概述
備忘錄模式提供了一種狀態恢復的實現機制,使得用户可以方便地回到一個特定的歷史步驟,當新的狀態無效或者存在問題時,可以使用暫時存儲起來的備忘錄將狀態復原,很多軟件都提供了撤銷(Undo)操作,如 Word、記事本、Photoshop、IDEA等軟件在編輯時按 Ctrl+Z 組合鍵時能撤銷當前操作,使文檔恢復到之前的狀態;還有在瀏覽器中的後退鍵、數據庫事務管理中的回滾操作、玩遊戲時的中間結果存檔功能、數據庫與操作系統的備份操作、棋類遊戲中的悔棋功能等都屬於這類。
定義:
又叫快照模式,在不破壞封裝性的前提下,捕獲一個對象的內部狀態,並在該對象之外保存這個狀態,以便以後當需要時能將該對象恢復到原先保存的狀態。
結構
備忘錄模式的主要角色如下:
- 發起人(Originator)角色:記錄當前時刻的內部狀態信息,提供創建備忘錄和恢復備忘錄數據的功能,實現其他業務功能,它可以訪問備忘錄裏的所有信息。
- 備忘錄(Memento)角色:負責存儲發起人的內部狀態,在需要的時候提供這些內部狀態給發起人。
- 管理者(Caretaker)角色:對備忘錄進行管理,提供保存與獲取備忘錄的功能,但其不能對備忘錄的內容進行訪問與修改。
備忘錄有兩個等效的接口:
窄接口:管理者(Caretaker)對象(和其他發起人對象之外的任何對象)看到的是備忘錄的窄接口(narror Interface),這個窄接口只允許他把備忘錄對象傳給其他的對象。但是不允許訪問和修改備忘錄
寬接口:與管理者看到的窄接口相反,發起人對象可以看到一個寬接口(wide Interface),這個寬接口允許它讀取所有的數據,以便根據這些數據恢復這個發起人對象的內部狀態。
案例實現
【例】遊戲挑戰BOSS
遊戲中的某個場景,一遊戲角色有生命力、攻擊力、防禦力等數據,在打Boss前和後一定會不一樣的,我們允許玩家如果感覺與Boss決鬥的效果不理想可以讓遊戲恢復到決鬥之前的狀態。
要實現上述案例,有兩種方式:
- “白箱”備忘錄模式
- “黑箱”備忘錄模式
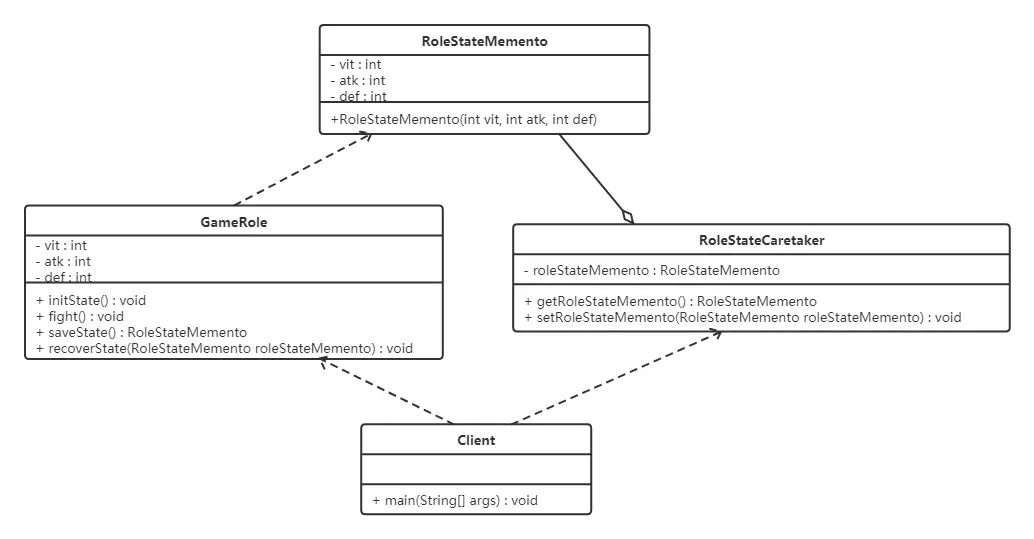
“白箱”備忘錄模式
備忘錄角色對任何對象都提供一個接口,即寬接口,備忘錄角色的內部所存儲的狀態就對所有對象公開。類圖如下:
代碼如下:
//遊戲角色類
public class GameRole {
private int vit; //生命力
private int atk; //攻擊力
private int def; //防禦力
//初始化狀態
public void initState() {
this.vit = 100;
this.atk = 100;
this.def = 100;
}
//戰鬥
public void fight() {
this.vit = 0;
this.atk = 0;
this.def = 0;
}
//保存角色狀態
public RoleStateMemento saveState() {
return new RoleStateMemento(vit, atk, def);
}
//回覆角色狀態
public void recoverState(RoleStateMemento roleStateMemento) {
this.vit = roleStateMemento.getVit();
this.atk = roleStateMemento.getAtk();
this.def = roleStateMemento.getDef();
}
public void stateDisplay() {
System.out.println("角色生命力:" + vit);
System.out.println("角色攻擊力:" + atk);
System.out.println("角色防禦力:" + def);
}
public int getVit() {
return vit;
}
public void setVit(int vit) {
this.vit = vit;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
}
//遊戲狀態存儲類(備忘錄類)
public class RoleStateMemento {
private int vit;
private int atk;
private int def;
public RoleStateMemento(int vit, int atk, int def) {
this.vit = vit;
this.atk = atk;
this.def = def;
}
public int getVit() {
return vit;
}
public void setVit(int vit) {
this.vit = vit;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
}
//角色狀態管理者類
public class RoleStateCaretaker {
private RoleStateMemento roleStateMemento;
public RoleStateMemento getRoleStateMemento() {
return roleStateMemento;
}
public void setRoleStateMemento(RoleStateMemento roleStateMemento) {
this.roleStateMemento = roleStateMemento;
}
}
//測試類
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("------------大戰Boss前------------");
//大戰Boss前
GameRole gameRole = new GameRole();
gameRole.initState();
gameRole.stateDisplay();
//保存進度
RoleStateCaretaker roleStateCaretaker = new RoleStateCaretaker();
roleStateCaretaker.setRoleStateMemento(gameRole.saveState());
System.out.println("------------大戰Boss後------------");
//大戰Boss時,損耗嚴重
gameRole.fight();
gameRole.stateDisplay();
System.out.println("------------恢復之前狀態------------");
//恢復之前狀態
gameRole.recoverState(roleStateCaretaker.getRoleStateMemento());
gameRole.stateDisplay();
}
}分析:白箱備忘錄模式是破壞封裝性的。但是通過程序員自律,同樣可以在一定程度上實現模式的大部分用意。
“黑箱”備忘錄模式
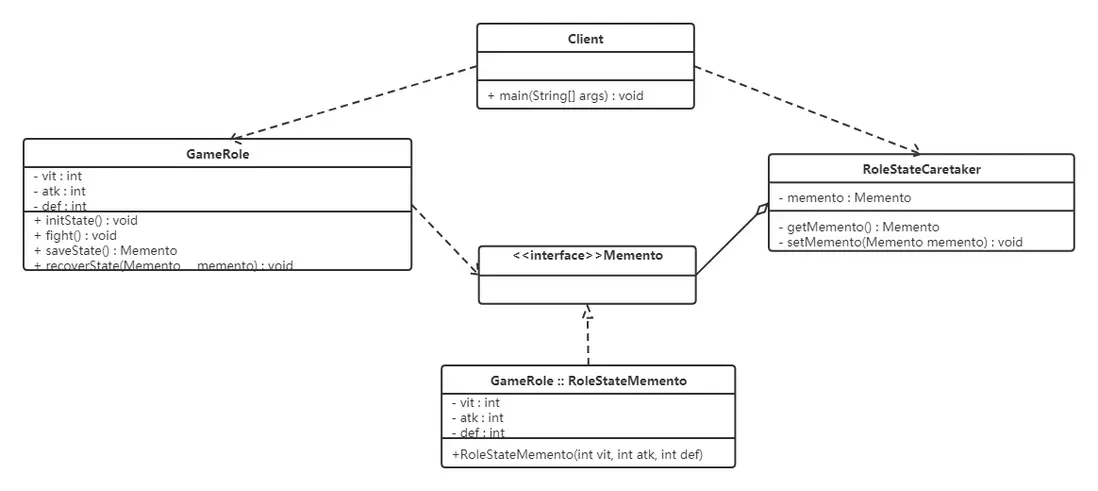
備忘錄角色對發起人對象提供一個寬接口,而為其他對象提供一個窄接口。在Java語言中,實現雙重接口的辦法就是將備忘錄類設計成發起人類的內部成員類。
將 RoleStateMemento 設為 GameRole 的內部類,從而將 RoleStateMemento 對象封裝在 GameRole 裏面;在外面提供一個標識接口 Memento 給 RoleStateCaretaker 及其他對象使用。這樣 GameRole 類看到的是 RoleStateMemento 所有的接口,而RoleStateCaretaker 及其他對象看到的僅僅是標識接口 Memento 所暴露出來的接口,從而維護了封裝型。類圖如下:
代碼如下:
窄接口Memento,這是一個標識接口,因此沒有定義出任何的方法
public interface Memento {
}定義發起人類 GameRole,並在內部定義備忘錄內部類 RoleStateMemento(該內部類設置為私有的)
//遊戲角色類
public class GameRole {
private int vit; //生命力
private int atk; //攻擊力
private int def; //防禦力
//初始化狀態
public void initState() {
this.vit = 100;
this.atk = 100;
this.def = 100;
}
//戰鬥
public void fight() {
this.vit = 0;
this.atk = 0;
this.def = 0;
}
//保存角色狀態
public Memento saveState() {
return new RoleStateMemento(vit, atk, def);
}
//回覆角色狀態
public void recoverState(Memento memento) {
RoleStateMemento roleStateMemento = (RoleStateMemento) memento;
this.vit = roleStateMemento.getVit();
this.atk = roleStateMemento.getAtk();
this.def = roleStateMemento.getDef();
}
public void stateDisplay() {
System.out.println("角色生命力:" + vit);
System.out.println("角色攻擊力:" + atk);
System.out.println("角色防禦力:" + def);
}
public int getVit() {
return vit;
}
public void setVit(int vit) {
this.vit = vit;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
private class RoleStateMemento implements Memento {
private int vit;
private int atk;
private int def;
public RoleStateMemento(int vit, int atk, int def) {
this.vit = vit;
this.atk = atk;
this.def = def;
}
public int getVit() {
return vit;
}
public void setVit(int vit) {
this.vit = vit;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
}
}負責人角色類 RoleStateCaretaker 能夠得到的備忘錄對象是以 Memento 為接口的,由於這個接口僅僅是一個標識接口,因此負責人角色不可能改變這個備忘錄對象的內容
//角色狀態管理者類
public class RoleStateCaretaker {
private Memento memento;
public Memento getMemento() {
return memento;
}
public void setMemento(Memento memento) {
this.memento = memento;
}
}客户端測試類
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("------------大戰Boss前------------");
//大戰Boss前
GameRole gameRole = new GameRole();
gameRole.initState();
gameRole.stateDisplay();
//保存進度
RoleStateCaretaker roleStateCaretaker = new RoleStateCaretaker();
roleStateCaretaker.setMemento(gameRole.saveState());
System.out.println("------------大戰Boss後------------");
//大戰Boss時,損耗嚴重
gameRole.fight();
gameRole.stateDisplay();
System.out.println("------------恢復之前狀態------------");
//恢復之前狀態
gameRole.recoverState(roleStateCaretaker.getMemento());
gameRole.stateDisplay();
}
}優缺點
優點:
- 提供了一種可以恢復狀態的機制。當用户需要時能夠比較方便地將數據恢復到某個歷史的狀態。
- 實現了內部狀態的封裝。除了創建它的發起人之外,其他對象都不能夠訪問這些狀態信息。
- 簡化了發起人類。發起人不需要管理和保存其內部狀態的各個備份,所有狀態信息都保存在備忘錄中,並由管理者進行管理,這符合單一職責原則。
缺點:
- 資源消耗大。如果要保存的內部狀態信息過多或者特別頻繁,將會佔用比較大的內存資源。
使用場景
- 需要保存與恢復數據的場景,如玩遊戲時的中間結果的存檔功能。
- 需要提供一個可回滾操作的場景,如 Word、記事本、Photoshop,idea等軟件在編輯時按 Ctrl+Z 組合鍵,還有數據庫中事務操作。
往期推薦
- 《SpringBoot》EasyExcel實現百萬數據的導入導出
- 《SpringBoot》史上最全SpringBoot相關注解介紹
- Spring框架IoC核心詳解
- 萬字長文帶你窺探Spring中所有的擴展點
- 如何實現一個通用的接口限流、防重、防抖機制
- 萬字長文帶你深入Redis底層數據結構
- volatile關鍵字最全原理剖析