Dubbo幾種負載均衡算法
在分佈式系統中,服務的高可用性和性能優化是至關重要的。Dubbo作為一款高性能的Java RPC框架,在服務治理方面提供了豐富的功能,其中負載均衡(Load Balancing)是一個關鍵特性。通過合理的負載均衡策略,可以有效地提高系統的整體性能和穩定性。本文將詳細介紹Dubbo提供的幾種負載均衡算法。
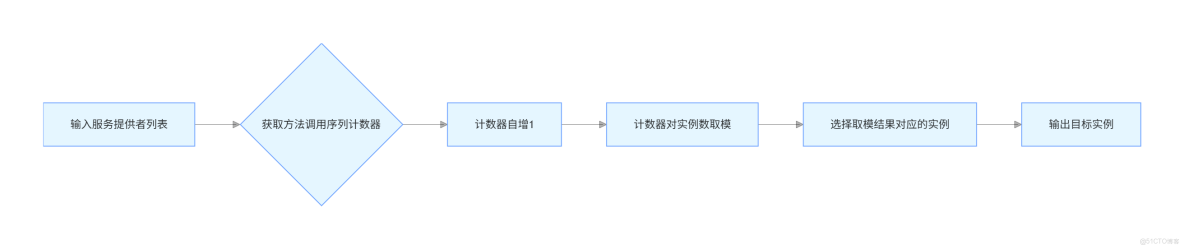
1. 隨機算法 (Random Load Balance)
隨機算法是最簡單的負載均衡策略之一,它通過隨機選擇一個服務提供者來分配請求。這種算法實現簡單,但由於完全依賴隨機性,可能會導致某些服務節點的壓力過大,而其他節點則相對空閒。
特點:
- 實現簡單
- 可能造成服務節點負載不均
使用場景:
- 對於服務調用次數較少且對響應時間要求不高的場景
2. 輪詢算法 (RoundRobin Load Balance)
輪詢算法按照順序循環選擇服務提供者,確保每個服務提供者的請求量大致相等。與隨機算法相比,輪詢算法能更好地平衡各個服務節點的負載。
特點:
- 負載均勻
- 實現簡單
使用場景:
- 適用於服務調用頻繁且需要均衡分佈的場景
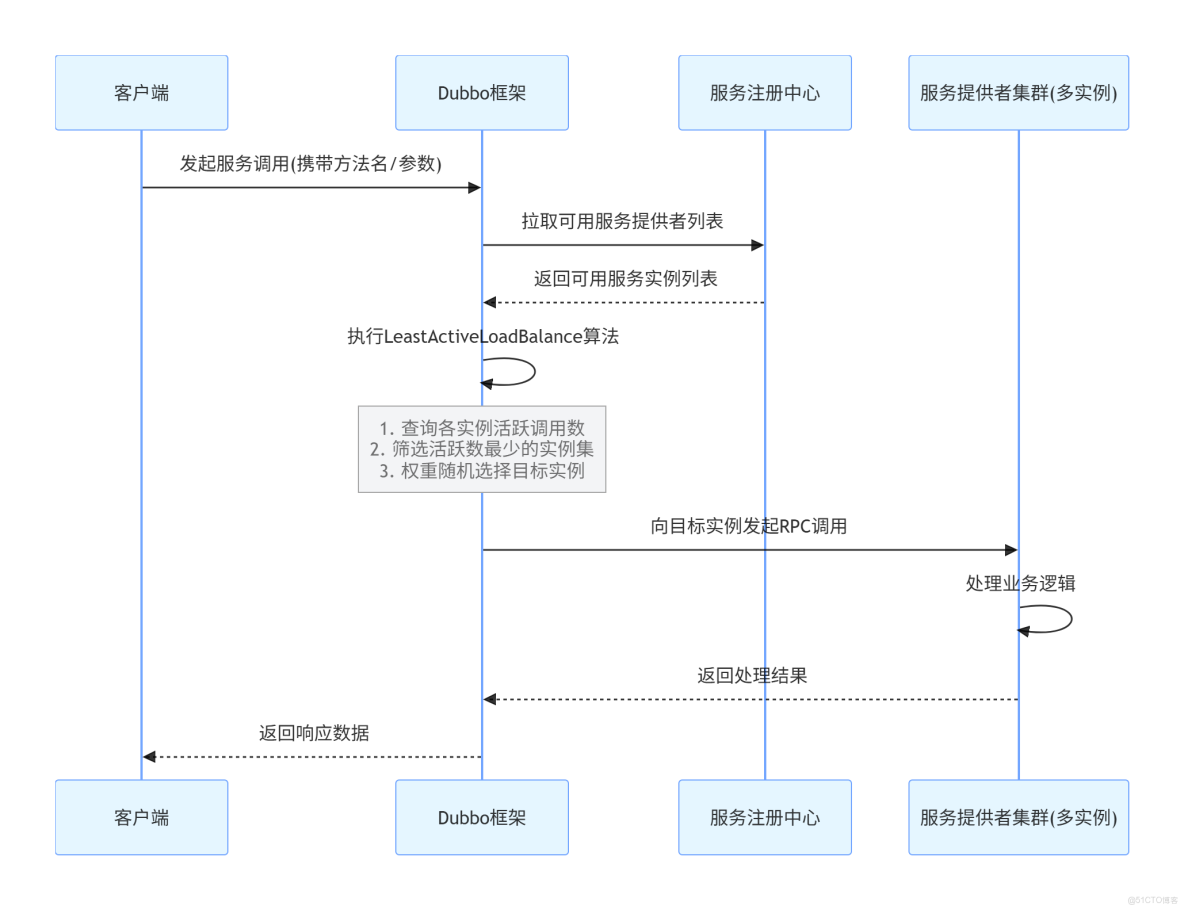
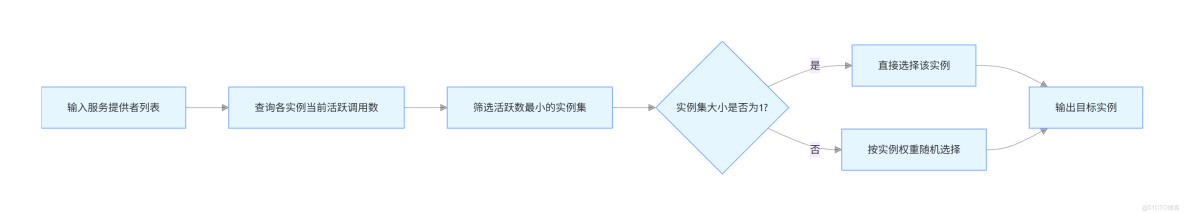
3. 最少活躍調用數算法 (LeastActive Load Balance)
最少活躍調用數算法選擇當前活躍調用數最小的服務提供者處理新的請求。這裏的“活躍調用數”是指正在處理中的請求數量。該算法旨在將請求分配給負載最輕的服務節點,從而提高整體的服務響應速度。
特點:
- 動態調整,根據實際負載情況分配請求
- 有效避免熱點問題
使用場景:
- 適用於服務調用頻率高且對響應時間敏感的場景
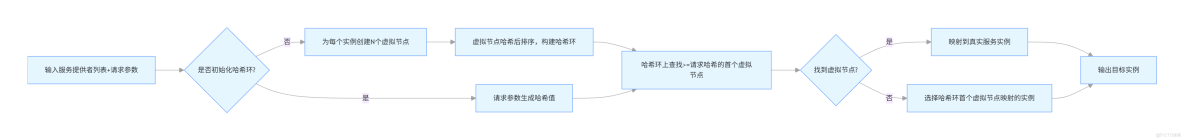
4. 基於一致哈希的負載均衡 (ConsistentHash Load Balance)
基於一致哈希的負載均衡算法通過哈希算法將請求映射到特定的服務提供者上,確保相同的請求總是被路由到同一台服務器。這種方法特別適合於需要會話保持或數據局部性的場景。
特點:
- 保證相同請求被路由到同一節點
- 減少了數據遷移的成本
使用場景:
- 適用於需要會話保持或數據局部性的應用
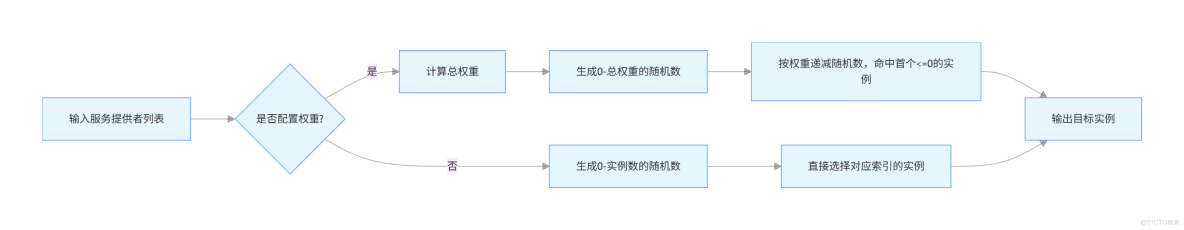
5. 帶權重的輪詢算法 (Weighted RoundRobin Load Balance)
帶權重的輪詢算法是在標準輪詢算法的基礎上增加了權重的概念,允許為不同的服務提供者設置不同的權重值。權重較高的服務提供者將獲得更多的請求分配機會,這有助於在資源不均等的情況下更合理地分配負載。
特點:
- 支持不同服務提供者之間的資源差異
- 靈活性高
使用場景:
- 適用於服務提供者之間存在資源差異的情況
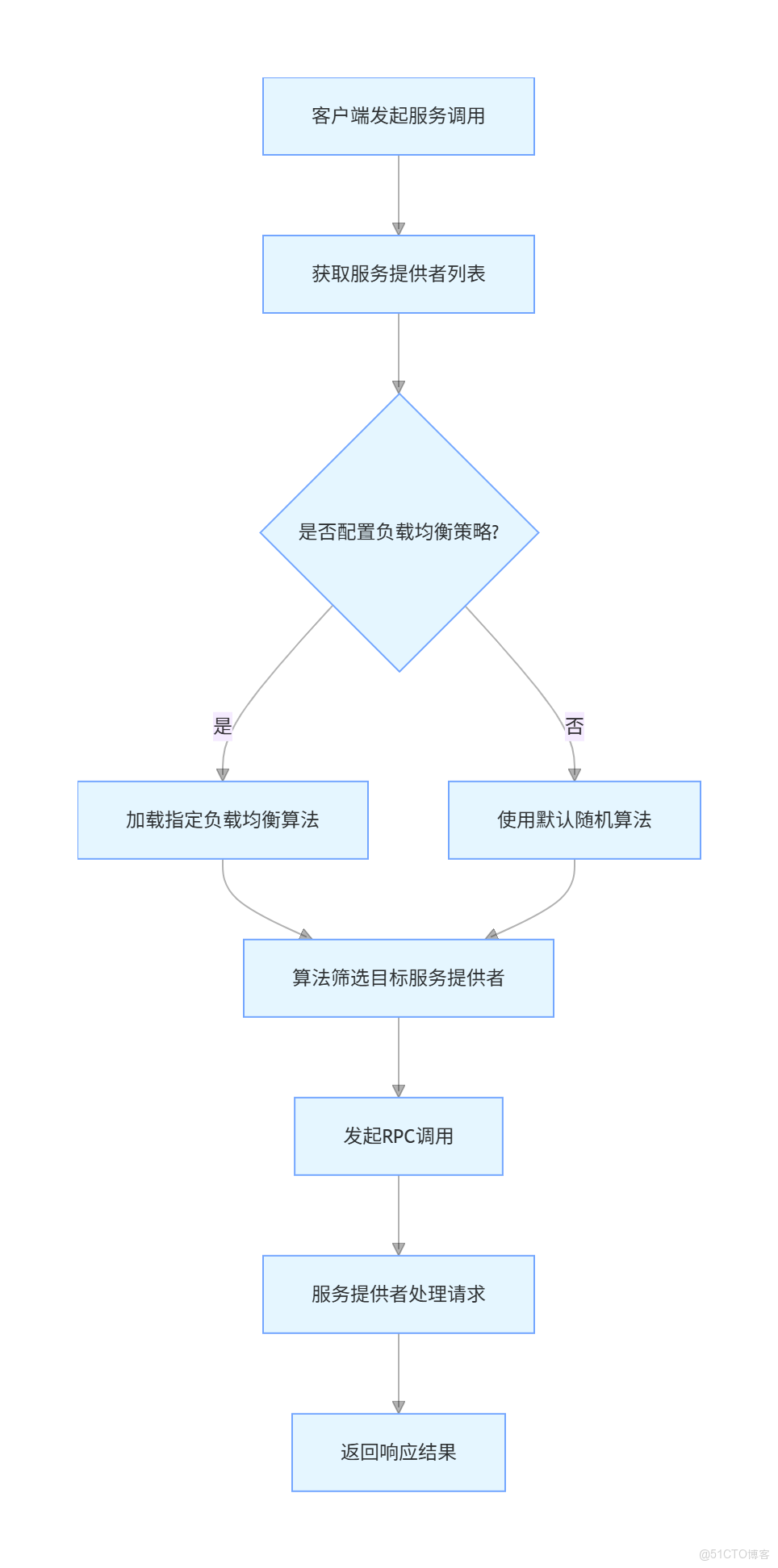
在 Dubbo 中,負載均衡(Load Balancing)是一個重要的特性,它確保了客户端請求能夠均勻地分發到多個服務提供者上,從而提高系統的可用性和響應速度。
Dubbo 提供了幾種內置的負載均衡策略,包括:
- Random LoadBalance:隨機選擇服務提供者。
- RoundRobin LoadBalance:輪詢選擇服務提供者。
- LeastActive LoadBalance:最少活躍調用數優先選擇。
- ConsistentHash LoadBalance:一致性哈希選擇。
下面是一些實際應用場景中的示例代碼,展示瞭如何在 Dubbo 中配置和使用這些負載均衡策略。
1. Random LoadBalance
<!-- 在服務消費者端的 Dubbo 配置文件中 -->
<bean id="reference" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig">
<property name="interface" value="com.example.DemoService"/>
<property name="loadbalance" value="random"/>
</bean>2. RoundRobin LoadBalance
<!-- 在服務消費者端的 Dubbo 配置文件中 -->
<bean id="reference" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig">
<property name="interface" value="com.example.DemoService"/>
<property name="loadbalance" value="roundrobin"/>
</bean>3. LeastActive LoadBalance
<!-- 在服務消費者端的 Dubbo 配置文件中 -->
<bean id="reference" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig">
<property name="interface" value="com.example.DemoService"/>
<property name="loadbalance" value="leastactive"/>
</bean>4. ConsistentHash LoadBalance
<!-- 在服務消費者端的 Dubbo 配置文件中 -->
<bean id="reference" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig">
<property name="interface" value="com.example.DemoService"/>
<property name="loadbalance" value="consistenthash"/>
<!-- 可以指定參數名稱和虛擬節點數量 -->
<property name="parameters">
<map>
<entry key="consistenthash.arguments" value="0"/>
<entry key="consistenthash.virtual-nodes" value="100"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>示例代碼説明
- Random LoadBalance:
loadbalance="random":隨機選擇一個服務提供者。
- RoundRobin LoadBalance:
loadbalance="roundrobin":按照順序依次選擇服務提供者。
- LeastActive LoadBalance:
loadbalance="leastactive":優先選擇活躍調用數最少的服務提供者。
- ConsistentHash LoadBalance:
loadbalance="consistenthash":根據參數進行一致性哈希選擇。consistenthash.arguments:指定參與哈希計算的參數索引。consistenthash.virtual-nodes:指定虛擬節點的數量,增加虛擬節點可以提高哈希分佈的均勻性。
實際應用場景
假設你有一個電商系統,其中有一個訂單服務,該服務有多個實例部署在不同的服務器上。為了保證高可用性和性能,你可以使用 Dubbo 的負載均衡策略來分發請求。
- Random LoadBalance:適用於請求量較小且對響應時間要求不高的場景。
- RoundRobin LoadBalance:適用於請求量較大且希望均勻分配請求的場景。
- LeastActive LoadBalance:適用於服務提供者的處理能力不同,希望優先選擇空閒的服務提供者的場景。
- ConsistentHash LoadBalance:適用於需要保持會話狀態或緩存數據一致性的場景,例如用户會話管理。
通過合理選擇和配置負載均衡策略,可以有效提升系統的穩定性和性能。Apache Dubbo 是一個高性能的 Java RPC 框架,廣泛用於構建分佈式服務架構。在 Dubbo 中,負載均衡(Load Balancing)是其核心特性之一,用於在多個服務提供者之間分配請求,以實現高可用性和性能優化。Dubbo 支持多種負載均衡策略,包括隨機、輪詢、最少活躍調用數和一致性哈希等。
下面將詳細介紹這些負載均衡策略及其對應的代碼實現:
1. 隨機負載均衡 (Random Load Balance)
隨機負載均衡是最簡單的負載均衡策略,通過隨機選擇服務提供者來分發請求。Dubbo 中的 RandomLoadBalance 類實現了這一策略。
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
@Override
protected Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size();
int totalWeight = 0;
boolean sameWeight = true;
// 計算總權重
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
totalWeight += weight;
if (sameWeight && i > 0 && weight != getWeight(invokers.get(0), invocation)) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
// 根據權重隨機選擇
int offset = random.nextInt(totalWeight);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
if (offset < 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
// 如果所有權重相同或總權重為0,則隨機選擇
return invokers.get(random.nextInt(length));
}
}2. 輪詢負載均衡 (RoundRobin Load Balance)
輪詢負載均衡通過按順序循環選擇服務提供者來分發請求。Dubbo 中的 RoundRobinLoadBalance 類實現了這一策略。
public class RoundRobinLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, AtomicPositiveInteger> sequences = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
protected Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
AtomicPositiveInteger sequence = sequences.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new AtomicPositiveInteger());
int length = invokers.size();
int index = sequence.getAndIncrement() % length;
return invokers.get(index);
}
}3. 最少活躍調用數負載均衡 (LeastActive Load Balance)
最少活躍調用數負載均衡策略會選擇當前活躍調用數最少的服務提供者來處理請求,以平衡負載。Dubbo 中的 LeastActiveLoadBalance 類實現了這一策略。
public class LeastActiveLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
@Override
protected Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size();
int leastActive = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
double leastWeight = Double.MAX_VALUE;
double totalWeight = 0.0;
List<Invoker<T>> leastActives = new ArrayList<>(length);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive();
int weight = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
totalWeight += weight;
if (leastActive > active || (leastActive == active && leastWeight > weight)) {
leastActive = active;
leastWeight = weight;
leastActives.clear();
leastActives.add(invoker);
} else if (leastActive == active && leastWeight == weight) {
leastActives.add(invoker);
}
}
if (!leastActives.isEmpty()) {
if (leastActives.size() == 1) {
return leastActives.get(0);
}
return getRandomInvoker(leastActives, totalWeight);
}
return getRandomInvoker(invokers, totalWeight);
}
private Invoker<T> getRandomInvoker(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, double totalWeight) {
int length = invokers.size();
if (totalWeight > 0) {
double offset = random.nextDouble() * totalWeight;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= getWeight(invokers.get(i));
if (offset <= 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
return invokers.get(random.nextInt(length));
}
}4. 一致性哈希負載均衡 (ConsistentHash Load Balance)
一致性哈希負載均衡通過哈希算法將請求路由到固定的服務提供者,以實現會話粘滯性。Dubbo 中的 ConsistentHashLoadBalance 類實現了這一策略。
public class ConsistentHashLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
private static final int DEFAULT_REPLICA_NUMBER = 160;
@Override
protected Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
Map<String, ConsistentHashSelector<T>> selectors = methodSelectors.get(url.getServiceKey());
if (selectors == null) {
selectors = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
methodSelectors.put(url.getServiceKey(), selectors);
}
ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = selectors.get(methodName);
if (selector == null || !selector.getUrl().equals(url)) {
selectors.put(methodName, new ConsistentHashSelector<T>(invokers, methodName, url));
selector = selectors.get(methodName);
}
return selector.select(invocation);
}
private class ConsistentHashSelector<T> {
private final List<Invoker<T>> invokers;
private final String methodName;
private final URL url;
private final int replicaNumber;
private final int[] hashCodes;
private final ConcurrentMap<Integer, Invoker<T>> virtualInvokers;
public ConsistentHashSelector(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, String methodName, URL url) {
this.invokers = invokers;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.url = url;
this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, "hash.nodes", DEFAULT_REPLICA_NUMBER);
this.hashCodes = new int[invokers.size() * replicaNumber];
this.virtualInvokers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(invokers.size() * replicaNumber);
int index = 0;
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber; i++) {
int hash = invoker.getUrl().hashCode() ^ i;
hashCodes[index] = hash;
virtualInvokers.put(hash, invoker);
index++;
}
}
Arrays.sort(hashCodes);
}
public Invoker<T> select(Invocation invocation) {
String key = toKey(invocation.getArguments());
int hash = getHash(key);
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(hashCodes, hash);
if (index < 0) {
index = -index - 1;
}
if (index >= hashCodes.length) {
index = 0;
}
return virtualInvokers.get(hashCodes[index]);
}
private String toKey(Object[] args) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
for (Object arg : args) {
if (arg != null) {
buf.append(arg.toString());
}
}
}
return buf.toString();
}
private int getHash(String key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
}
}以上是 Dubbo 中幾種常見的負載均衡策略及其對應的代碼實現。每種策略都有其適用場景,可以根據實際需求選擇合適的負載均衡策略。