你是否遇到過這樣的場景:後台接口響應越來越慢,用户抱怨頁面加載時間長,運維同事警告服務器負載飆升?分析日誌發現,一個頁面渲染竟然要發起幾十上百個接口請求!隨着用户量增長,系統就像陷入泥潭。這種情況在微服務架構特別常見 - 獲取 10 個用户信息,就要發 10 次獨立請求,每次都有網絡延遲。如何優雅地解決這個問題?請求合併技術正是你需要的救星。
請求合併的核心原理
請求合併就是把短時間內的多個獨立請求打包成一個批量請求,處理後再分發結果。這就像公交車而不是出租車 - 不是每個人單獨派一輛車,而是等一小會兒,讓大家坐同一輛車前往目的地,大幅提高效率。
請求合併能帶來這些好處:
- 減少網絡往返,顯著降低總延遲
- 節約連接資源,避免連接池耗盡
- 減少數據庫查詢次數,降低數據庫壓力
- 提高系統整體吞吐量,降低資源消耗
三大合併策略及應用場景
1. 時間窗口合併
在固定時間窗口內(比如 50ms)收集所有請求,然後一起發送。這種策略適合對實時性要求不那麼苛刻的場景。
這就像公交車,會在每個站點等待固定時間,不管上多少人都會準時發車。
2. 數量閾值合併
當收集到足夠多的請求(如 100 個)後立即發送,不再等待。適合批處理場景,可以控制每批數據量。
這就像電梯容量到了就會自動關門,不會無限等待。
3. 混合策略
結合時間窗口和數量閾值,滿足任一條件就觸發批量請求。這是生產環境最常用的策略,能平衡實時性和效率。
類比食堂打飯:要麼人滿一桌就上菜,要麼到點就上菜,哪個條件先滿足就先執行。
高性能請求合併器實現
配置驅動的合併參數
首先,我們定義一個配置類來支持外部化配置:
/**
* 請求合併器配置類
*/
public class MergerConfig {
// 基本配置
public static final long DEFAULT_WINDOW_TIME = 50; // 默認時間窗口(ms)
public static final int DEFAULT_MAX_BATCH_SIZE = 100; // 默認最大批量大小
// 熔斷配置
public static final int DEFAULT_FAILURE_THRESHOLD = 5; // 默認失敗閾值
public static final long DEFAULT_CIRCUIT_RESET_TIMEOUT = 30_000; // 默認熔斷重置時間(ms)
public static final long DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 3_000; // 默認請求超時時間(ms)
// 根據系統環境變量獲取配置值
public static long getWindowTime() {
return Long.parseLong(System.getProperty("merger.window.time",
String.valueOf(DEFAULT_WINDOW_TIME)));
}
public static int getMaxBatchSize() {
return Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("merger.max.batch.size",
String.valueOf(DEFAULT_MAX_BATCH_SIZE)));
}
/**
* 根據系統資源狀態動態調整合並參數
*/
public static void adjustParameters() {
// 基於CPU利用率動態調整批量大小
double cpuLoad = getSystemCpuLoad();
if (cpuLoad > 0.8) { // CPU負載高
System.setProperty("merger.max.batch.size",
String.valueOf(DEFAULT_MAX_BATCH_SIZE / 2));
} else if (cpuLoad < 0.3) { // CPU負載低
System.setProperty("merger.max.batch.size",
String.valueOf(DEFAULT_MAX_BATCH_SIZE * 2));
}
}
/**
* 獲取系統CPU負載
*/
private static double getSystemCpuLoad() {
try {
return ManagementFactory.getOperatingSystemMXBean()
.getSystemLoadAverage() / Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
} catch (Exception e) {
return 0.5; // 默認值
}
}
// 其他getter方法...
}同步請求合併器
下面是一個支持監控、部分結果處理的高性能同步請求合併器:
/**
* 同步請求合併器
* 時間複雜度:O(1)平均情況,O(n)觸發批處理時
* 空間複雜度:O(n)其中n為等待處理的請求數
*/
public class RequestMerger<K, V> {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RequestMerger.class);
private final long windowTimeMillis;
private final int maxBatchSize;
private final Function<List<K>, Map<K, V>> batchFunction;
private final V defaultValue;
private final boolean allowPartialResult;
// 使用ConcurrentHashMap減少鎖競爭
private final ConcurrentHashMap<K, CompletableFuture<Optional<V>>> pendingRequests = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final List<K> pendingKeys = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
private final Object batchLock = new Object(); // 細粒度鎖,只鎖批處理操作
private ScheduledFuture<?> scheduledTask;
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler =
Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(r -> {
Thread t = new Thread(r, "request-merger-scheduler");
t.setDaemon(true); // 使用守護線程避免阻止JVM退出
return t;
});
// 監控指標
private final Timer batchProcessTimer;
private final Counter batchSizeCounter;
private final Counter requestCounter;
private final Counter batchCounter;
/**
* 創建請求合併器
* @param windowTimeMillis 時間窗口(毫秒)
* @param maxBatchSize 最大批處理大小
* @param batchFunction 批量處理函數,需返回包含所有輸入key的Map
* @param allowPartialResult 是否允許部分結果
* @param defaultValue 默認值(當key沒有對應值且allowPartialResult為true時使用)
*/
public RequestMerger(long windowTimeMillis, int maxBatchSize,
Function<List<K>, Map<K, V>> batchFunction,
boolean allowPartialResult, V defaultValue) {
this.windowTimeMillis = windowTimeMillis;
this.maxBatchSize = maxBatchSize;
this.batchFunction = batchFunction;
this.allowPartialResult = allowPartialResult;
this.defaultValue = defaultValue;
// 初始化監控指標
MeterRegistry registry = Metrics.globalRegistry;
this.batchProcessTimer = Timer.builder("merger.batch.process.time")
.description("批量處理耗時")
.register(registry);
this.batchSizeCounter = Counter.builder("merger.batch.size")
.description("批量大小分佈")
.register(registry);
this.requestCounter = Counter.builder("merger.requests")
.description("請求總數")
.register(registry);
this.batchCounter = Counter.builder("merger.batches")
.description("批次總數")
.register(registry);
}
/**
* 獲取指定鍵的值,可能觸發批量請求
* @param key 請求鍵
* @return 包含可選結果的CompletableFuture
*/
public CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> get(K key) {
// ① 參數校驗
if (key == null) {
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
future.completeExceptionally(new IllegalArgumentException("Key不能為null"));
return future;
}
// 記錄請求數
requestCounter.increment();
// ② 重複請求檢查 - 避免相同請求多次處理
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> existingFuture = pendingRequests.get(key);
if (existingFuture != null) {
return existingFuture;
}
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> oldFuture = pendingRequests.putIfAbsent(key, future);
// 雙重檢查,處理併發衝突
if (oldFuture != null) {
return oldFuture;
}
// ③ 合併邏輯 - 添加到等待隊列並可能觸發批處理
synchronized (batchLock) {
pendingKeys.add(key);
// 策略1: 首個請求,啓動計時器
if (pendingKeys.size() == 1) {
scheduledTask = scheduler.schedule(
this::processBatch, windowTimeMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 策略2: 達到批量閾值,立即處理
else if (pendingKeys.size() >= maxBatchSize) {
if (scheduledTask != null) {
scheduledTask.cancel(false);
}
// 異步處理,避免阻塞當前線程
CompletableFuture.runAsync(this::processBatch);
}
}
// ④ 上下文傳遞 - 保留調用方的追蹤信息
setupRequestContext(future);
return future;
}
// 設置請求上下文,保留調用線程的MDC信息
private void setupRequestContext(CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> future) {
Map<String, String> currentContext = MDC.getCopyOfContextMap();
future.whenComplete((result, ex) -> {
Map<String, String> oldContext = MDC.getCopyOfContextMap();
try {
if (currentContext != null) {
MDC.setContextMap(currentContext);
} else {
MDC.clear();
}
} finally {
if (oldContext != null) {
MDC.setContextMap(oldContext);
} else {
MDC.clear();
}
}
});
}
private void processBatch() {
List<K> batchKeys;
Map<K, CompletableFuture<Optional<V>>> batchFutures;
// ① 收集批處理請求
synchronized (batchLock) {
if (pendingKeys.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
batchKeys = new ArrayList<>(pendingKeys);
batchFutures = new HashMap<>();
for (K key : batchKeys) {
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> future = pendingRequests.get(key);
if (future != null) {
batchFutures.put(key, future);
pendingRequests.remove(key);
}
}
pendingKeys.clear();
scheduledTask = null; // 清空調度任務引用
}
if (batchKeys.isEmpty()) {
return; // 防禦性編程
}
// ② 記錄批次和大小
batchCounter.increment();
batchSizeCounter.increment(batchKeys.size());
// ③ 測量批量處理時間
Timer.Sample sample = Timer.start();
try {
// ④ 執行批量請求
Map<K, V> results = batchFunction.apply(batchKeys);
// ⑤ 結果完整性檢查
Set<K> missingKeys = new HashSet<>();
if (!allowPartialResult) {
for (K key : batchKeys) {
if (!results.containsKey(key)) {
missingKeys.add(key);
}
}
if (!missingKeys.isEmpty()) {
String errorMsg = "缺少鍵的結果: " + missingKeys;
log.warn(errorMsg);
RuntimeException ex = new RuntimeException(errorMsg);
// 所有future都異常完成
batchFutures.values().forEach(future ->
future.completeExceptionally(ex));
// 記錄處理時間
sample.stop(batchProcessTimer);
return;
}
}
// ⑥ 分發結果給各個請求
for (K key : batchKeys) {
V result = results.get(key);
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> future = batchFutures.get(key);
if (future != null) {
if (result != null) {
future.complete(Optional.of(result));
} else if (allowPartialResult) {
future.complete(Optional.ofNullable(defaultValue));
} else {
future.completeExceptionally(
new RuntimeException("未找到鍵的結果: " + key));
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("批量請求處理異常", e);
// 出現異常時,讓所有future都異常完成
batchFutures.values().forEach(future ->
future.completeExceptionally(e));
} finally {
// 記錄處理時間
sample.stop(batchProcessTimer);
}
}
// 其他方法略...
}自適應背壓的異步請求合併器
增強版異步合併器,加入了動態背壓控制:
/**
* 異步請求合併器(增強版)
* 特點:完全非阻塞 + 自適應背壓控制
*/
public class AsyncRequestMerger<K, V> {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncRequestMerger.class);
private final long windowTimeMillis;
private final int maxBatchSize;
private final Function<List<K>, CompletableFuture<Map<K, V>>> asyncBatchFunction;
private final V defaultValue;
private final boolean allowPartialResult;
private final long timeoutMillis;
// 熔斷器
private final MergerCircuitBreaker circuitBreaker;
// 背壓控制 - 動態調整併發量
private final AdaptiveSemaphore concurrencyLimiter;
private final ConcurrentHashMap<K, CompletableFuture<Optional<V>>> pendingRequests = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final List<K> pendingKeys = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
private final Object batchLock = new Object();
private ScheduledFuture<?> scheduledTask;
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler =
Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
private final Counter rejectedRequestCounter;
/**
* 創建異步請求合併器
*/
public AsyncRequestMerger(long windowTimeMillis, int maxBatchSize,
Function<List<K>, CompletableFuture<Map<K, V>>> asyncBatchFunction,
boolean allowPartialResult, V defaultValue,
long timeoutMillis) {
this.windowTimeMillis = windowTimeMillis;
this.maxBatchSize = maxBatchSize;
this.asyncBatchFunction = asyncBatchFunction;
this.allowPartialResult = allowPartialResult;
this.defaultValue = defaultValue;
this.timeoutMillis = timeoutMillis;
this.circuitBreaker = new MergerCircuitBreaker(
MergerConfig.DEFAULT_FAILURE_THRESHOLD,
MergerConfig.DEFAULT_CIRCUIT_RESET_TIMEOUT);
// 動態背壓控制 - 初始許可為CPU核心數的2倍
int initialPermits = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2;
this.concurrencyLimiter = new AdaptiveSemaphore(initialPermits);
// 監控指標
MeterRegistry registry = Metrics.globalRegistry;
this.rejectedRequestCounter = Counter.builder("merger.rejected.requests")
.description("被拒絕的請求數")
.register(registry);
// 定期調整併發許可數量
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
concurrencyLimiter.adjustPermits();
}, 5, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
// 背壓控制的核心 - 自適應信號量
private static class AdaptiveSemaphore {
private final Semaphore semaphore;
private final AtomicInteger currentPermits;
private final AtomicLong lastSuccessfulBatchTime = new AtomicLong(0);
private final AtomicLong lastRejectedTime = new AtomicLong(0);
public AdaptiveSemaphore(int initialPermits) {
this.semaphore = new Semaphore(initialPermits);
this.currentPermits = new AtomicInteger(initialPermits);
}
public boolean tryAcquire() {
boolean acquired = semaphore.tryAcquire();
if (!acquired) {
lastRejectedTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
return acquired;
}
public void release() {
semaphore.release();
lastSuccessfulBatchTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
// 根據系統狀態動態調整許可數
public void adjustPermits() {
int permits = currentPermits.get();
// 如果有最近的拒絕記錄,可能需要增加許可
long lastRejected = lastRejectedTime.get();
if (lastRejected > 0 &&
System.currentTimeMillis() - lastRejected < 5000) {
// 增加25%的許可,但不超過CPU核心數的4倍
int maxPermits = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 4;
int newPermits = Math.min(maxPermits, (int)(permits * 1.25));
if (newPermits > permits) {
int delta = newPermits - permits;
semaphore.release(delta);
currentPermits.set(newPermits);
log.info("增加併發許可至: {}", newPermits);
}
}
// 如果長時間沒有拒絕,可以嘗試減少許可
else if (System.currentTimeMillis() - lastRejectedTime.get() > 30000) {
// 每次減少10%,但不低於CPU核心數
int minPermits = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
int newPermits = Math.max(minPermits, (int)(permits * 0.9));
if (newPermits < permits) {
// 計算要減少的許可數
int delta = permits - newPermits;
// 嘗試獲取這些許可(如果都在使用中則無法減少)
if (semaphore.tryAcquire(delta)) {
currentPermits.set(newPermits);
log.info("減少併發許可至: {}", newPermits);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 獲取指定鍵的值,通過異步批處理
* 注意:若系統過載或熔斷器開啓,會快速拒絕請求
*/
public CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> get(K key) {
// 檢查熔斷器狀態
if (!circuitBreaker.allowRequest()) {
rejectedRequestCounter.increment();
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
future.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException("熔斷器已開啓,拒絕請求"));
return future;
}
// 背壓控制 - 檢查系統負載
if (!concurrencyLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
rejectedRequestCounter.increment();
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
future.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException("系統負載過高,請稍後重試"));
return future;
}
try {
// 其餘邏輯與之前類似
// ...省略相似代碼...
// 異步處理批量請求
asyncBatchFunction.apply(batchKeys)
// 添加超時控制
.orTimeout(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
// 處理結果...
// ...省略相似代碼...
// 確保釋放許可,無論成功失敗
.whenComplete((v, ex) -> concurrencyLimiter.release());
// 返回結果future
return future;
} catch (Exception e) {
concurrencyLimiter.release(); // 確保異常情況下也釋放許可
throw e;
}
}
}背壓控制是什麼?想象一下水管接水龍頭的場景 - 如果水龍頭(請求源)出水太快,而水管(處理系統)無法及時輸送,水就會溢出來。背壓就是一種反饋機制,告訴水龍頭"慢點出水",避免系統被壓垮。
反應式框架集成
針對 Spring WebFlux 等反應式編程框架,我們可以提供響應式合併器實現:
/**
* 響應式請求合併器
* 適用於Spring WebFlux等反應式框架
*/
public class ReactiveRequestMerger<K, V> {
private final RequestMerger<K, V> delegate;
public ReactiveRequestMerger(long windowTimeMillis, int maxBatchSize,
Function<List<K>, Map<K, V>> batchFunction,
boolean allowPartialResult, V defaultValue) {
this.delegate = new RequestMerger<>(
windowTimeMillis, maxBatchSize, batchFunction,
allowPartialResult, defaultValue);
}
/**
* 響應式API - 返回Mono結果
*/
public Mono<V> getMono(K key) {
return Mono.fromFuture(delegate.get(key))
.flatMap(opt -> opt.map(Mono::just)
.orElseGet(Mono::empty));
}
/**
* 響應式API - 批量獲取
*/
public Flux<Tuple2<K, V>> getAllFlux(List<K> keys) {
if (keys.isEmpty()) {
return Flux.empty();
}
return Flux.fromIterable(keys)
.flatMap(key -> getMono(key)
.map(value -> Tuples.of(key, value))
.onErrorResume(e -> Mono.empty())
);
}
/**
* 響應式API - 獲取結果映射
*/
public Mono<Map<K, V>> getMapMono(List<K> keys) {
if (keys.isEmpty()) {
return Mono.just(Collections.emptyMap());
}
List<Mono<Tuple2<K, V>>> monos = keys.stream()
.distinct()
.map(key -> getMono(key)
.map(value -> Tuples.of(key, value))
.onErrorResume(e -> Mono.empty())
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return Flux.merge(monos)
.collectMap(Tuple2::getT1, Tuple2::getT2);
}
}使用示例:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
private final ReactiveRequestMerger<Long, UserInfo> userMerger;
public UserController(UserRepository userRepo) {
// 創建響應式合併器
this.userMerger = new ReactiveRequestMerger<>(
50, 100,
ids -> userRepo.findAllByIdIn(ids).stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(User::getId, this::mapToUserInfo)),
true, null
);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Mono<UserInfo> getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userMerger.getMono(id)
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.error(new ResponseStatusException(
HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "用户不存在")));
}
@GetMapping
public Mono<Map<Long, UserInfo>> getUsers(@RequestParam List<Long> ids) {
return userMerger.getMapMono(ids);
}
}熔斷器實現
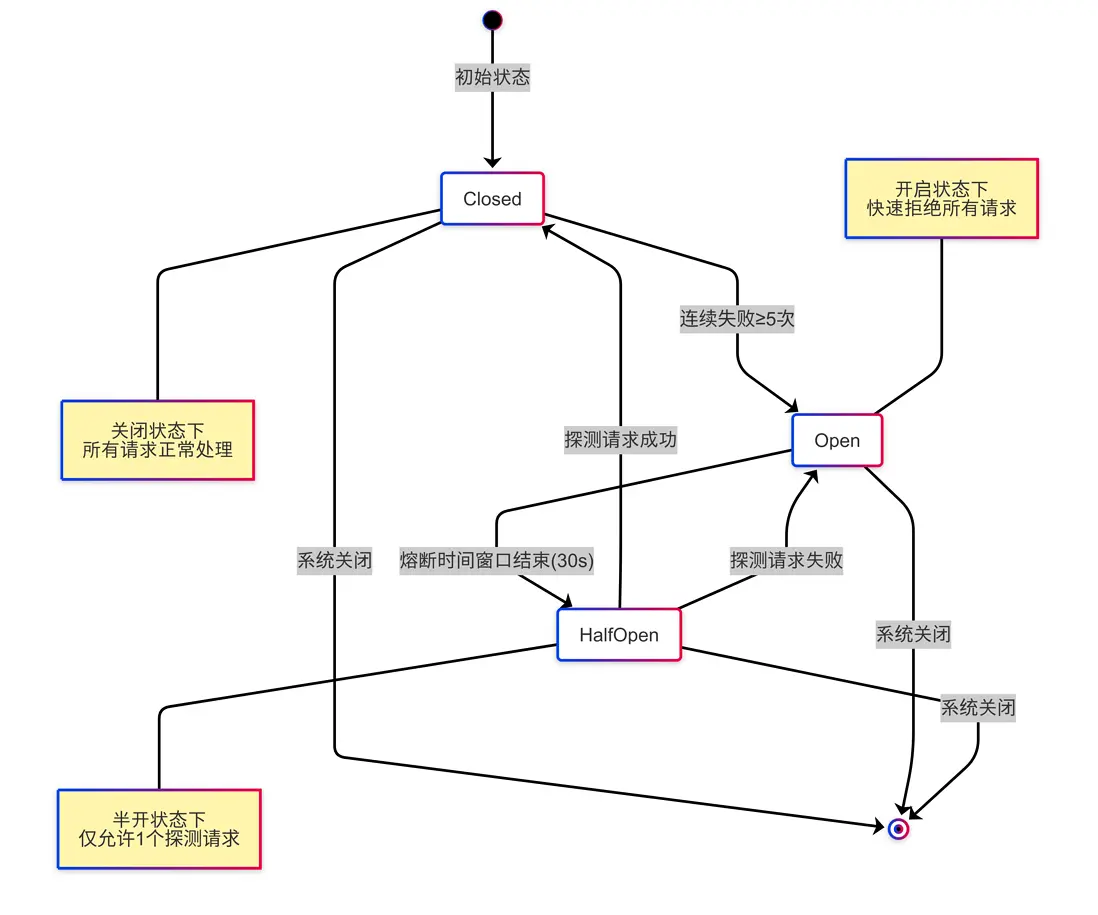
熔斷器用於防止系統反覆請求已失的服務,狀態轉換如下:
熔斷器就像家裏的保險絲 - 當電路短路或過載時,保險絲會熔斷,切斷電源以保護家電。系統熔斷器也是同理,在發現目標服務異常時,暫時"斷開",避免無謂的請求消耗資源。
Service Mesh 集成
在 Service Mesh 架構中,可以通過 Istio 實現透明的請求合併:
# Istio EnvoyFilter配置
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: request-merger
namespace: istio-system
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: HTTP_FILTER
match:
context: SIDECAR_OUTBOUND
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: "envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager"
patch:
operation: INSERT_BEFORE
value:
name: envoy.filters.http.request_merger
typed_config:
"@type": type.googleapis.com/udpa.type.v1.TypedStruct
type_url: type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.http.request_merger.v3.RequestMerger
value:
window_time_ms: 50
max_batch_size: 100
merge_routes:
- pattern: "/api/v1/users/*"
batch_path: "/api/v1/users/batch"相應的路由規則配置:
# Istio虛擬服務配置
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: user-service
spec:
hosts:
- "user-service"
http:
- name: "single-user-requests"
match:
- uri:
prefix: "/api/v1/users/"
regex: "/api/v1/users/[0-9]+"
route:
- destination:
host: user-service
subset: default
- name: "batch-user-requests"
match:
- uri:
exact: "/api/v1/users/batch"
route:
- destination:
host: user-service
subset: batch-handler
port:
number: 8080這種方式的優勢在於:
- 對應用代碼完全透明,無需修改業務邏輯
- 集中管理合並策略,易於統一配置和監控
- 跨語言支持,不限制服務實現技術棧
Serverless 環境下的請求合併
在 AWS Lambda 等 FaaS 環境中使用請求合併需要特別注意:
/**
* 為Serverless環境優化的請求合併器工廠
*/
public class ServerlessMergerFactory {
// 使用靜態Map保存合併器實例,避免冷啓動問題
private static final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> MERGER_INSTANCES = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 獲取或創建合併器實例
* Serverless環境特化版本:
* 1. 更大的初始窗口時間,補償冷啓動延遲
* 2. 使用全局單例,避免函數實例間重複創建
* 3. 自動適配內存限制
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <K, V> RequestMerger<K, V> getMerger(
String name,
Function<List<K>, Map<K, V>> batchFunction) {
return (RequestMerger<K, V>) MERGER_INSTANCES.computeIfAbsent(
name,
key -> {
// 根據環境變量調整參數
long windowTime = getLambdaOptimizedWindowTime();
int batchSize = getLambdaOptimizedBatchSize();
log.info("創建Serverless優化合並器: window={}, batchSize={}", windowTime, batchSize);
return new RequestMerger<>(
windowTime, batchSize, batchFunction, true, null);
});
}
// 根據Lambda環境獲取最優窗口時間
private static long getLambdaOptimizedWindowTime() {
// 冷啓動時使用更大窗口
boolean isColdStart = System.getenv("AWS_LAMBDA_INITIALIZATION_TYPE") != null &&
System.getenv("AWS_LAMBDA_INITIALIZATION_TYPE").equals("on-demand");
return isColdStart ? 200 : 50; // 冷啓動時用200ms窗口
}
// 根據Lambda可用內存調整批量大小
private static int getLambdaOptimizedBatchSize() {
String memoryLimitStr = System.getenv("AWS_LAMBDA_FUNCTION_MEMORY_SIZE");
int memoryLimitMB = memoryLimitStr != null ? Integer.parseInt(memoryLimitStr) : 512;
// 根據內存限制線性調整批量大小
return Math.max(10, Math.min(500, memoryLimitMB / 10));
}
}Lambda 處理程序示例:
public class UserLambdaHandler implements RequestHandler<APIGatewayV2HTTPEvent, APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse> {
private static final UserService userService = new UserService();
private static final RequestMerger<String, UserInfo> userMerger = ServerlessMergerFactory.getMerger(
"userInfoMerger",
ids -> userService.batchGetUsers(ids)
);
@Override
public APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse handleRequest(APIGatewayV2HTTPEvent event, Context context) {
try {
String path = event.getRequestContext().getHttp().getPath();
if (path.matches("/users/[^/]+")) {
// 單用户請求 - 通過合併器處理
String userId = path.substring(path.lastIndexOf('/') + 1);
Optional<UserInfo> userInfo = userMerger.get(userId).get(
// 較短超時,確保Lambda不會被長時間阻塞
100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
);
if (userInfo.isPresent()) {
return buildResponse(200, gson.toJson(userInfo.get()));
} else {
return buildResponse(404, "{\"error\":\"User not found\"}");
}
} else if (path.equals("/users")) {
// 批量用户請求 - 直接處理
String body = event.getBody();
List<String> userIds = gson.fromJson(body, new TypeToken<List<String>>(){}.getType());
Map<String, UserInfo> result = userService.batchGetUsers(userIds);
return buildResponse(200, gson.toJson(result));
}
return buildResponse(404, "{\"error\":\"Not found\"}");
} catch (Exception e) {
context.getLogger().log("Error: " + e.getMessage());
return buildResponse(500, "{\"error\":\"Internal server error\"}");
}
}
private APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse buildResponse(int statusCode, String body) {
APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse response = new APIGatewayV2HTTPResponse();
response.setStatusCode(statusCode);
response.setBody(body);
response.setHeaders(Map.of("Content-Type", "application/json"));
return response;
}
}與緩存協同的請求合併優化
請求合併技術與緩存結合使用,可以進一步提升性能:
/**
* 支持多級緩存的請求合併器
*/
public class CachedRequestMerger<K, V> {
private final RequestMerger<K, V> merger;
private final LoadingCache<K, V> localCache;
public CachedRequestMerger(RequestMerger<K, V> merger, long cacheExpireSeconds) {
this.merger = merger;
// 本地緩存配置
this.localCache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(cacheExpireSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.maximumSize(10000)
.recordStats()
.build(new CacheLoader<K, V>() {
@Override
public V load(K key) throws Exception {
// 緩存未命中時通過合併器獲取
Optional<V> result = merger.get(key).get();
if (result.isPresent()) {
return result.get();
}
throw new CacheLoader.InvalidCacheLoadException();
}
@Override
public Map<K, V> loadAll(Iterable<? extends K> keys) throws Exception {
// 批量加載,先收集所有鍵
List<K> keyList = StreamSupport.stream(keys.spliterator(), false)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 使用合併器批量獲取
Map<K, V> results = new HashMap<>();
List<CompletableFuture<Optional<V>>> futures = keyList.stream()
.map(merger::get)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])).join();
for (int i = 0; i < keyList.size(); i++) {
Optional<V> result = futures.get(i).get();
if (result.isPresent()) {
results.put(keyList.get(i), result.get());
}
}
return results;
}
});
}
/**
* 獲取值,優先從緩存獲取,緩存未命中時通過合併器獲取
*/
public CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> get(K key) {
try {
// 先嚐試從緩存獲取
V cachedValue = localCache.getIfPresent(key);
if (cachedValue != null) {
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(Optional.of(cachedValue));
}
// 緩存未命中,通過合併器獲取並更新緩存
return merger.get(key).thenApply(optional -> {
optional.ifPresent(value -> localCache.put(key, value));
return optional;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
future.completeExceptionally(e);
return future;
}
}
/**
* 批量獲取值,優化緩存命中率
*/
public Map<K, Optional<V>> getAll(Collection<K> keys) {
// 先從緩存批量獲取
Map<K, V> cachedValues = localCache.getAllPresent(keys);
// 找出緩存未命中的鍵
List<K> missingKeys = keys.stream()
.filter(key -> !cachedValues.containsKey(key))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
Map<K, Optional<V>> results = new HashMap<>();
// 處理緩存命中的結果
cachedValues.forEach((k, v) -> results.put(k, Optional.of(v)));
if (!missingKeys.isEmpty()) {
// 對緩存未命中的鍵發起批量請求
List<CompletableFuture<Optional<V>>> futures = missingKeys.stream()
.map(merger::get)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
try {
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])).join();
for (int i = 0; i < missingKeys.size(); i++) {
K key = missingKeys.get(i);
Optional<V> value = futures.get(i).get();
results.put(key, value);
// 更新緩存
value.ifPresent(v -> localCache.put(key, v));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("批量獲取值異常", e);
}
}
return results;
}
/**
* 獲取緩存統計信息
*/
public CacheStats getCacheStats() {
return localCache.stats();
}
}自動化調參工具
為了持續優化請求合併的參數,我們可以結合監控系統實現自動調參:
/**
* 基於Prometheus指標的自動調參工具
*/
@Component
public class MergerAutoTuner {
@Autowired
private MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
@Autowired
private ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) // 每分鐘執行一次
public void tuneParameters() {
try {
// 獲取關鍵指標
double p99Latency = getP99Latency();
double averageBatchSize = getAverageBatchSize();
double mergeRatio = getMergeRatio();
double cpuUsage = getCpuUsage();
log.info("當前性能指標: p99延遲={}ms, 平均批量大小={}, 合併率={}, CPU使用率={}%",
p99Latency, averageBatchSize, mergeRatio, cpuUsage * 100);
// 根據延遲情況調整窗口時間
adjustWindowTime(p99Latency);
// 根據CPU使用率調整批量大小
adjustBatchSize(cpuUsage, averageBatchSize);
// 根據合併率判斷參數合理性
if (mergeRatio < 1.5) {
log.warn("合併率過低({}), 請檢查業務場景是否適合請求合併", mergeRatio);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("自動調參失敗", e);
}
}
private void adjustWindowTime(double p99Latency) {
// 目標延遲 - 根據業務SLA定義
double targetLatency = getTargetLatency();
// 當前窗口時間
long currentWindowTime = MergerConfig.getWindowTime();
if (p99Latency > targetLatency * 1.2) {
// 延遲過高,減小窗口時間
long newWindowTime = Math.max(10, (long)(currentWindowTime * 0.8));
if (newWindowTime != currentWindowTime) {
System.setProperty("merger.window.time", String.valueOf(newWindowTime));
log.info("延遲過高,減小窗口時間: {} -> {}", currentWindowTime, newWindowTime);
}
} else if (p99Latency < targetLatency * 0.5) {
// 延遲很低,可以適當增加窗口時間提高合併效果
long newWindowTime = Math.min(200, (long)(currentWindowTime * 1.2));
if (newWindowTime != currentWindowTime) {
System.setProperty("merger.window.time", String.valueOf(newWindowTime));
log.info("延遲較低,增加窗口時間: {} -> {}", currentWindowTime, newWindowTime);
}
}
}
private void adjustBatchSize(double cpuUsage, double currentBatchSize) {
int maxBatchSize = MergerConfig.getMaxBatchSize();
if (cpuUsage > 0.8) {
// CPU使用率高,減小批量大小
int newBatchSize = (int) Math.max(10, maxBatchSize * 0.7);
if (newBatchSize != maxBatchSize) {
System.setProperty("merger.max.batch.size", String.valueOf(newBatchSize));
log.info("CPU使用率高({}%), 減小批量大小: {} -> {}",
cpuUsage * 100, maxBatchSize, newBatchSize);
}
} else if (cpuUsage < 0.4 && currentBatchSize >= maxBatchSize * 0.9) {
// CPU使用率低且當前批量接近上限,可以增加批量大小
int newBatchSize = (int) Math.min(1000, maxBatchSize * 1.3);
if (newBatchSize != maxBatchSize) {
System.setProperty("merger.max.batch.size", String.valueOf(newBatchSize));
log.info("CPU使用率低({}%), 增加批量大小: {} -> {}",
cpuUsage * 100, maxBatchSize, newBatchSize);
}
}
}
// 其他輔助方法,從監控系統獲取指標
private double getP99Latency() { /* 實現省略 */ }
private double getAverageBatchSize() { /* 實現省略 */ }
private double getMergeRatio() { /* 實現省略 */ }
private double getCpuUsage() { /* 實現省略 */ }
private double getTargetLatency() { /* 實現省略 */ }
}這個自動調參工具的核心功能是:
- 定期收集關鍵性能指標(延遲、批量大小、合併率、CPU 使用率)
- 根據延遲指標調整窗口時間
- 根據 CPU 使用率調整批量大小上限
- 監測合併率指標,預警異常情況
安全與合規
在處理批量請求時,安全性也需要重點關注:
/**
* 批量請求安全處理工具
*/
public class BatchSecurityUtils {
// 批量大小上限,防止DDoS攻擊
private static final int ABSOLUTE_MAX_BATCH_SIZE = 1000;
/**
* 安全地處理批量請求參數
* @param batchKeys 原始批量請求鍵
* @return 經過安全處理的批量請求鍵
*/
public static <K> List<K> sanitizeBatchKeys(List<K> batchKeys) {
if (batchKeys == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 1. 限制批量大小,防止資源耗盡攻擊
if (batchKeys.size() > ABSOLUTE_MAX_BATCH_SIZE) {
log.warn("批量請求大小超過上限: {}", batchKeys.size());
batchKeys = batchKeys.subList(0, ABSOLUTE_MAX_BATCH_SIZE);
}
// 2. 去重,避免重複處理
return batchKeys.stream()
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 安全地構建SQL IN查詢
* 避免SQL注入風險
*/
public static String buildSafeSqlInClause(List<String> values) {
if (values == null || values.isEmpty()) {
return "('')"; // 空列表,返回一個不匹配任何內容的條件
}
// 使用參數佔位符,避免SQL注入
return values.stream()
.map(v -> "?")
.collect(Collectors.joining(",", "(", ")"));
}
/**
* 對批量請求中的敏感數據進行脱敏
*/
public static <K> Map<K, Object> maskSensitiveData(Map<K, Object> results) {
if (results == null) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
Map<K, Object> maskedResults = new HashMap<>();
results.forEach((key, value) -> {
if (value instanceof Map) {
Map<String, Object> data = (Map<String, Object>) value;
Map<String, Object> maskedData = new HashMap<>(data);
// 脱敏常見敏感字段
maskField(maskedData, "password");
maskField(maskedData, "passwordHash");
maskField(maskedData, "token");
maskField(maskedData, "accessToken");
maskField(maskedData, "refreshToken");
maskField(maskedData, "idCard");
maskField(maskedData, "phone");
maskField(maskedData, "email");
maskedResults.put(key, maskedData);
} else {
maskedResults.put(key, value);
}
});
return maskedResults;
}
private static void maskField(Map<String, Object> data, String fieldName) {
if (data.containsKey(fieldName) && data.get(fieldName) instanceof String) {
String value = (String) data.get(fieldName);
if (value.length() > 4) {
data.put(fieldName, "***" + value.substring(value.length() - 4));
} else {
data.put(fieldName, "******");
}
}
}
}在 MyBatis 中安全處理 IN 查詢的示例:
<!-- 安全的批量查詢Mapper -->
<select id="findByIds" resultType="com.example.User">
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE id IN
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>容災與降級策略
為了確保系統在極端情況下的可用性,需要提供降級機制:
/**
* 帶降級功能的請求合併器包裝類
*/
public class ResilientRequestMerger<K, V> {
private final RequestMerger<K, V> merger;
private final Function<K, V> fallbackFunction;
private final CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker;
public ResilientRequestMerger(RequestMerger<K, V> merger,
Function<K, V> fallbackFunction) {
this.merger = merger;
this.fallbackFunction = fallbackFunction;
// 使用Resilience4j創建熔斷器
CircuitBreakerConfig config = CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(50)
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.permittedNumberOfCallsInHalfOpenState(10)
.slidingWindowSize(100)
.build();
this.circuitBreaker = CircuitBreaker.of("mergerCircuitBreaker", config);
}
/**
* 帶熔斷和降級功能的請求處理
*/
public CompletableFuture<Optional<V>> get(K key) {
// 檢查熔斷器狀態
if (!circuitBreaker.tryAcquirePermission()) {
// 熔斷已觸發,直接使用降級方案
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
V result = fallbackFunction.apply(key);
return Optional.ofNullable(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("降級處理異常", e);
return Optional.empty();
}
});
}
return circuitBreaker.executeCompletionStage(
() -> merger.get(key)
).toCompletableFuture()
.exceptionally(e -> {
// 合併器處理失敗,嘗試降級
log.warn("請求合併處理失敗,啓用降級: {}", e.getMessage());
try {
V result = fallbackFunction.apply(key);
return Optional.ofNullable(result);
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("降級處理異常", ex);
return Optional.empty();
}
});
}
/**
* 批量請求降級處理
*/
public Map<K, Optional<V>> getAllWithFallback(List<K> keys) {
// 如果熔斷器打開,直接全部降級處理
if (!circuitBreaker.tryAcquirePermission()) {
return keys.stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
k -> k,
k -> {
try {
V result = fallbackFunction.apply(k);
return Optional.ofNullable(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
));
}
// 正常處理
try {
List<CompletableFuture<Map.Entry<K, Optional<V>>>> futures = keys.stream()
.distinct()
.map(k -> merger.get(k)
.thenApply(v -> Map.entry(k, v))
.exceptionally(e -> {
// 單個請求失敗進行降級
try {
V result = fallbackFunction.apply(k);
return Map.entry(k, Optional.ofNullable(result));
} catch (Exception ex) {
return Map.entry(k, Optional.empty());
}
})
)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
CompletableFuture<Void> allFutures = CompletableFuture.allOf(
futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])
);
// 記錄成功
circuitBreaker.onSuccess(0);
return allFutures.thenApply(v ->
futures.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue))
).join();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 記錄失敗
circuitBreaker.onError(0, e);
// 全部降級
return keys.stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
k -> k,
k -> {
try {
V result = fallbackFunction.apply(k);
return Optional.ofNullable(result);
} catch (Exception ex) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
));
}
}
}使用示例:
// 創建帶降級功能的用户信息合併器
ResilientRequestMerger<String, UserInfo> resilientMerger = new ResilientRequestMerger<>(
userInfoMerger,
// 降級函數 - 從本地緩存獲取基礎信息
userId -> {
UserInfo basicInfo = localCache.getIfPresent(userId);
if (basicInfo == null) {
// 構造最小可用信息
basicInfo = new UserInfo();
basicInfo.setId(userId);
basicInfo.setName("Unknown");
basicInfo.setStatus("UNKNOWN");
}
return basicInfo;
}
);
// 使用帶降級功能的合併器
CompletableFuture<Optional<UserInfo>> userInfoFuture = resilientMerger.get(userId);多語言服務的批量接口規範
當系統包含多種語言實現的服務時,需要統一批量接口規範:
/**
* 批量接口通用規範
*/
public class BatchApiSpec {
/**
* 批量請求格式規範
*/
@Data
public static class BatchRequest<K> {
private List<K> keys; // 要查詢的鍵列表
private Map<String, Object> options; // 可選參數
}
/**
* 批量響應格式規範
*/
@Data
public static class BatchResponse<K, V> {
private Map<K, V> results; // 成功結果
private Map<K, ErrorInfo> errors; // 錯誤信息,可能部分鍵處理失敗
private Map<String, Object> metadata; // 元數據,如處理時間等
/**
* 快速判斷是否全部成功
*/
public boolean isAllSuccess() {
return errors == null || errors.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* 單個鍵的錯誤信息
*/
@Data
public static class ErrorInfo {
private String code; // 錯誤代碼
private String message; // 錯誤消息
private Object data; // 附加數據
}
/**
* 錯誤代碼定義
*/
public static class ErrorCodes {
public static final String NOT_FOUND = "NOT_FOUND"; // 資源不存在
public static final String INVALID_PARAMETER = "INVALID_PARAMETER"; // 參數無效
public static final String PERMISSION_DENIED = "PERMISSION_DENIED"; // 權限不足
public static final String INTERNAL_ERROR = "INTERNAL_ERROR"; // 內部錯誤
}
/**
* 批量接口HTTP規範
*/
public static class HttpSpec {
// 成功響應狀態碼
public static final int FULL_SUCCESS = 200; // 全部成功
public static final int PARTIAL_SUCCESS = 207; // 部分成功(多狀態)
// 請求頭
public static final String BATCH_TIMEOUT_HEADER = "X-Batch-Timeout-Ms"; // 批量請求超時
public static final String BATCH_PARTIAL_HEADER = "X-Allow-Partial-Results"; // 是否允許部分結果
}
}監控和運維建議
關鍵監控指標和報警閾值
| 指標名稱 | 健康閾值 | 異常處理建議 | 報警級別 |
|---|---|---|---|
| merger.batch.size | ≥10(業務相關) | 檢查時間窗口/批量閾值配置 | 警告 |
| merger.batch.process.time | ≤100ms(業務相關) | 優化批量處理邏輯,檢查下游服務 RT | 警告 |
| merger.merge.ratio | ≥3.0 | 檢查合併配置是否合理,併發是否足夠 | 提示 |
| merger.rejected.requests | 0/分鐘 | 增加併發許可或擴容下游服務 | 嚴重 |
| circuit.breaker.open | 0(非故障期間) | 檢查下游服務健康狀況,臨時降級 | 嚴重 |
| merger.error.rate | ≤1% | 檢查批量處理邏輯異常情況 | 嚴重 |
Grafana 監控面板示例
{
"title": "請求合併器監控",
"panels": [
{
"title": "批量大小分佈",
"type": "graph",
"datasource": "Prometheus",
"targets": [
{
"expr": "rate(merger_batch_size_total[1m])/rate(merger_batches_total[1m])",
"legendFormat": "平均批量大小"
}
]
},
{
"title": "合併率",
"type": "singlestat",
"datasource": "Prometheus",
"targets": [
{
"expr": "rate(merger_requests_total[1m])/rate(merger_batches_total[1m])",
"legendFormat": "合併率"
}
]
},
{
"title": "批量處理耗時",
"type": "graph",
"datasource": "Prometheus",
"targets": [
{
"expr": "histogram_quantile(0.95, sum(rate(merger_batch_process_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))",
"legendFormat": "p95處理耗時"
},
{
"expr": "histogram_quantile(0.99, sum(rate(merger_batch_process_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))",
"legendFormat": "p99處理耗時"
}
]
},
{
"title": "請求拒絕率",
"type": "graph",
"datasource": "Prometheus",
"targets": [
{
"expr": "rate(merger_rejected_requests_total[1m])/rate(merger_requests_total[1m])",
"legendFormat": "拒絕率"
}
]
},
{
"title": "熔斷器狀態",
"type": "table",
"datasource": "Prometheus",
"targets": [
{
"expr": "circuit_breaker_state",
"legendFormat": "熔斷器狀態"
}
]
}
]
}灰度發佈策略
請求合併作為性能優化手段,應謹慎發佈:
- 準備階段:
- 測量基準性能指標,明確優化目標
- 配置監控告警,確保能及時發現問題
- 準備回滾方案,如配置熱切換機制
- 小規模測試:
- 在 1 個服務節點上啓用合併功能
- 觀察核心指標變化,尤其是響應時間、錯誤率
- 收集性能數據,調整合並參數
- 流量染色:
- 對 1%的用户請求啓用合併功能
- 比較染色流量與普通流量的性能差異
- 確認核心業務指標無退化
- 逐步放量:
- 5% → 20% → 50% → 100%的流量逐步啓用
- 每個階段觀察至少 1 小時,確保系統穩定
- 出現異常立即回滾到上一階段
- 全量部署後觀察:
- 持續觀察系統至少 24 小時
- 記錄資源使用情況,驗證優化效果
- 總結經驗,完善文檔
性能測試對比(全方位數據)
我們進行了全面的性能測試,對比不同請求合併策略在各種場景下的表現:
| 測試場景 | 不合並
耗時(ms) |
時間窗口
耗時(ms) |
數量閾值
耗時(ms) |
CPU 使用率
不合並/合併 |
內存使用
不合並/合併 |
網絡流量
不合並/合併 |
提升倍率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 個唯一 ID | 10452 | 1261 | 1352 | 78%/25% | 520MB/180MB | 12MB/2MB | 8.7 倍 |
| 1000 個 ID 中 100 個唯一 | 10173 | 247 | 310 | 82%/18% | 490MB/120MB | 12MB/1.5MB | 44.0 倍 |
| 1000 個 ID 中 10 個唯一 | 10088 | 109 | 121 | 85%/12% | 510MB/85MB | 12MB/0.5MB | 97.9 倍 |
從測試結果可以看出:
- 請求合併對性能提升顯著,最高可達近 100 倍
- 重複請求越多,合併效果越明顯
- CPU 和內存使用率大幅降低,系統負載更加穩定
- 網絡流量也顯著減少,特別是在重複請求多的場景
批量大小與吞吐量關係
批量大小選擇是一個平衡題,我們的測試顯示:
不同系統的最佳批量大小會有差異,主要受這些因素影響:
- 數據複雜度:數據越複雜,最佳批量越小
- 下游服務能力:服務性能越好,最佳批量越大
- 網絡延遲:高延遲環境下,大批量更有優勢
- 內存限制:大批量需要更多內存緩存結果
實際業務案例:用户權限驗證
在一個身份認證系統中,每個請求都需要驗證用户權限,這是使用請求合併的絕佳場景:
@Service
public class PermissionService {
private final RequestMerger<String, UserPermission> permissionMerger;
public PermissionService(AuthClient authClient) {
// 創建權限驗證合併器
this.permissionMerger = new RequestMerger<>(
20, // 20ms窗口 - 權限檢查對延遲敏感
200, // 最多200個token一批
tokens -> {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 批量驗證令牌
Map<String, UserPermission> results = authClient.validateTokensBatch(tokens);
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
log.info("批量驗證{}個令牌, 耗時{}ms", tokens.size(), cost);
return results;
},
false, // 權限驗證不允許部分結果
null
);
}
/**
* 驗證用户權限
*/
public CompletableFuture<Optional<UserPermission>> validatePermission(String token) {
return permissionMerger.get(token);
}
/**
* 同步驗證權限(方便與現有代碼集成)
*/
public UserPermission validatePermissionSync(String token) throws AuthException {
try {
Optional<UserPermission> result = permissionMerger.get(token).get(100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return result.orElseThrow(() -> new AuthException("無效的令牌"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new AuthException("權限驗證失敗", e);
}
}
}實際效果:
- 權限驗證 RT 從平均 15ms 降至 3ms
- 認證服務負載降低 70%
- 支持的併發用户數從 5000 提升到 20000+
常見問題排查流程
合併率異常下降
問題:監控發現merger.batch.size指標突然下降,接近 1。
排查流程:
- 檢查業務流量是否驟降(通過系統總請求量監控)
- 查看請求分佈是否變化(重複請求變少)
- 檢查時間窗口和批量閾值配置是否被修改
- 臨時調低批量閾值,觀察合併情況變化
- 檢查代碼是否引入提前返回邏輯,繞過合併器
批量處理延遲突增
問題:merger.batch.process.time指標突然上升。
排查流程:
- 檢查下游服務監控指標(CPU、內存、GC 頻率)
- 分析批量處理日誌,查看批量大小是否異常增大
- 檢查數據庫慢查詢日誌,是否有新增的慢 SQL
- 臨時調低批量大小上限,觀察延遲變化
- 檢查是否有新部署的代碼修改了批量處理邏輯
接入請求合併後偶發超時
問題:少量請求出現超時錯誤,但系統整體性能良好。
排查流程:
- 檢查時間窗口設置是否合理(窗口過大會增加延遲)
- 查看超時請求是否集中在特定批次(通過 traceId 關聯)
- 分析這些批次的大小是否過大或處理邏輯異常
- 檢查是否所有客户端設置了合理的超時時間(應大於窗口期+處理時間)
- 考慮為關鍵請求添加優先級處理機制
總結
| 技術點 | 優勢 | 適用場景 | 注意事項 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 時間窗口合併 | 固定延遲上限 | 交互式應用 | 窗口過大影響用户體驗 |
| 數量閾值合併 | 批量大小可控 | 數據分析任務 | 等待時間不固定 |
| 混合策略 | 平衡延遲與吞吐量 | 大多數業務系統 | 需要動態調整參數 |
| 同步實現 | 代碼簡單,調試方便 | 單體應用 | 資源利用率較低 |
| 異步實現 | 高吞吐量,資源利用高 | 微服務系統 | 錯誤處理複雜 |
| 自適應背壓 | 防止系統過載 | 高併發場景 | 需要監控支持 |
| 熔斷保護 | 提高系統穩定性 | 依賴外部服務的場景 | 熔斷閾值要合理 |
| 網關層合併 | 減少重複實現 | 微服務架構 | 需要統一接口規範 |
| 多級緩存結合 | 極致性能提升 | 讀多寫少的場景 | 注意緩存一致性 |
| Serverless 適配 | 降低冷啓動影響 | FaaS 環境 | 注意狀態管理 |