目錄
- 開始測試
-
尋根
- TCP half-open
- keepalive
- 重傳 timeout
- Zero window timeout
-
應用 socket 層的 timeout 設置
- TCP_USER_TIMEOUT
- SO_RCVTIMEO / SO_SNDTIMEO
- poll timeout
- 尋根總結
- 較真有什麼用
-
空閒連接的 keepalive 檢查
- 作為 upstream(服務端) 時
- 作為 downstream(客户端) 時
- TCP_USER_TIMEOUT
-
Envoy 應用層健康檢測
- 健康檢測與連接池
- 健康檢測與 endpoint 發現
- 主動健康檢測: Health checking
- 被動健康檢測: Outlier detection
- 健康檢測與 EDS,聽誰的?
-
Envoy 應用層的超時
- Envoy 應用層的連接級超時
-
Envoy 應用層的請求級超時
- 對 downstream(client) 的請求讀超時
- 對 upstream(server) 的響應等待超時
- 談超時,別忘記 retry 影響
- 思考
- 一點總結
- 主要參考
如果圖片不清,請轉到原文
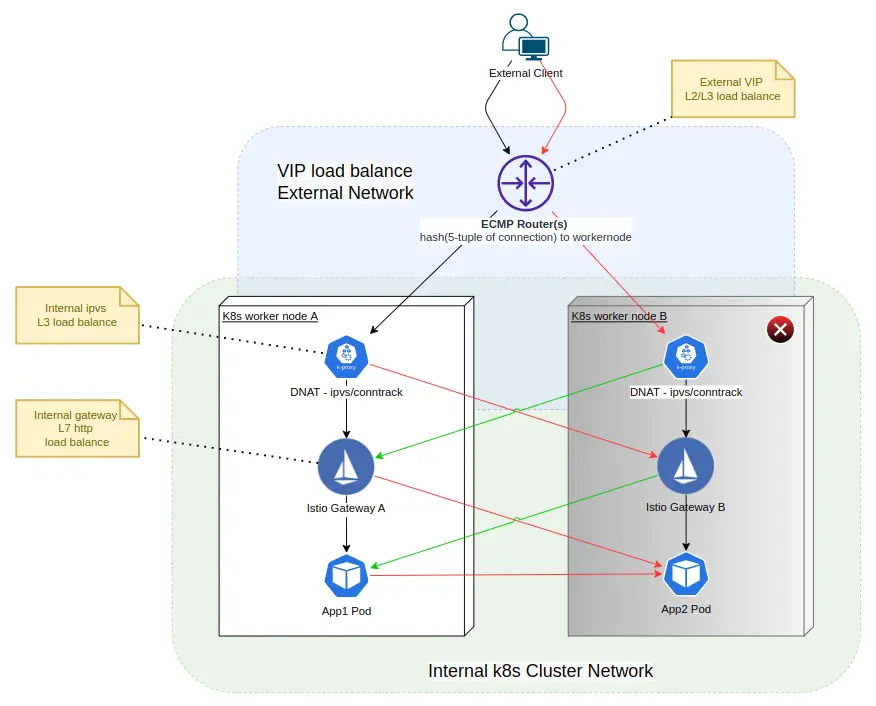
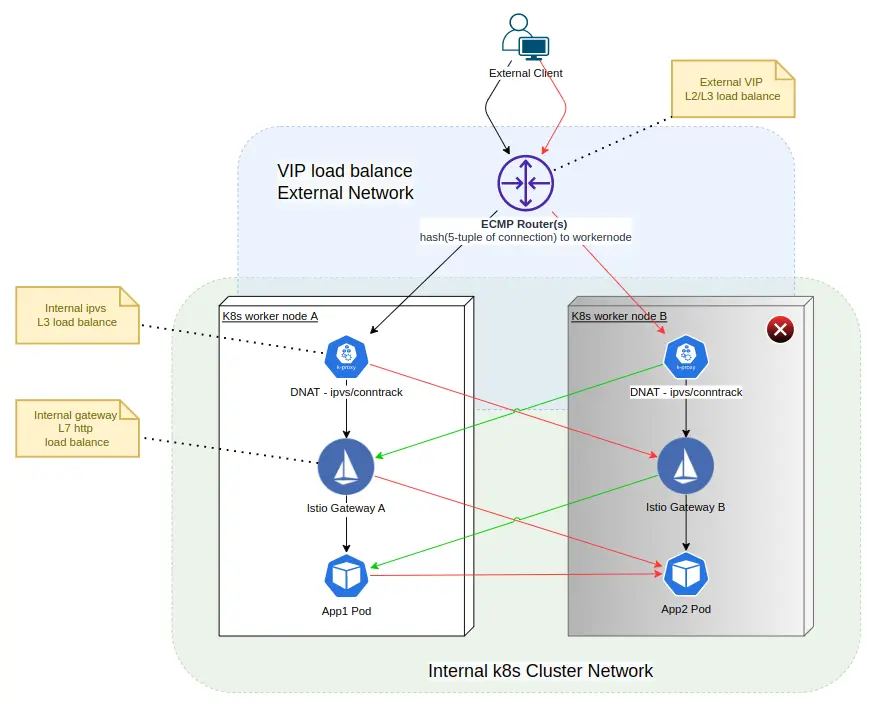
最近,需要對 k8s cluster + VIP load balance + Istio 的環境做一些 HA / Chaos Testing(混沌測試) 。如下圖,在此環境中,需要看看 worker node B 在非正常關機或網絡分區的情況下,對外部用户(Client) 的影響:
- 請求成功率影響
- 性能(TPS/Response Time)影響
上圖需要説明一下:
- 對外部的 VIP(虛擬IP) 的 TCP/IP 層負載均衡,是通過 ECMP(Equal-Cost Multi-Path) 的 Modulo-N 算法,分配負載,它本質上就是用 TCP 連接的 5 元組(協議、srcIP、srcPort、dstIP、dstPort)去分配外部流量了。注意,這種負載均衡算法是
無狀態的,在目標數量發生變化時,負載均衡算法的結果也會發生變化。即是不穩定算法。 - dstIP 為 VIP 的 TCP 流量,來到 woker node 後,再由 ipvs/conntrack 規則做有狀態的,DNAT,dstIP 被映射和轉換為任意一個 Istio Gateway POD 的地址。注意,這種負載均衡算法是
有狀態的,在目標數量發生變化時,原有連接的負載均衡結果不會發生變化。即算是穩定算法。 -
Istio Gateway POD 對 HTTP/TCP 流量也做了負載均衡。兩種協議的區別是:
- 對於 HTTP。同一 downstream(流量發出方) 的一個連接的多個請求,可能被負載均衡到不同的 upstream(流量目標)
- 對於 TCP。同一 downstream(流量發出方) 的一個連接的多個數據包,會被負載均衡到同一 upstream(流量目標)
開始測試
Chaos Testing 的方法是暴力關閉 worker node B 。如上圖,可以推斷出紅色與綠色線的連接,都會直接影響到。從客户端看到的影響是:
- 請求成功率只降低了 0.01%
- TPS 降低了 1/2,持續了半小時後,才恢復回來。
- Avg Response Time(平均響應時間) 基本不變
需要注意的是,單個 Worker Node 的各類資源不是這個測試的性能瓶頸。那麼,問題出現在什麼地方?
客户端是個 JMeter 程序,通過細看其產生的測試報告,發現 worker node 關閉後,Avg Response Time 是變化不大。但 P99 與 MAX 的 Response Time 變得異常地大。可見,Avg Response Time 這東西隱藏了很多東西,測試的線程,很可能是 Block(阻塞)在什麼地方了,才導致 TPS 下降。
經過一翻折騰,後來修改了外部客户端的 JMeter 的超時時間為 6s,問題解決。 worker node 關閉後, TPS 快速恢復。
尋根
外部客户端的問題解決了。就可以收工開飯了。但作為一個愛折騰的人,我想找尋其原因。更想知道,這個情況是真快速恢復了,還是暗藏也什麼隱患。
開始前先講一個概念:
TCP half-open
📖 TCP half-open
根據 RFC 793,當 TCP 連接一端的主機崩潰,或者在沒有通知另一端的情況下刪除了套接字時,TCP 連接被稱為
半打開。如果半打開端空閒(即無數據/keepalive發送),則連接可能會在無限時間段內保持半打開狀態。
在 worker node B 關閉後,從 外部客户端 的角度看,如上圖,其到 worker node B 的 TCP 連接可能處於兩種狀態:
-
client kernel 層由於發送(或重發) 數據、或閒置到達 keepalive 時間,需要發送數據包到對端。 worker node A 收到這個數據包,由於是不合法的 TCP,所以可能的情況是:
- 響應了 TCP RESET。client 收到後關閉了連接。client Block(阻塞)在 socket 的線程也因連接被關閉而返回,繼續運行且關閉 socket
- 由於 DNAT 映射表找不到相關的連接,數據包直接 drop 了,不響應。client Block在 socket 的線程繼續Block。即發生了
TCP half-open
- client 連接沒啓用 keepalive,或閒置未到達 keepalive 時間,內核層也無數據需要發送(或重發),client 線程 Block 在 socket read 等待,即發生了
TCP half-open
可以看到,對於 client 來説,在很大概率下,要發現一個連接已經失效了,均需要一定的時間。在最差的情況下,如沒啓動 keepalive,可能永遠發現不了 TCP half-open。
keepalive
來自 [TCP/IP Illustrated Volume 1]
keepalive 探測是一個空的(或 1 字節)
segment(段),其序列號比迄今為止從對端(peer)看到的最大ACK號小 1。 因為這個序列號已經被peer接收,peer再收到這個空segment不會有任何副作用,但它會引發一個peer返回一個ACK,用於確定peer是否存活。探測 probe segment及其ACK均不包含任何新數據。
探測 probe segment如果丟失,TCP 也不會重新傳輸。 [RFC1122] 規定,由於這一事實,單個keepalive探測收不到ACK不應被視為對端已死的充分證據。 需要多次間隔探測。
如果 socket 打開了 SO_KEEPALIVE ,那麼就是啓用了 keepalive。
對於啓用了 keepalive 的 TCP連接,Linux 有如下全局默認配置:
https://www.kernel.org/doc/ht...
-
tcp_keepalive_time - INTEGER
How often TCP sends out keepalive messages when keepalive is enabled. Default: 2 hours.
-
tcp_keepalive_probes - INTEGER
How many keepalive probes TCP sends out, until it decides that the connection is broken. Default value: 9.
-
tcp_keepalive_intvl - INTEGER
How frequently the probes are send out. Multiplied by tcp_keepalive_probes it is time to kill not responding connection, after probes started. Default value: 75 sec i.e. connection will be aborted after ~11 minutes of retries.
同時,Linux 也提供了為每個 socket 獨立指定的配置項:
https://man7.org/linux/man-pa...
TCP_KEEPCNT (since Linux 2.4)
The maximum number of keepalive probes TCP should send
before dropping the connection. This option should not be
used in code intended to be portable.
TCP_KEEPIDLE (since Linux 2.4)
The time (in seconds) the connection needs to remain idle
before TCP starts sending keepalive probes, if the socket
option SO_KEEPALIVE has been set on this socket. This
option should not be used in code intended to be portable.
TCP_KEEPINTVL (since Linux 2.4)
The time (in seconds) between individual keepalive probes.
This option sh可以計算,默認情況 下,一個連接的最快被 keepalive 關閉的時長:
TCP_KEEPIDLE + TCP_KEEPINTVL * TCP_KEEPCNT = 2*60*60 + 75*9 = 2小時 + 11分鐘重傳 timeout
https://www.kernel.org/doc/Do...
- tcp_retries2 - INTEGER
This value influences the timeout of an alive TCP connection, when RTO retransmissions remain unacknowledged. Given a value of N, a hypothetical TCP connection following exponential backoff with an initial RTO of TCP_RTO_MIN would retransmit N times before killing the connection at the (N+1)th RTO.The default value of 15 yields a hypothetical timeout of 924.6 seconds and is a lower bound for the effective timeout. TCP will effectively time out at the first RTO which exceeds the hypothetical timeout.RFC 1122 recommends at least 100 seconds for the timeout, which corresponds to a value of at least 8.上面配置項,配置重傳狀態下,要指數退讓多少次重傳,內核才關閉連接。默認的配置是 15。計算轉換成時間約是 924s,約 15 分鐘。
Zero window timeout
當對端通告其窗口大小為零時,這表明對端 TCP 接收緩衝區已滿,無法接收更多數據。它可能是由於對端資源緊張而數據處理太慢,最終導致 TCP 接收緩衝區被填滿。
理論上,對端在處理完接收窗口中堆積的數據後,會用 ACK 來通知窗口開放。但因各種原因,有時候,這個 ACK 會丟失。
所以,有數據未發出的發送方需要定期探測窗口大小。發送方會從未送達的緩存中,選擇頭一個字節數據發送作為探測包。當探測超過一定次數,對方不響應,或一直響應0窗口時,連接會自動關閉。Linux 中默認是 15 次。配置項是:tcp_retries2。它的探測重試機制和 TCP 重傳是類似的。
參考:https://blog.cloudflare.com/w...,Zero%20window,-ESTAB%20is...%20forever
應用 socket 層的 timeout 設置
TCP_USER_TIMEOUT
man tcp
TCP_USER_TIMEOUT (since Linux 2.6.37)
This option takes an unsigned int as an argument. When
the value is greater than 0, it specifies the maximum
amount of time in milliseconds that transmitted data may
remain unacknowledged, or bufferred data may remain
untransmitted (due to zero window size) before TCP will
forcibly close the corresponding connection and return
ETIMEDOUT to the application. If the option value is
specified as 0, TCP will use the system default.
Increasing user timeouts allows a TCP connection to
survive extended periods without end-to-end connectivity.
Decreasing user timeouts allows applications to "fail
fast", if so desired. Otherwise, failure may take up to
20 minutes with the current system defaults in a normal
WAN environment.
This option can be set during any state of a TCP
connection, but is effective only during the synchronized
states of a connection (ESTABLISHED, FIN-WAIT-1, FIN-
WAIT-2, CLOSE-WAIT, CLOSING, and LAST-ACK). Moreover,
when used with the TCP keepalive (SO_KEEPALIVE) option,
TCP_USER_TIMEOUT will override keepalive to determine when
to close a connection due to keepalive failure.
The option has no effect on when TCP retransmits a packet,
nor when a keepalive probe is sent.
This option, like many others, will be inherited by the
socket returned by accept(2), if it was set on the
listening socket.
Further details on the user timeout feature can be found
in RFC 793 and RFC 5482 ("TCP User Timeout Option").即,指定在發送得不到確認(收不到 ACK) ,或對端接收窗口為0 多久後,內核才關閉連接並返回錯誤給應用。
需要注意的是,TCP_USER_TIMEOUT 會影響 keepalive 的 TCP_KEEPCNT 配置效果:
https://blog.cloudflare.com/w...
With
TCP_USER_TIMEOUTset, theTCP_KEEPCNTis totally ignored. If you wantTCP_KEEPCNTto make sense, the only sensibleUSER_TIMEOUTvalue is slightly smaller than:TCP_USER_TIMEOUT < TCP_KEEPIDLE + TCP_KEEPINTVL * TCP_KEEPCNT
SO_RCVTIMEO / SO_SNDTIMEO
https://man7.org/linux/man-pa...
SO_RCVTIMEO and SO_SNDTIMEO
Specify the receiving or sending timeouts until reporting
an error. The argument is a struct timeval. If an input
or output function blocks for this period of time, and
data has been sent or received, the return value of that
function will be the amount of data transferred; if no
data has been transferred and the timeout has been
reached, then -1 is returned with errno set to EAGAIN or
EWOULDBLOCK, or EINPROGRESS (for connect(2)) just as if
the socket was specified to be nonblocking. If the
timeout is set to zero (the default), then the operation
will never timeout. Timeouts only have effect for system
calls that perform socket I/O (e.g., read(2), recvmsg(2),
send(2), sendmsg(2)); timeouts have no effect for
select(2), poll(2), epoll_wait(2), and so on.需要注意的是,本例中,我們的 client 是 JMeter,是 java 實現的,他用了 socket.setSoTimeout 方法來設置超時。根據:
https://stackoverflow.com/que...
和我看到的源碼,Linux 實現上應該是用了下一節説明的 select/poll 的 timeout 參數,而不是上面的 socket Options 。
https://github.com/openjdk/jd...
Java JMeter 在 catch 到 SocketTimeoutException 後,就主動 close 了 socket。並重連,所以死 socket 的問題是在應用層解決了。
poll timeout
https://man7.org/linux/man-pa...
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);尋根總結
參考:https://blog.cloudflare.com/w...
要保證連接在各種狀態下均可以比較快地檢測出超時的情況:
- 啓用
TCP keepalive,並配置合理的時間。 這是在空閒連接情況下保持一些數據流動所必需的。 - 將
TCP_USER_TIMEOUT設置為TCP_KEEPIDLE+TCP_KEEPINTVL*TCP_KEEPCNT。 - 在應用層用讀寫超時檢測,並在超時後應用主動關閉連接。(這是本文的情況)
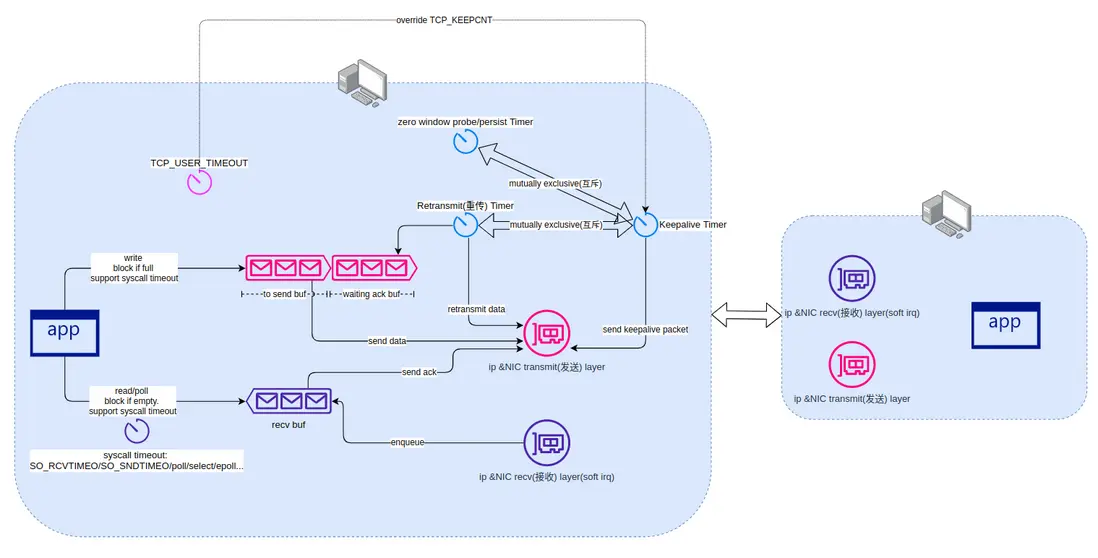
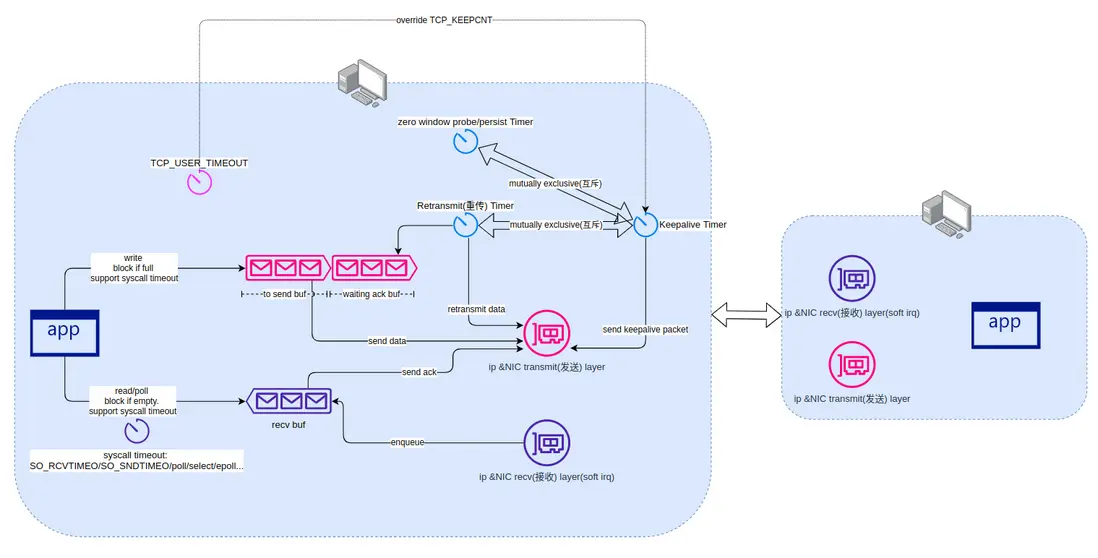
為何有 TCP keepalive 了,還要 TCP_USER_TIMEOUT ? 原因是如果發生網絡分區,重傳狀態下的連接,是不會觸發 keepalive 探測的。我將原理記錄到下圖:
較真有什麼用
🤔 ❓ 説到這裏,有同學會問,説到底,這次,你就是調整了個應用層的讀超時就行了。研究和較真那麼多其它的幹嘛?
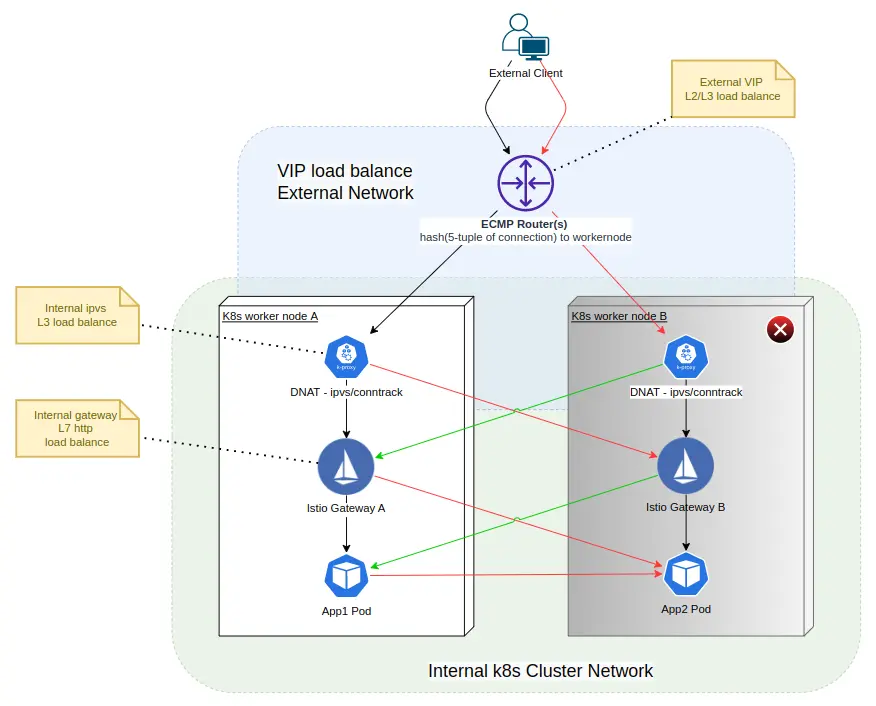
這時,我們回到下圖的 “初心” 來,看看是不是所有隱患都解決了:
很明顯,只解決了 External Client 到 k8s worker node B 的紅線部分。其它紅、綠線,沒調查過。這些 tcp half-opent 連接,是用 tcp keepalive 、tcp retransmit timeout、應用(Envoy) 層 timeout 機制快速關閉了,還是長期未檢測到問題而關閉不及時,甚至是連接泄漏(connection leak)?
空閒連接的 keepalive 檢查
作為 upstream(服務端) 時
以下可見, Istio gateway 默認無啓用 keepalive:
$ kubectl exec -it $ISTIO_GATEWAY_POD -- ss -oipn 'sport 15001 or sport 15001 or sport 8080 or sport 8443'
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
tcp ESTAB 0 0 192.222.46.71:8080 10.111.10.101:51092 users:(("envoy",pid=45,fd=665))
sack cubic wscale:11,11 rto:200 rtt:0.064/0.032 mss:8960 pmtu:9000 rcvmss:536 advmss:8960 cwnd:10 segs_in:2 send 11200000000bps lastsnd:31580 lastrcv:31580 lastack:31580 pacing_rate 22400000000bps delivered:1 rcv_space:62720 rcv_ssthresh:56576 minrtt:0.064這時,可以用 EnvoyFilter 加上 keepalive:
參考:
https://support.f5.com/csp/ar...
https://www.envoyproxy.io/doc...
https://github.com/istio/isti...
https://istio-operation-bible...
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: ingress-gateway-socket-options
namespace: istio-system
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: LISTENER
match:
context: GATEWAY
listener:
name: 0.0.0.0_8080
portNumber: 8080
patch:
operation: MERGE
value:
socket_options:
- description: enable keep-alive
int_value: 1
level: 1
name: 9
state: STATE_PREBIND
- description: idle time before first keep-alive probe is sent
int_value: 7
level: 6
name: 4
state: STATE_PREBIND
- description: keep-alive interval
int_value: 5
level: 6
name: 5
state: STATE_PREBIND
- description: keep-alive probes count
int_value: 2
level: 6
name: 6
state: STATE_PREBINDistio-proxy sidecar 也可以用類似的方法設置。
作為 downstream(客户端) 時
參考:https://istio.io/latest/docs/...
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: bookinfo-redis
spec:
host: myredissrv.prod.svc.cluster.local
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
tcp:
connectTimeout: 30ms
tcpKeepalive:
time: 60s
interval: 20s
probes: 4TCP_USER_TIMEOUT
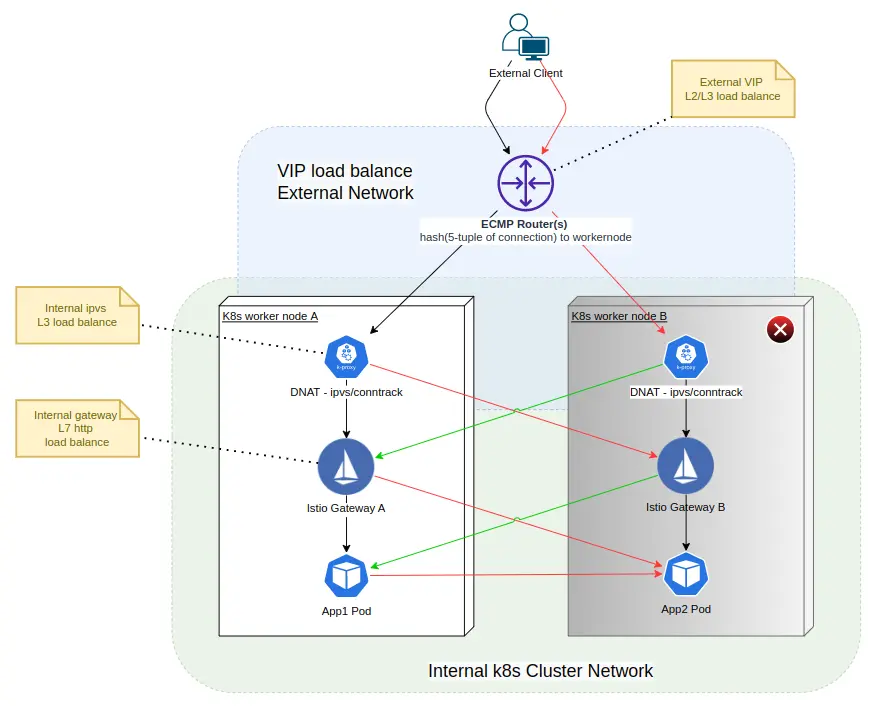
故事説到這裏,應該結束了,但,還沒有。回顧一下之前的兩個圖:
這時,retransmit timer 會定時在 TCP 層作重傳。這裏有兩個可能性:
- Calico 在 worker node B 斷電後,快速發現問題,更新了 worker node A 的路由表,刪除了到 worker node B 的路由。
- 未及時更新路由
而默認的 retransmit timer,需要 15 分鐘才會關閉連接並通知應用。如何加快?
可以用上文提到的 TCP_USER_TIMEOUT 加速 half-open TCP 在重傳狀態下發現問題 :
https://github.com/istio/isti...
https://github.com/istio/isti...
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: sampleoptions
namespace: istio-system
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: CLUSTER
match:
context: SIDECAR_OUTBOUND
cluster:
name: "outbound|12345||foo.ns.svc.cluster.local"
patch:
operation: MERGE
value:
upstream_bind_config:
source_address:
address: "0.0.0.0"
port_value: 0
protocol: TCP
socket_options:
- name: 18 #TCP_USER_TIMEOUT
int_value: 10000
level: 6上面加速了 die upstream(服務端崩潰) 的發現,對於 die downstream,可能可以用類似的方法,配置在 listener。
Envoy 應用層健康檢測
故事説到這裏,真應該結束了,但,還沒有。
應用層的健康檢測,也可能可以加速發現 upstream cluster 的 TCP half-open ,或者説是 endpoint outlier 問題。<mark>注意,這裏的健康檢測,不是 k8s 的 liveness/readiness probe。是 pod 到 pod 間的健康檢測,包括 pod 與 pod 間的連通性。</mark>
Envoy 有兩種健康檢測:
- 主動健康檢測: Health checking
- 被動健康檢測: Outlier detection
健康檢測與連接池
見:Health checking interactions
如果 Envoy 配置為主動或被動健康檢查,則所有 從可用狀態轉換為不可用狀態的主機的連接池都將關閉。 如果主機康復重新進入負載平衡,它將創建新的連接,這將最大限度地解決死連接的問題(由於 ECMP 路由或其他原因)。
健康檢測與 endpoint 發現
見:On eventually consistent service discovery
主動健康檢測: Health checking
https://www.envoyproxy.io/doc...
被動健康檢測: Outlier detection
https://istio.io/latest/docs/...
https://www.envoyproxy.io/doc...
https://www.envoyproxy.io/doc...
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: httpbin
spec:
host: httpbin
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
http:
http1MaxPendingRequests: 1 #The maximum number of requests that will be queued while waiting for a ready connection pool connection
outlierDetection:
consecutive5xxErrors: 1
interval: 1s
baseEjectionTime: 3m
maxEjectionPercent: 100
EOF健康檢測與 EDS,聽誰的?
當 worker node B 斷電後, 其中運行的 pod 的狀態最終(默認大概10分鐘)到了 Terminaling。 k8s 會通知 istiod 去刪除這個 endpoint。那麼問題來了,到底,是 EDS 快,還是 health check 檢測到失效快,Envoy 以哪個數據為負載選擇的依據?
這個問題在這個文檔中,有一些討論:
On eventually consistent service discovery
Envoy was designed from the beginning with the idea that service discovery does not require full consistency. Instead, Envoy assumes that hosts come and go from the mesh in an eventually consistent way. Our recommended way of deploying a service to service Envoy mesh configuration uses eventually consistent service discovery along with active health checking (Envoy explicitly health checking upstream cluster members) to determine cluster health. This paradigm has a number of benefits:
- All health decisions are fully distributed. Thus, network partitions are gracefully handled (whether the application gracefully handles the partition is a different story).
- When health checking is configured for an upstream cluster, Envoy uses a 2x2 matrix to determine whether to route to a host:
Discovery Status(服務發現狀態) Health Check OK Health Check Failed Discovered Route(參與負載均衡) Don’t Route Absent(缺失) <mark>Route(參與負載均衡)</mark> Don’t Route / Delete
Host discovered / health check OK
Envoy will route to the target host.
<mark>Host absent / health check OK:</mark>
Envoy will route to the target host. This is very important since the design assumes that the discovery service can fail at any time. If a host continues to pass health check even after becoming absent from the discovery data, Envoy will still route. Although it would be impossible to add new hosts in this scenario, existing hosts will continue to operate normally. When the discovery service is operating normally again the data will eventually re-converge.
Host discovered / health check FAIL
Envoy will not route to the target host. Health check data is assumed to be more accurate than discovery data.
Host absent / health check FAIL
Envoy will not route and will delete the target host. This is the only state in which Envoy will purge host data.
有一點沒完全理解的是,這裏的
Absent是指 EDS 服務訪問失敗時 Absent,還是訪問成功了,但結果中沒再出現一個原有的 endpoint。
回顧一下之前的圖:
大概可以知道,什麼地方可以考慮用 health check 配置來加速問題發現。
Envoy 應用層的超時
Envoy 應用層的連接級超時
- 新建連接超時:connect_timeout,Istio 默認 10s,這個配置影響到 outlier detection 的時效。
-
空閒連接超時:idle_timeout ,默認 1 小時
- Istio destination-rule
- 最大連接時長:max_connection_duration,默認無限
Envoy 應用層的請求級超時
對 downstream(client) 的請求讀超時
Envoy:
- Envoy 應用層的請求接收超時:request_timeout,默認無限
- header 讀超時:request_headers_timeout,默認無限
- 更多見:https://www.envoyproxy.io/doc...
對 upstream(server) 的響應等待超時
即從完整讀取 downsteam 的 request 後開始算,到從 upstream 完整讀取 response 的時間。見:
Envoy Route timeouts
https://istio.io/latest/docs/...
談超時,別忘記 retry 影響
見:Istio retry
思考
如果斷電的 worker node 重新啓動, 以前的對端可以快速收到 TCP RST 而斷開失效連接嗎?
如果斷電的 worker node 的連接處理鏈路上有 NAT/conntrack 參與,會話與端口映射狀態丟失後,一定會返回 TCP RST 嗎?還是 drop 了?
一點總結
本文寫得有點亂。説實話,有的配置和原理相互關聯與影響,要完全梳理難度很大:
- TCP 層的各種 timeout
- syscall 的各種 timeout
- 應用層的各種 timeout
- Health check 與 Outlier detection
- Retry
希望有一天,有人(或者自己)可以説清楚這些事情。本文的目標是把事情的變量都先記錄下來,確定一個範圍,再去細分推敲原理。希望對讀者有用 🥂
主要參考
- https://blog.cloudflare.com/w...
- https://codearcana.com/posts/...
- https://www.evanjones.ca/tcp-...