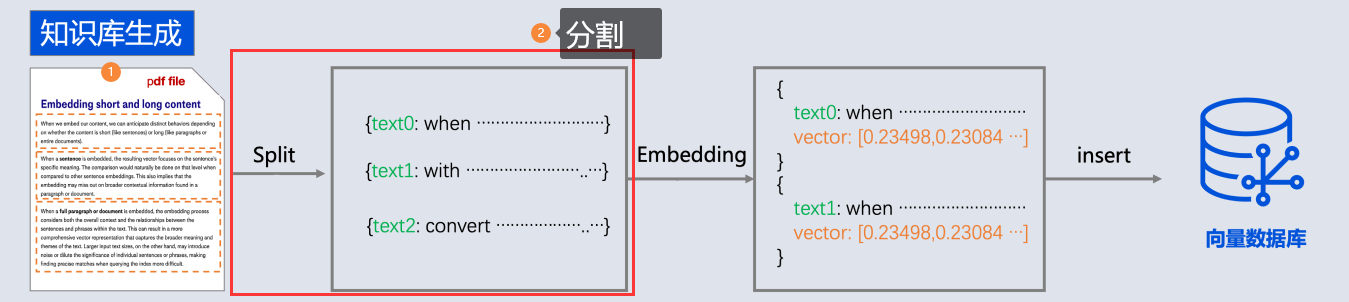
由於文本讀取過來後, 還需要分成一段一段的片段(分塊chunk), 分塊是為了更好地拆分語義單元,這樣在後面可以更精確地進行語義相似性檢索,也可以避免LLM的Token限制。
SpringAi就提供了一個文檔拆分器:
- TextSplitter 抽象類
- TokenTextSplitter 按token分隔
TokenTextSplitter
- chunkSize (默認值: 800) 100
○ 每個文本塊的目標大小,以token為單位 - minChunkSizeChars (默認值: 350) 建議小一點
○ 如果塊超過最小塊字符數( 按照塊的最後. ! ? \n 符號截取)
○ 如果塊沒超過最小塊字符數, 不會按照符號截取(保留原塊)。
本服務條款適用於您對圖靈航空 的體驗。預訂航班,即表示您同意這些條款。
1. 預訂航班
- 通過我們的網站或移動應用程序預訂。
- 預訂時需要全額付款。 \n
- 確保個人信息(姓名、ID 等)的準確性,因為更正可能會產生 25
- minChunkLengthToEmbed (默認值: 5) 5
○ 丟棄短於此長度的文本塊(如果去掉\r\n, 只剩5個有效文本, 那就丟掉)
本服務條
-
maxNumChunks(默認值: 10000)
○ 最多能分多少個塊, 超過了就不管了 -
keepSeparator(默認值: true)
○ 是否在塊中保留分隔符、換行符 \r\n
@Test
public void testTokenTextSplitter(@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", resource.getFilename());
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
TokenTextSplitter splitter = new TokenTextSplitter(1000, 400, 10, 5000, true);
List<Document> apply = splitter.apply(documents);
apply.forEach(System.out::println);
}
整個流程如下:
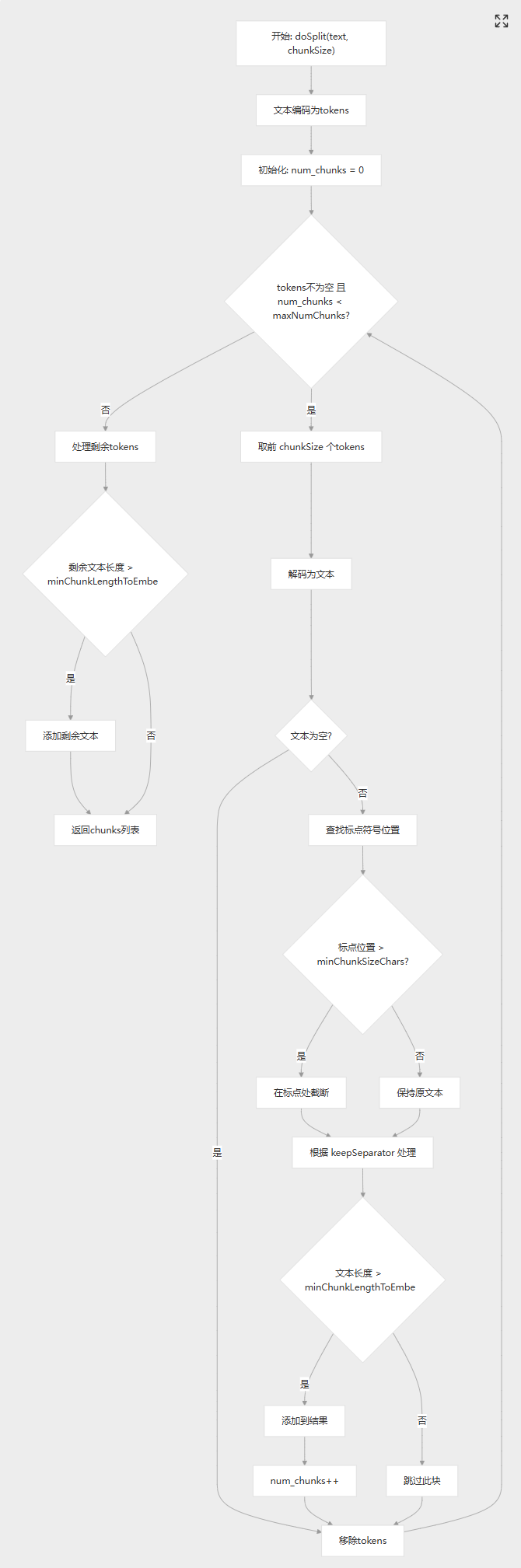
自定分割器:
支持中英文:同時支持中文和英文標點符號
package com.xushu.springai.rag.ELT;
public class ChineseTokenTextSplitter extends TextSplitter {
private static final int DEFAULT_CHUNK_SIZE = 800;
private static final int MIN_CHUNK_SIZE_CHARS = 350;
private static final int MIN_CHUNK_LENGTH_TO_EMBED = 5;
private static final int MAX_NUM_CHUNKS = 10000;
private static final boolean KEEP_SEPARATOR = true;
private final EncodingRegistry registry = Encodings.newLazyEncodingRegistry();
private final Encoding encoding = this.registry.getEncoding(EncodingType.CL100K_BASE);
// The target size of each text chunk in tokens
private final int chunkSize;
// The minimum size of each text chunk in characters
private final int minChunkSizeChars;
// Discard chunks shorter than this
private final int minChunkLengthToEmbed;
// The maximum number of chunks to generate from a text
private final int maxNumChunks;
private final boolean keepSeparator;
public ChineseTokenTextSplitter() {
this(DEFAULT_CHUNK_SIZE, MIN_CHUNK_SIZE_CHARS, MIN_CHUNK_LENGTH_TO_EMBED, MAX_NUM_CHUNKS, KEEP_SEPARATOR);
}
public ChineseTokenTextSplitter(boolean keepSeparator) {
this(DEFAULT_CHUNK_SIZE, MIN_CHUNK_SIZE_CHARS, MIN_CHUNK_LENGTH_TO_EMBED, MAX_NUM_CHUNKS, keepSeparator);
}
public ChineseTokenTextSplitter(int chunkSize, int minChunkSizeChars, int minChunkLengthToEmbed, int maxNumChunks,
boolean keepSeparator) {
this.chunkSize = chunkSize;
this.minChunkSizeChars = minChunkSizeChars;
this.minChunkLengthToEmbed = minChunkLengthToEmbed;
this.maxNumChunks = maxNumChunks;
this.keepSeparator = keepSeparator;
}
public static Builder builder() {
return new Builder();
}
@Override
protected List<String> splitText(String text) {
return doSplit(text, this.chunkSize);
}
protected List<String> doSplit(String text, int chunkSize) {
if (text == null || text.trim().isEmpty()) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<Integer> tokens = getEncodedTokens(text);
List<String> chunks = new ArrayList<>();
int num_chunks = 0;
// maxNumChunks多能分多少個塊, 超過了就不管了
while (!tokens.isEmpty() && num_chunks < this.maxNumChunks) {
// 按照chunkSize進行分隔
List<Integer> chunk = tokens.subList(0, Math.min(chunkSize, tokens.size()));
String chunkText = decodeTokens(chunk);
// Skip the chunk if it is empty or whitespace
if (chunkText.trim().isEmpty()) {
tokens = tokens.subList(chunk.size(), tokens.size());
continue;
}
// Find the last period or punctuation mark in the chunk
int lastPunctuation =
Math.max(chunkText.lastIndexOf('.'),
Math.max(chunkText.lastIndexOf('?'),
Math.max(chunkText.lastIndexOf('!'),
Math.max(chunkText.lastIndexOf('\n'),
// 添加上我們中文的分割符號
Math.max(chunkText.lastIndexOf('。'),
Math.max(chunkText.lastIndexOf('?'),
chunkText.lastIndexOf('!')
))))));
// 按照句子截取之後長度 > minChunkSizeChars
if (lastPunctuation != -1 && lastPunctuation > this.minChunkSizeChars) {
// 保留按照句子截取之後的內容
chunkText = chunkText.substring(0, lastPunctuation + 1);
}
// 按照句子截取之後長度 < minChunkSizeChars 保留原塊
// keepSeparator=true 替換/r/n =false不管
String chunkTextToAppend = (this.keepSeparator) ? chunkText.trim()
: chunkText.replace(System.lineSeparator(), " ").trim();
// 替換/r/n之後的內容是不是<this.minChunkLengthToEmbed 忽略
if (chunkTextToAppend.length() > this.minChunkLengthToEmbed) {
chunks.add(chunkTextToAppend);
}
// Remove the tokens corresponding to the chunk text from the remaining tokens
tokens = tokens.subList(getEncodedTokens(chunkText).size(), tokens.size());
num_chunks++;
}
// Handle the remaining tokens
if (!tokens.isEmpty()) {
String remaining_text = decodeTokens(tokens).replace(System.lineSeparator(), " ").trim();
if (remaining_text.length() > this.minChunkLengthToEmbed) {
chunks.add(remaining_text);
}
}
return chunks;
}
private List<Integer> getEncodedTokens(String text) {
Assert.notNull(text, "Text must not be null");
return this.encoding.encode(text).boxed();
}
private String decodeTokens(List<Integer> tokens) {
Assert.notNull(tokens, "Tokens must not be null");
var tokensIntArray = new IntArrayList(tokens.size());
tokens.forEach(tokensIntArray::add);
return this.encoding.decode(tokensIntArray);
}
public static final class Builder {
private int chunkSize = DEFAULT_CHUNK_SIZE;
private int minChunkSizeChars = MIN_CHUNK_SIZE_CHARS;
private int minChunkLengthToEmbed = MIN_CHUNK_LENGTH_TO_EMBED;
private int maxNumChunks = MAX_NUM_CHUNKS;
private boolean keepSeparator = KEEP_SEPARATOR;
private Builder() {
}
public Builder withChunkSize(int chunkSize) {
this.chunkSize = chunkSize;
return this;
}
public Builder withMinChunkSizeChars(int minChunkSizeChars) {
this.minChunkSizeChars = minChunkSizeChars;
return this;
}
public Builder withMinChunkLengthToEmbed(int minChunkLengthToEmbed) {
this.minChunkLengthToEmbed = minChunkLengthToEmbed;
return this;
}
public Builder withMaxNumChunks(int maxNumChunks) {
this.maxNumChunks = maxNumChunks;
return this;
}
public Builder withKeepSeparator(boolean keepSeparator) {
this.keepSeparator = keepSeparator;
return this;
}
public ChineseTokenTextSplitter build() {
return new ChineseTokenTextSplitter(this.chunkSize, this.minChunkSizeChars, this.minChunkLengthToEmbed,
this.maxNumChunks, this.keepSeparator);
}
}
}
分隔經驗:
過細分塊的潛在問題
- 語義割裂: 破壞上下文連貫性,影響模型理解。
- 計算成本增加:分塊過細會導致向量嵌入和檢索次數增多,增加時間和算力開銷。
- 信息冗餘與干擾:碎片化的文本塊可能引入無關內容,干擾檢索結果的質量,降低生成答案的準確性。
分塊過大的弊端
- 信息丟失風險:過大的文本塊可能超出嵌入模型的輸入限制,導致關鍵信息未被有效編碼。
- 檢索精度下降:大塊內容可能包含多主題混合,與用户查詢的相關性降低,影響模型反饋效果。
| 場景 | 分塊策略 | 參數參考 |
|---|---|---|
| 微博/短文本 | 句子級分塊,保留完整語義 | 每塊100-200字符 |
| 學術論文 | 段落級分塊,疊加10%重疊 | 每塊300-500字符 |
| 法律合同 | 條款級分塊,嚴格按條款分隔 | 每塊200-400字符 |
| 長篇小説 | 章節級分塊,過長段落遞歸拆分為段落 | 每塊500-1000字符 |
不要過分指望按照文本主題進行分隔, 因為實戰中的資料太多而且沒有規律, 根本沒辦法保證每個chunk是一個完整的主題內容, 哪怕人為干預也很難。 所以實戰中往往需要結合資料來決定分割器,大多數情況就是按token數分, 因為沒有完美的, 還可以加入人工干預,或者大模型分隔。
分塊五種策略
以下是 RAG 的五種分塊策略:
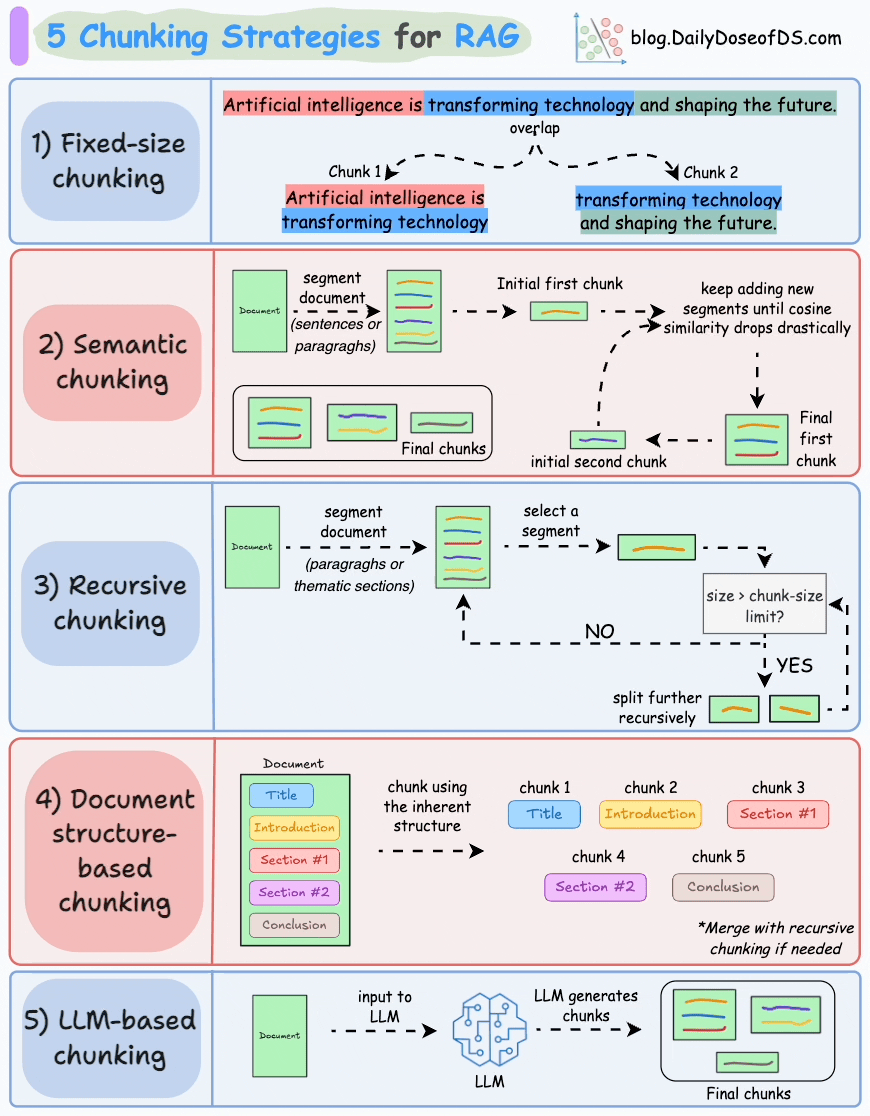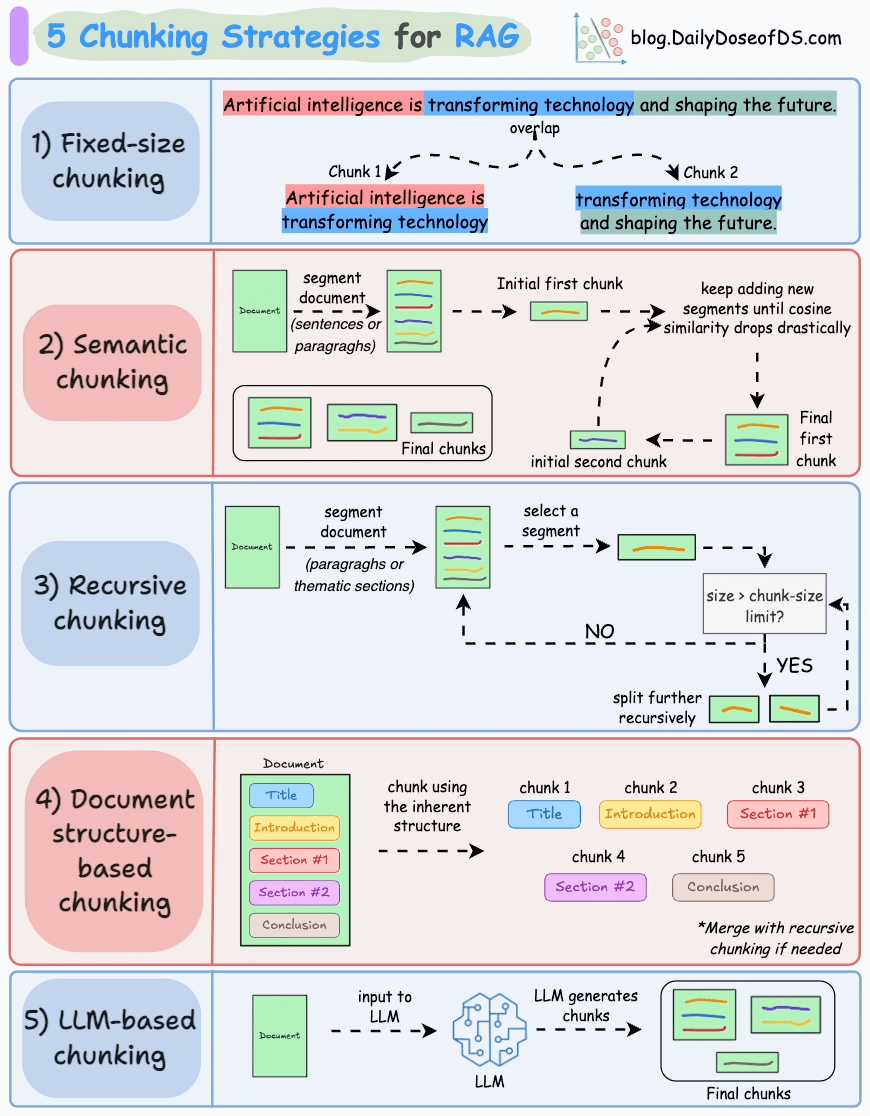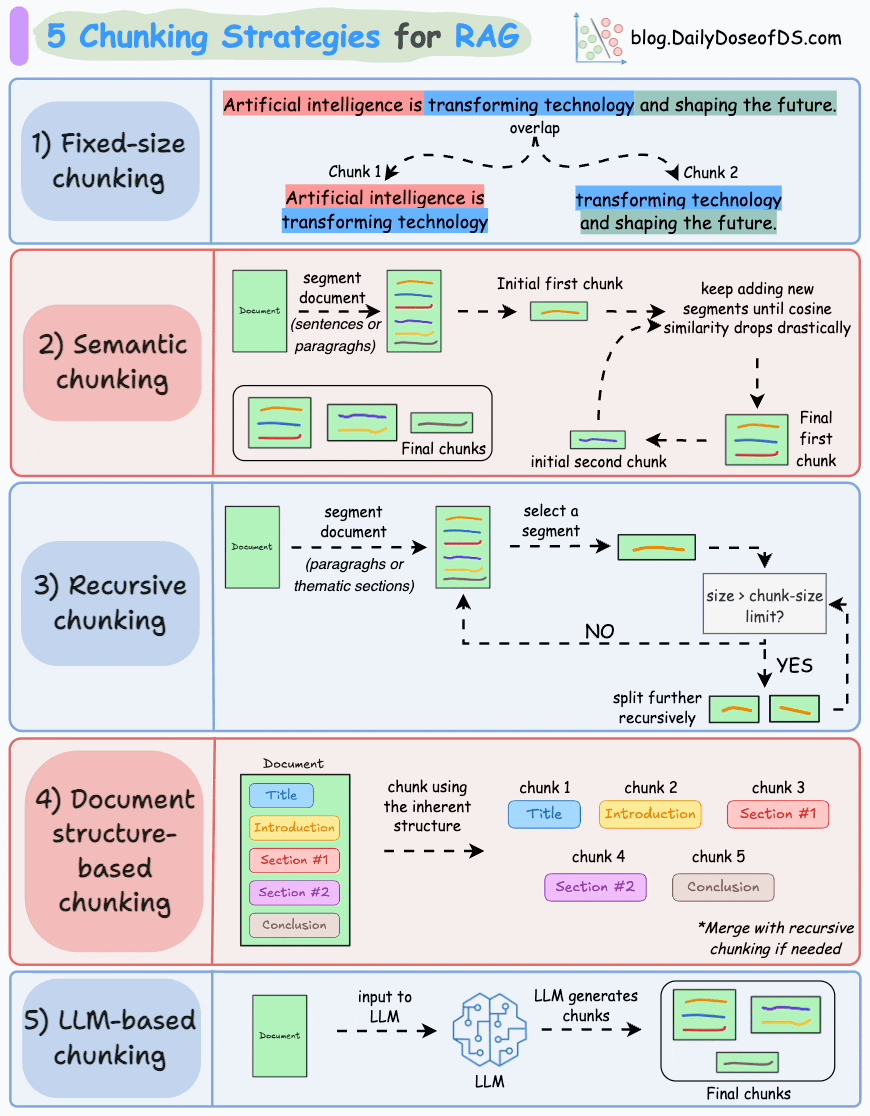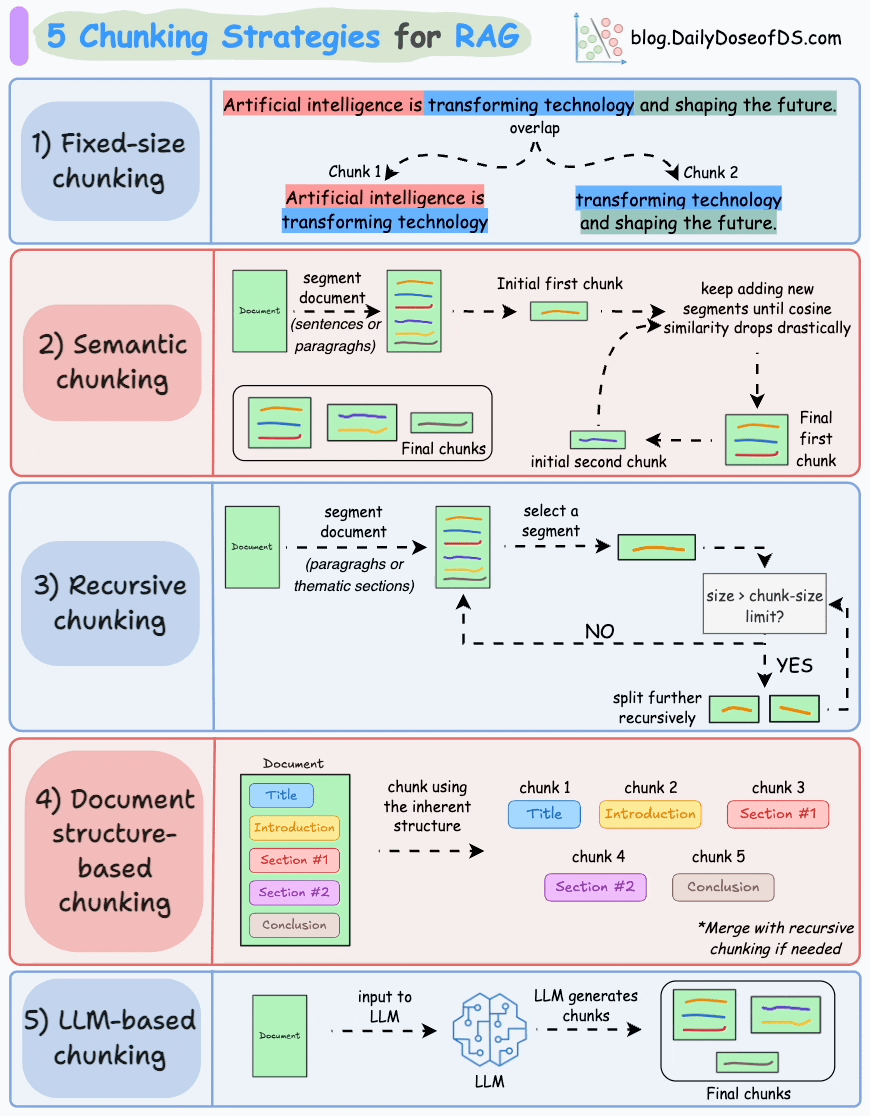
1)固定大小分塊
生成塊的最直觀和直接的方法是根據預定義的字符、單詞或標記數量將文本分成統一的段。

由於直接分割會破壞語義流,因此建議在兩個連續的塊之間保持一些重疊(上圖藍色部分)。
這很容易實現。而且,由於所有塊的大小相同,它簡化了批處理。
但有一個大問題。這通常會打斷句子(或想法)。因此,重要的信息很可能會分散到不同的塊之間。
2)語義分塊
這個想法很簡單。
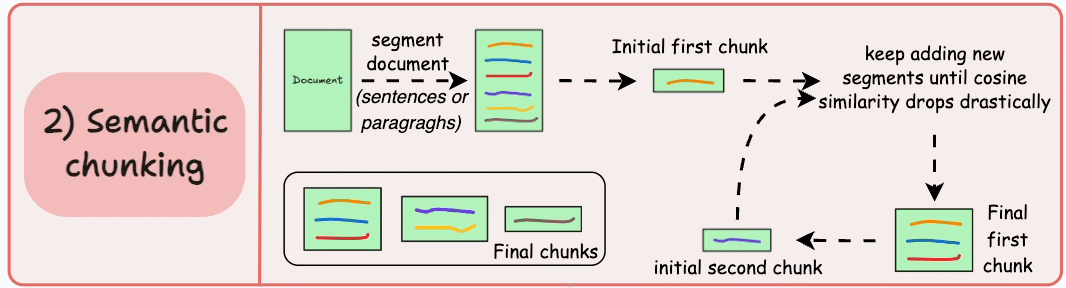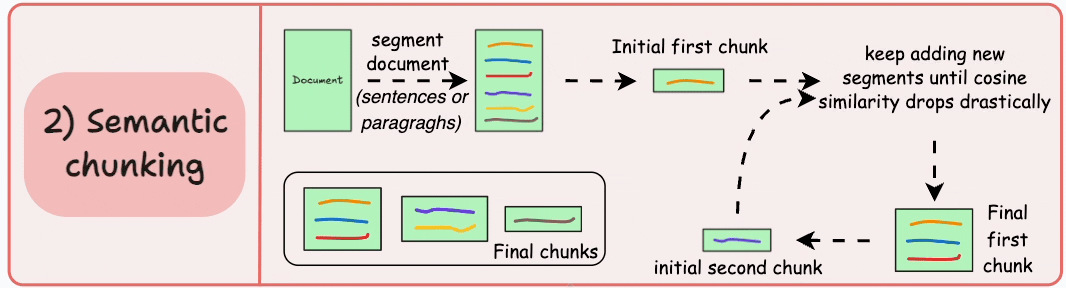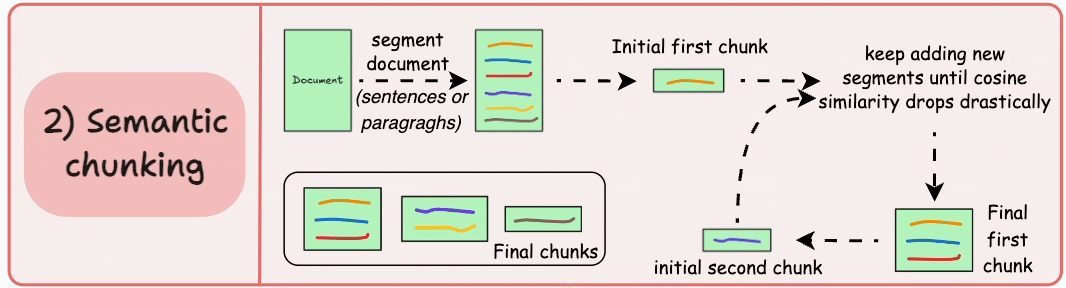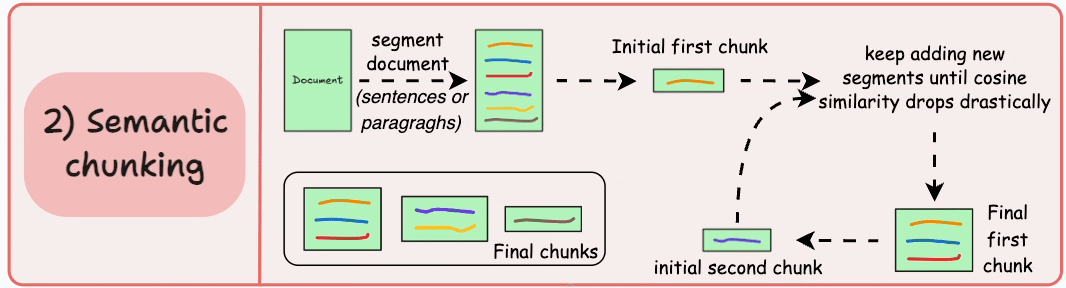
- 根據句子、段落或主題部分等有意義的單位對文檔進行細分。
- 接下來,為每個片段創建嵌入。
- 假設我從第一個片段及其嵌入開始。
- 如果第一個段的嵌入與第二個段的嵌入具有較高的餘弦相似度,則這兩個段形成一個塊。
- 這種情況一直持續到餘弦相似度顯著下降。
- 一旦發生這種情況,我們就開始新的部分並重復。
輸出可能如下所示:
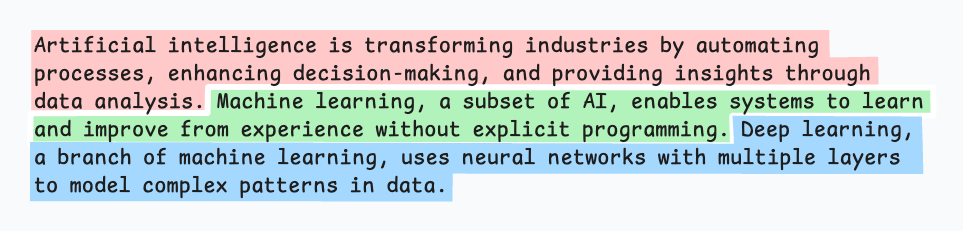
與固定大小的塊不同,這保持了語言的自然流暢並保留了完整的想法。
由於每個塊都更加豐富,它提高了檢索準確性,進而使 LLM 產生更加連貫和相關的響應。
一個小問題是,它依賴於一個閾值來確定餘弦相似度是否顯著下降,而這個閾值在不同文檔之間可能會有所不同。
3)遞歸分塊
這也很簡單。
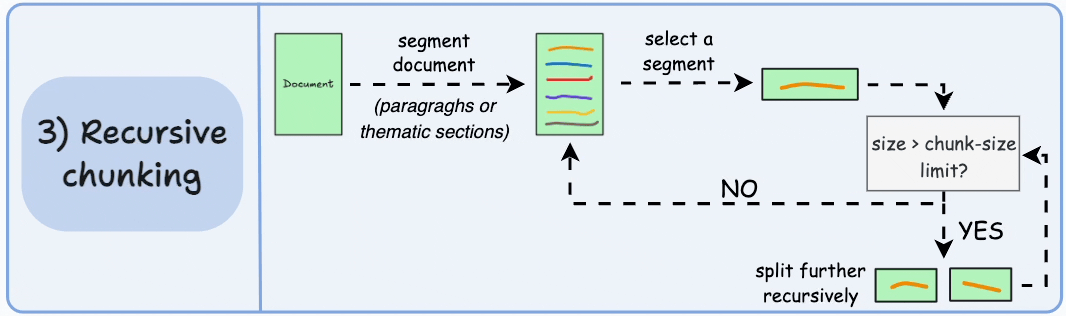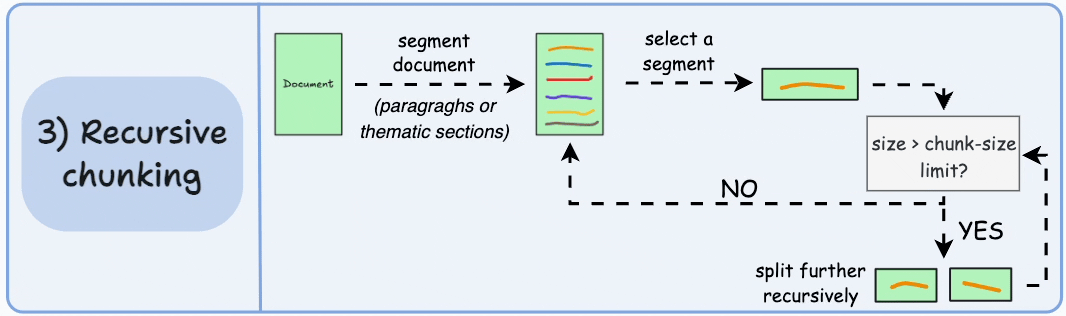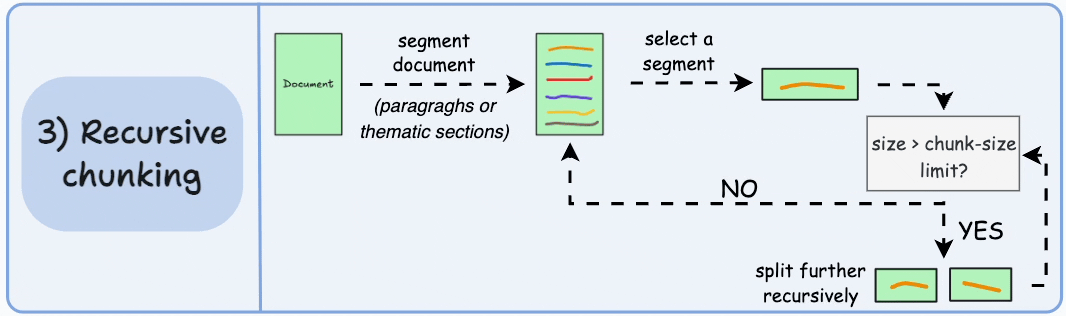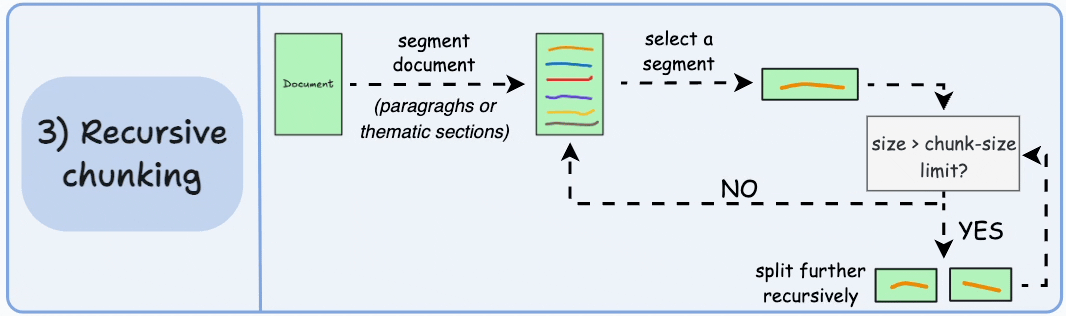
首先,根據固有分隔符(如段落或章節)進行分塊。
接下來,如果每個塊的大小超出了預定義的塊大小限制,則將其拆分成更小的塊。但是,如果塊符合塊大小限制,則不再進行進一步拆分。
輸出可能如下所示:
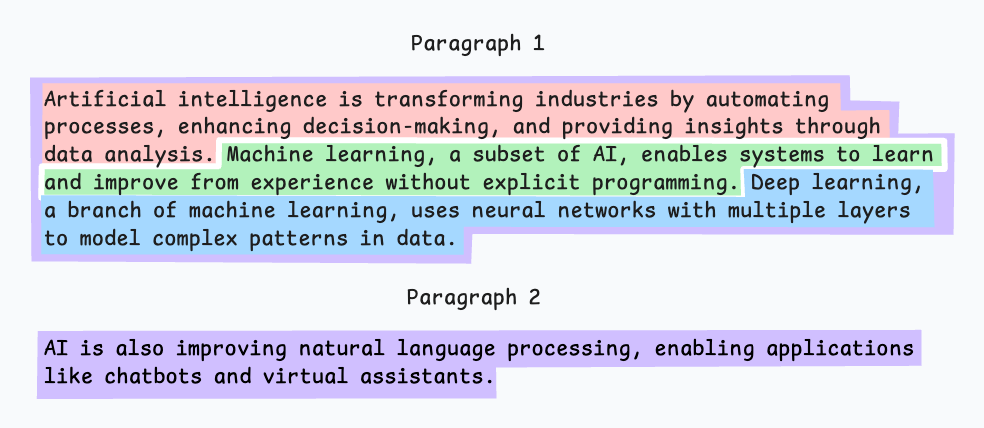
如上圖:
- 首先,我們定義兩個塊(紫色的兩個段落)。
- 接下來,第 1 段被進一步分成更小的塊。
與固定大小的塊不同,這種方法還保持了語言的自然流暢性並保留了完整的想法。
然而,在實施和計算複雜性方面存在一些額外的開銷。
4)基於文檔結構的分塊
這是另一種直觀的方法。
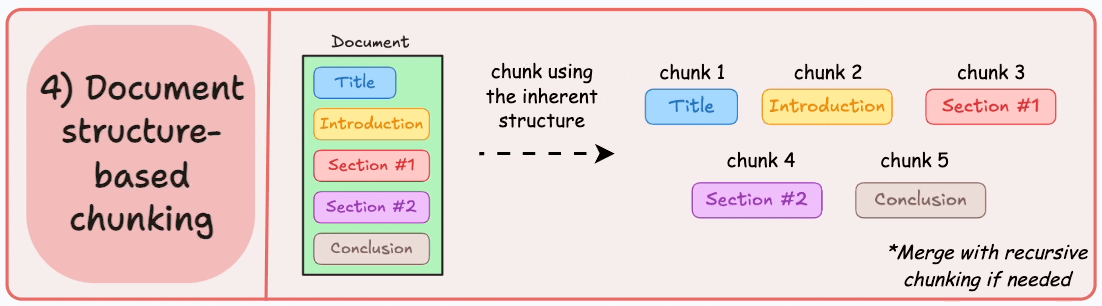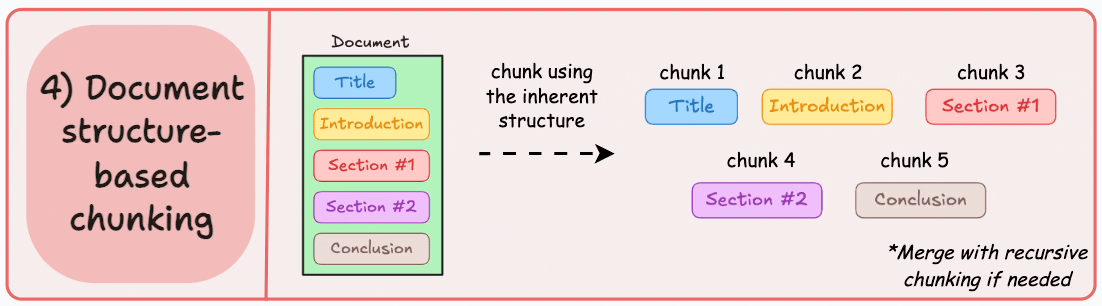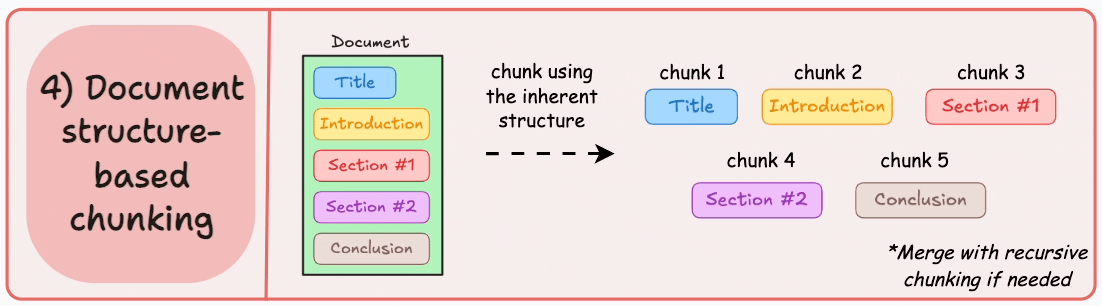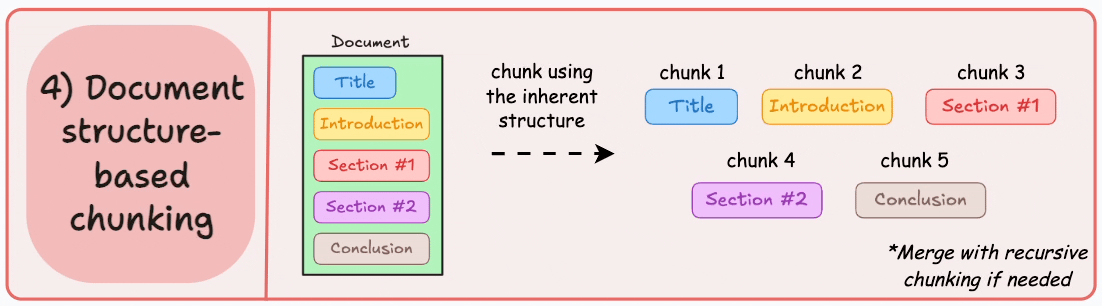
它利用文檔的固有結構(如標題、章節或段落)來定義塊邊界。
這樣,它就通過與文檔的邏輯部分對齊來保持結構完整性。
輸出可能如下所示:
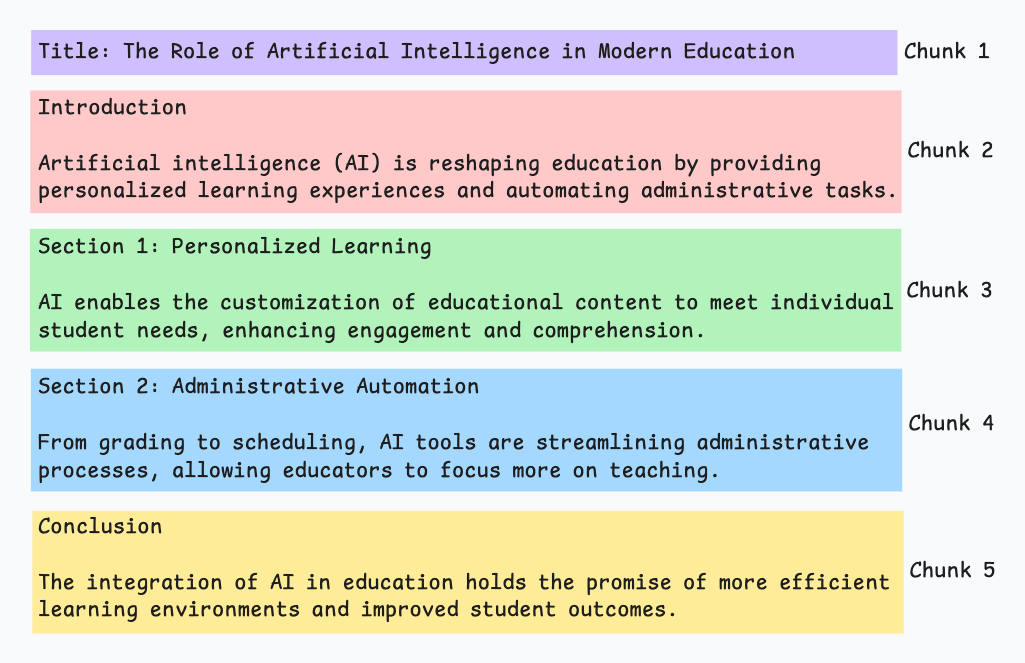
也就是説,這種方法假設文檔具有清晰的結構,但事實可能並非如此。
此外,塊的長度可能會有所不同,可能會超出模型令牌的限制。您可以嘗試使用遞歸拆分進行合併。
5)基於LLM的分塊

既然每種方法都有優點和缺點,為什麼不使用 LLM 來創建塊呢?
可以提示 LLM 生成語義上孤立且有意義的塊。
顯然,這種方法將確保較高的語義準確性,因為 LLM 可以理解超越簡單啓發式方法(用於上述四種方法)的上下文和含義。
唯一的問題是,它是這裏討論的所有五種技術中計算要求最高的分塊技術。
此外,由於 LLM 通常具有有限的上下文窗口,因此需要注意這一點。
每種技術都有其自身的優勢和劣勢。
我觀察到語義分塊在很多情況下效果很好,但同樣,您需要進行測試。
選擇將在很大程度上取決於內容的性質、嵌入模型的功能、計算資源等。
我們很快就會對這些策略進行實際演示。
同時,如果您錯過了,昨天我們討論了構建依賴於成對內容相似性的強大 NLP 系統的技術(RAG 就是其中之一)。
ContentFormatTransformer
檢索到的內容最終會發給大模型, 由該組件決定發送到模型的RAG內容
private static final String DEFAULT_TEXT_TEMPLATE = String.format("%s\n\n%s", TEMPLATE_METADATA_STRING_PLACEHOLDER,
TEMPLATE_CONTENT_PLACEHOLDER);
即:假設:
● 文本內容:"The World is Big and Salvation Lurks Around the Corner"
● 元數據:Map.of("fileName", "xushu.pdf")
最終發送給大模型的格式化內容是:
source: xushu.pdf
The World is Big and Salvation Lurks Around the Corner
很少會去改, 瞭解即可
KeywordMetadataEnriching
使用生成式AI模型從文檔內容中提取關鍵詞並將其添加為元數據,為文檔添加關鍵詞標籤,提升檢索精度
new KeywordMetadataEnricher(chatModel, 5);
- chatModel 需要提取關鍵字的模型
- 關鍵字數量
@Test
public void testKeywordMetadataEnricher(
@Autowired DashScopeChatModel chatModel,
@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", resource.getFilename());
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
ChineseTokenTextSplitter splitter = new ChineseTokenTextSplitter();
List<Document> apply = splitter.apply(documents);
// 通過傳入大模型,讓大模型提取文件內容當中的 5 個關鍵字
KeywordMetadataEnricher enricher = new KeywordMetadataEnricher(chatModel, 5);
// 關鍵字的提取,根據標籤提取
apply= enricher.apply(apply);
for (Document document : apply) {
System.out.println(document.getText());
System.out.println(document.getText().length());
}
apply.forEach(System.out::println);
}
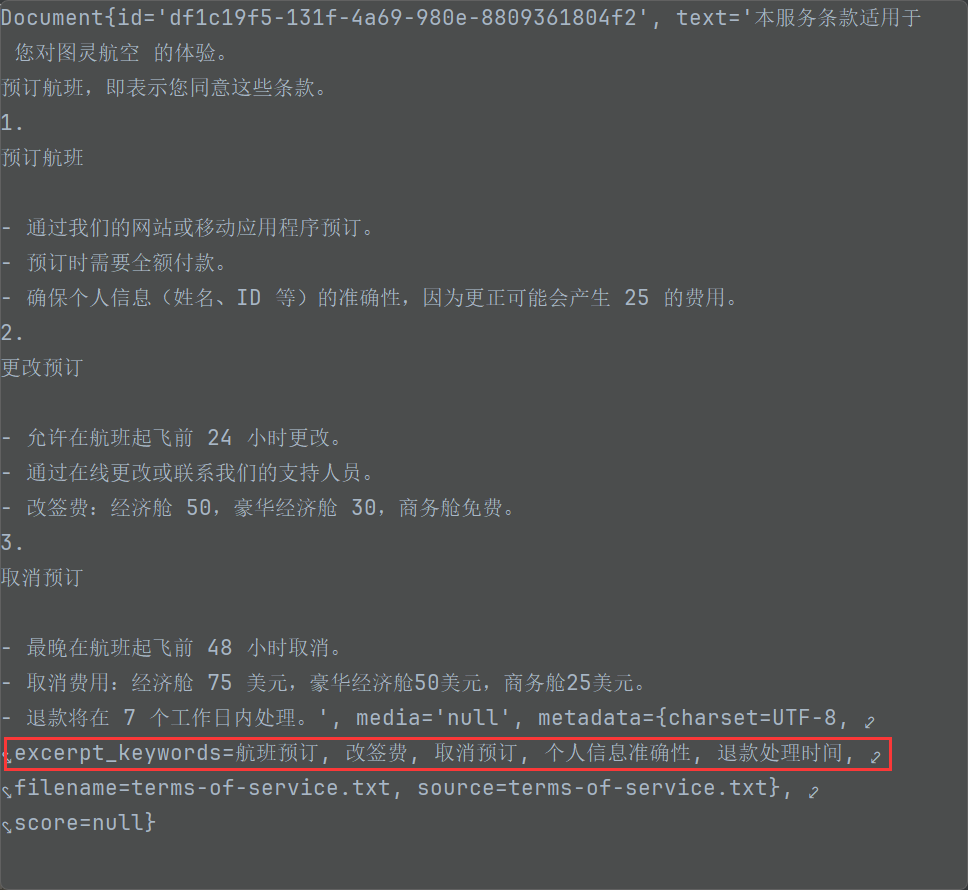
提取到的關鍵字的作用:
幫助做元數據過濾。 並不參數向量數據庫的相似性檢索
KeywordMetadataEnriching 生成出來的關鍵字無法進行元數據過濾?
SummaryMetadataEnricher
使用生成式AI模型為文檔創建摘要並將其添加為元數據。它可以為當前文檔以及相鄰文檔(前一個和後一個)生成摘要,以提供更豐富的上下文信息 。
場景: 有順序關聯的文檔,比如西遊記小説的RAG,‘三打白骨精的故事以及後續劇情’。
- 技術文檔:前後章節有依賴關係
- 教程內容:步驟之間有邏輯順序
- 法律文檔:條款之間有關聯性
- 學術論文:章節間有邏輯遞進
@Test
public void testSummaryMetadataEnricher(
@Autowired DashScopeChatModel chatModel,
@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", resource.getFilename());
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
ChineseTokenTextSplitter splitter = new ChineseTokenTextSplitter();
List<Document> apply = splitter.apply(documents);
SummaryMetadataEnricher enricher = new SummaryMetadataEnricher(chatModel,
List.of(SummaryMetadataEnricher.SummaryType.PREVIOUS,
SummaryMetadataEnricher.SummaryType.CURRENT,
SummaryMetadataEnricher.SummaryType.NEXT));
apply = enricher.apply(apply);
}
文本向量化

向量化存儲之前在“文本向量化”介紹了, 就是通過向量模型庫進行向量化
代碼:
依然通過Qwen向量模型進行向量化: 將第分割的chunk進行向量化
@Test
public void testTokenTextSplitter(
@Autowired DashScopeEmbeddingModel embeddingModel,
@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", resource.getFilename());
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
ChineseTokenTextSplitter splitter = new ChineseTokenTextSplitter(100);
List<Document> apply = splitter.apply(documents);
for (Document document : apply) {
float[] embedded = embeddingModel.embed(document);
}
}
存儲向量
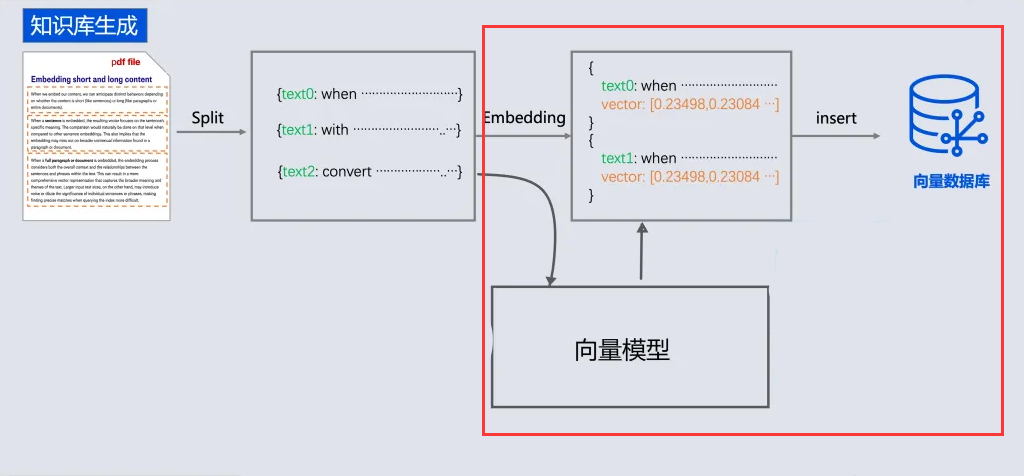
但是我告訴你其實 , 我們通過向量數據庫存儲document, 可以省略向量化這一步, 向量數據庫會在底層自動完成向量化
for (Document document : apply) {
float[] embedded = embeddingModel.embed(document);
}
// 替換為: 寫入=向量化+存儲
vectorStore.write(apply);
@Test
public void testTokenTextSplitter(
@Autowired VectorStore vectorStore,
@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", resource.getFilename());
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
ChineseTokenTextSplitter splitter = new ChineseTokenTextSplitter(100);
List<Document> apply = splitter.apply(documents);
vectorStore.add(apply);
}
向量數據庫檢索
代碼:
需要先將文本進行向量化, 然後去向量數據庫查詢,
// 3. 相似性查詢
SearchRequest searchRequest = SearchRequest
.builder().query("預定航班")
.topK(5)
.similarityThreshold(0.3)
.build();
List<Document> results = vectorStore.similaritySearch(searchRequest);
// 4.輸出
System.out.println(results);
完整代碼:
@Test
public void testRag(
@Autowired VectorStore vectorStore,
@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
// 1. 讀取
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", resource.getFilename());
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
// 2.分隔
ChineseTokenTextSplitter splitter = new ChineseTokenTextSplitter(100);
List<Document> apply = splitter.apply(documents);
// 3. 向量化+寫入
vectorStore.write(apply);
// 3. 相似性查詢
SearchRequest searchRequest = SearchRequest
.builder().query("退費需要多少費用")
.topK(5)
.similarityThreshold(0.3)
.build();
List<Document> results = vectorStore.similaritySearch(searchRequest);
// 4.輸出
System.out.println(results);
}
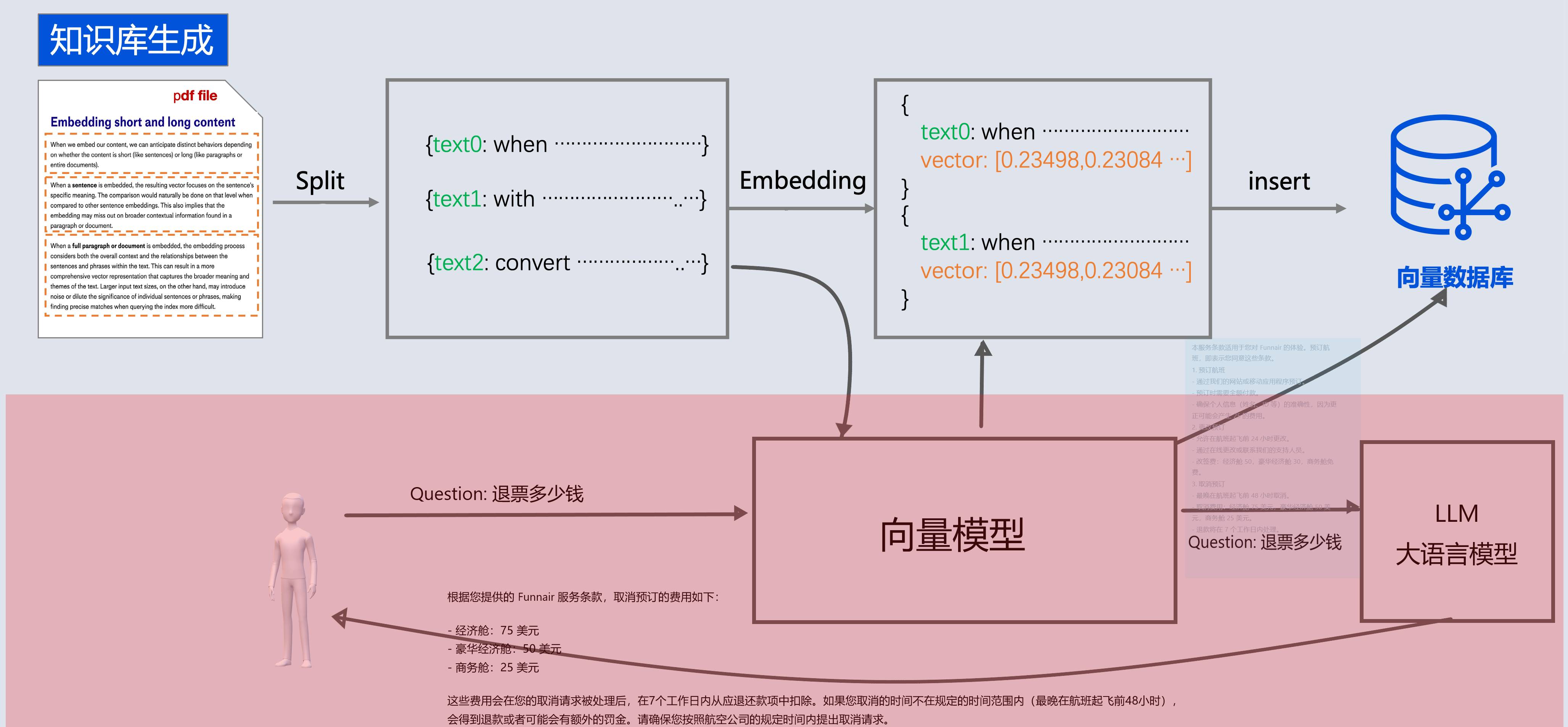
對話階段
如果結合ChatClient 可以直接將檢索和Advisor整合在一起
@Test
public void testRagToLLM(
@Autowired VectorStore vectorStore,
@Autowired DashScopeChatModel chatModel,
@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", resource.getFilename());
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
ChineseTokenTextSplitter splitter = new ChineseTokenTextSplitter(100);
List<Document> apply = splitter.apply(documents);
vectorStore.write(apply);
// 3. 相似性查詢
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.build();
String message="退費需要多少費用?";
String content = chatClient.prompt().user(message)
.advisors(
new SimpleLoggerAdvisor(),
QuestionAnswerAdvisor.builder(vectorStore)
.searchRequest(
SearchRequest
.builder().query(message)
.topK(5)
.similarityThreshold(0.3)
.build())
.build()
).call().content();
System.out.println(content);
}
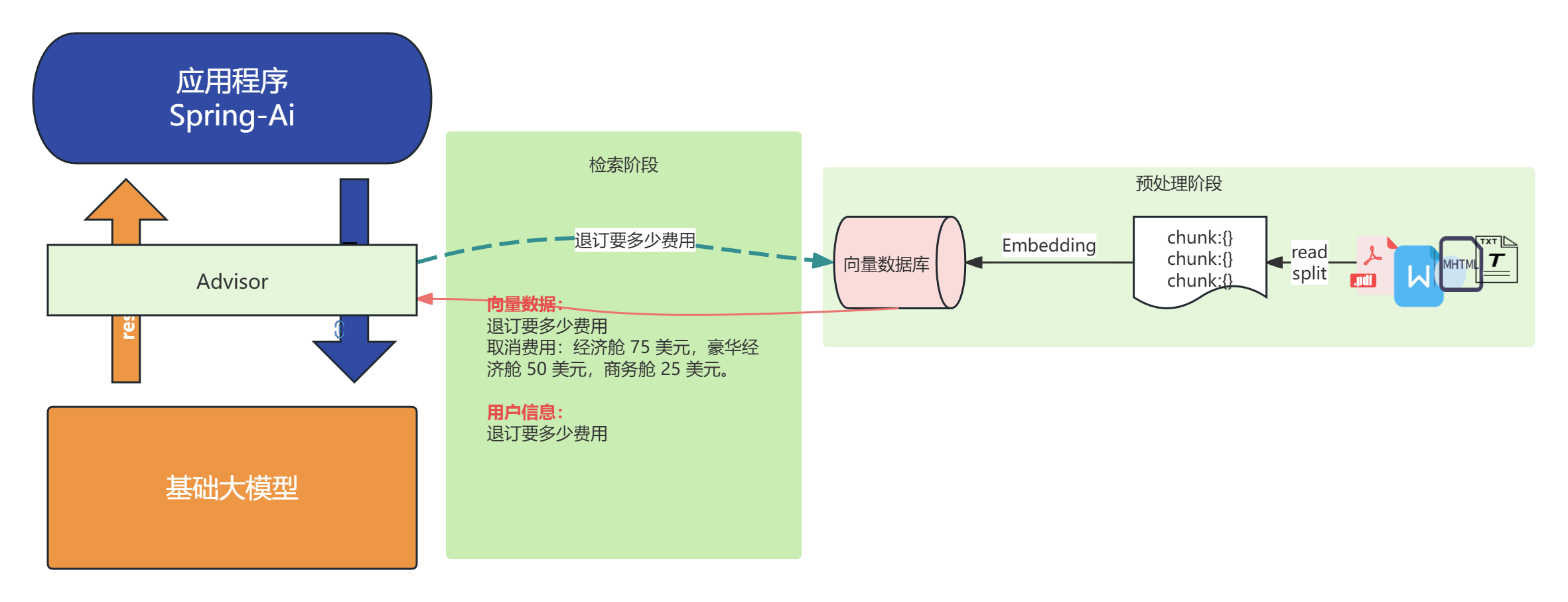
SpringAI整個過程原理:
提升檢索精度—rerank(重排序)
為什麼需要 rerank
傳統的向量檢索存在幾個關鍵問題:
語義相似度的侷限性:向量檢索主要基於餘弦相似度等數學計算,但相似的向量表示不一定意味着內容一定絕對相關。單純的向量相似度無法充分理解查詢的真實意圖和上下文。
排序質量不佳:初始檢索的排序往往不是最優的,可能將不太相關的文檔排在前面,尤其性能差的向量模型更為明顯。
上下文理解缺失:傳統檢索(完全依賴向量數據庫和向量模型)缺乏對查詢和文檔完整上下文的深度理解,容易出現語義漂移問題。
重排序:
主要在檢索階段進行改進:

二階段優化架構: rerank 採用"粗排+精排"的兩階段架構。第一階段快速檢索大量候選文檔,第二階段使用專門的重排序模型進行精確評分。
專業化模型: 重排序模型(如gte-rerank-hybrid)專門針對文檔相關性評估進行訓練,能夠更準確地計算查詢與文檔的語義匹配度。
分數閾值過濾: 通過設置最小分數閾值,可以過濾掉低質量的文檔,確保只有高相關性的內容被保留。在實現中可以看到這個過濾邏輯:
動態參數調整: 支持根據實際效果動態調整 topN 等參數,優化最終返回的文檔數量和質量。
代碼
説明:
為了更好的測試
- 我這裏用的事ollama一個性能較差的向量模型, 這樣才能更好體現他瞎排的順序
- 我分隔的比較小new ChineseTokenTextSplitter(80,10,5,10000,true);為了有更多的document;
- 粗排需要設置數量較大的topk(建議200) , 精排(默認topN5)
@SpringBootTest
public class RerankTest {
@BeforeEach
public void init(
@Autowired VectorStore vectorStore,
@Value("classpath:rag/terms-of-service.txt") Resource resource) {
// 讀取
TextReader textReader = new TextReader(resource);
textReader.getCustomMetadata().put("filename", resource.getFilename());
List<Document> documents = textReader.read();
// 分隔
ChineseTokenTextSplitter splitter = new ChineseTokenTextSplitter(80,10,5,10000,true);
List<Document> apply = splitter.apply(documents);
// 存儲向量(內部會自動向量化)
vectorStore.add(apply);
}
@TestConfiguration
static class TestConfig {
@Bean
public VectorStore vectorStore(OllamaEmbeddingModel embeddingModel) {
return SimpleVectorStore.builder(embeddingModel).build();
}
}
@Test
public void testRerank(
@Autowired DashScopeChatModel dashScopeChatModel,
@Autowired VectorStore vectorStore,
@Autowired DashScopeRerankModel rerankModel) {
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(dashScopeChatModel)
.build();
RetrievalRerankAdvisor retrievalRerankAdvisor =
new RetrievalRerankAdvisor(vectorStore, rerankModel
, SearchRequest.builder().topK(200).build());
String content = chatClient.prompt().user("退票費用")
.advisors(retrievalRerankAdvisor)
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(content);
}
}
重排前:
排第一的doucment跟退費並沒有關係:

重排後:
排第一的document:
最後:
“在這個最後的篇章中,我要表達我對每一位讀者的感激之情。你們的關注和回覆是我創作的動力源泉,我從你們身上吸取了無盡的靈感與勇氣。我會將你們的鼓勵留在心底,繼續在其他的領域奮鬥。感謝你們,我們總會在某個時刻再次相遇。”












