基礎佈局
1. 線性佈局(Colum/Row)
1.1 基本概念
線性佈局是開發中最常用的佈局,通過線性容器Row和Column構建。其子元素在線性方向上(水平方向和垂直方向)依次排列。
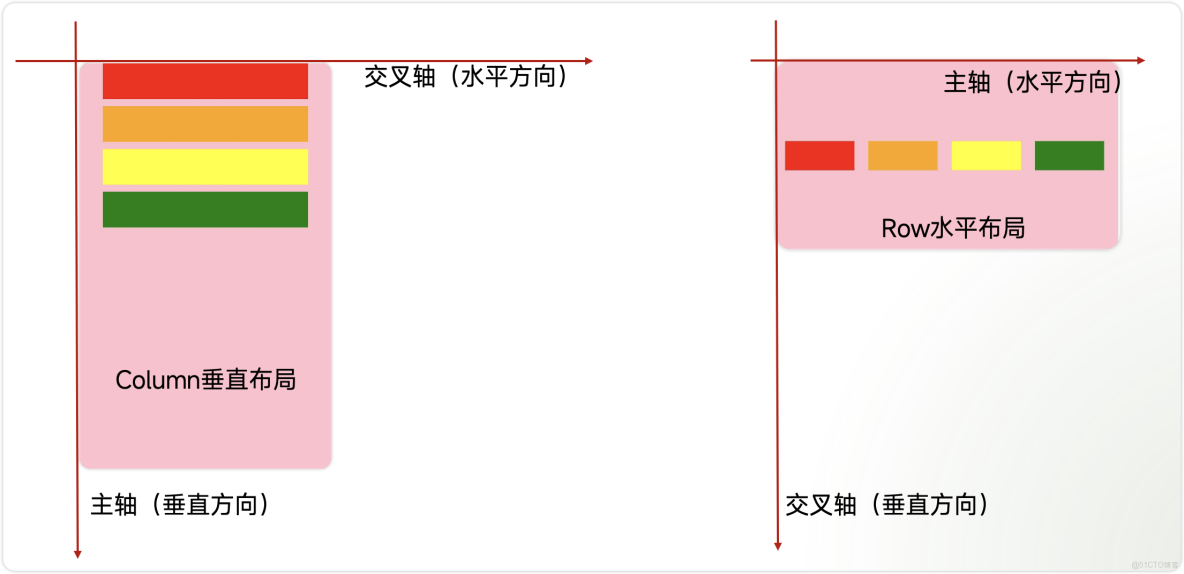
● Column:容器內子元素按照垂直方向排列。
● Row:容器內子元素按照水平方向排列。
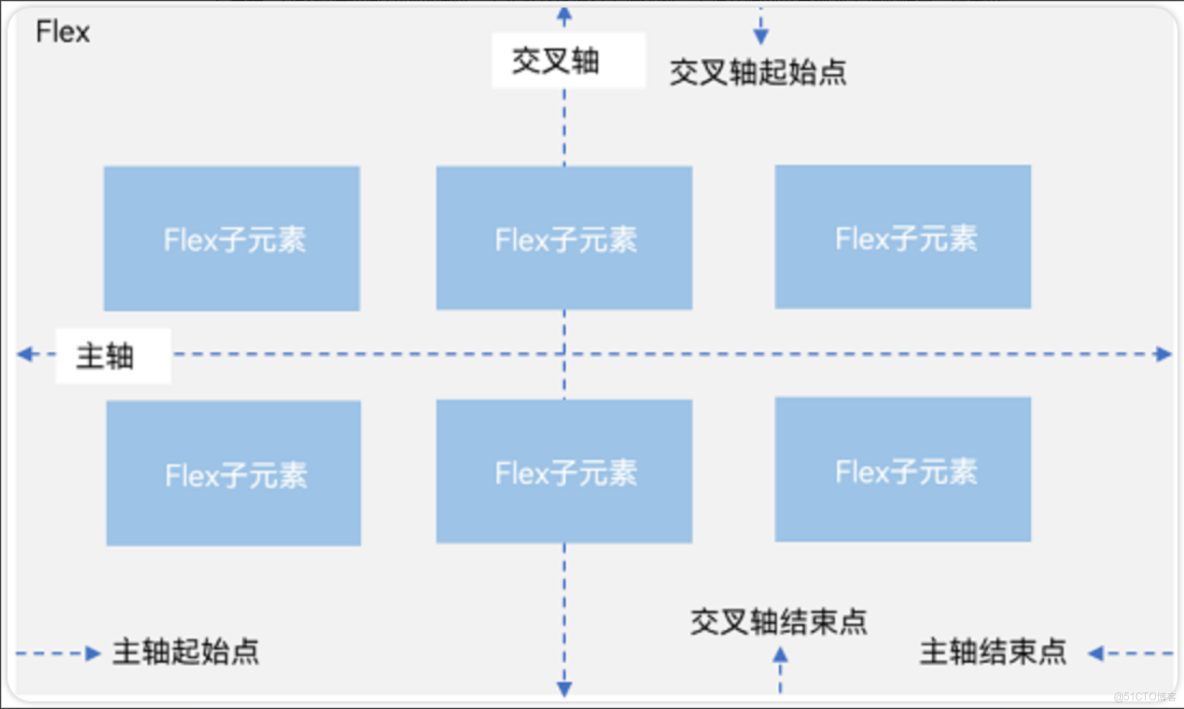
主軸和交叉軸
● 主軸:線性佈局在佈局方向上的軸線稱為主軸,Column主軸為垂直方向,Row主軸為水平方向。
● 交叉軸:垂直於主軸方向的軸線稱為交叉軸,Column交叉軸為水平方向,Row交叉軸為垂直方向。
1.2 子元素的排列間距
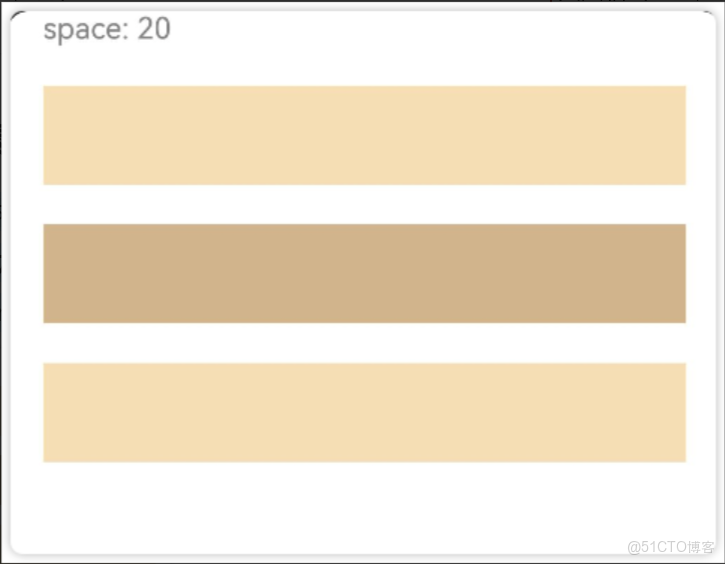
通過{ space: 25 }用來設置佈局元素在排列方向上的間距。
● Column 垂直方向的間距
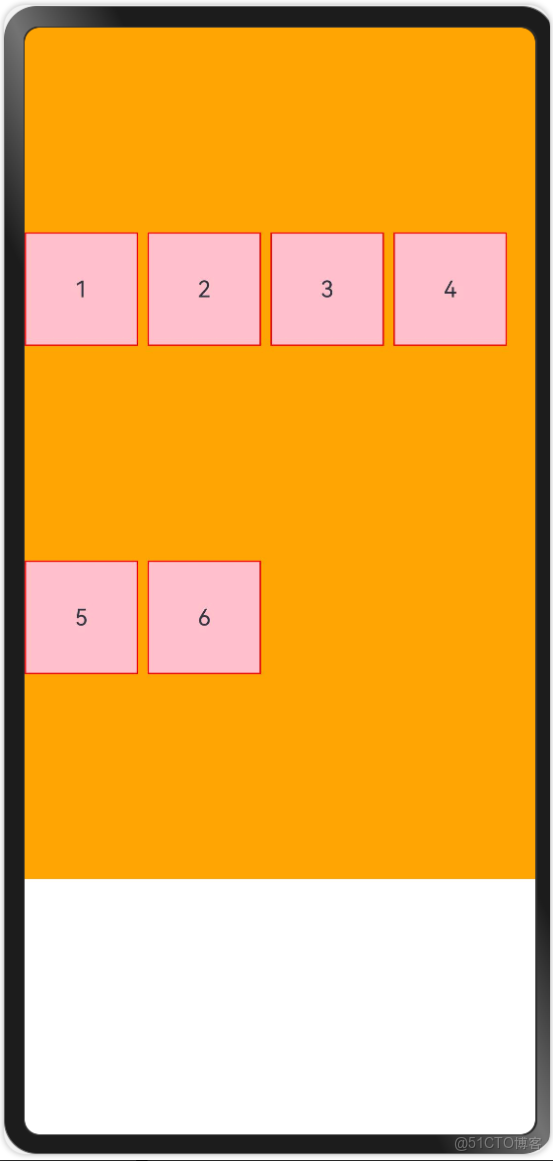
如下圖所示,Column垂直排列了4個元素,他們之間的間距為20。
實現上圖效果的代碼如下:
Column({ space: 20 }) {
Text('space: 20').fontSize(15).fontColor(Color.Gray).width('90%')
Row().width('90%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Row().width('90%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Row().width('90%').height(50).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
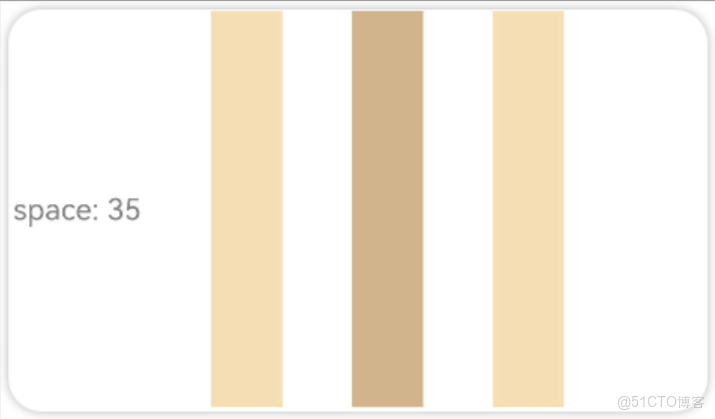
}.width('100%')● Row 水平方向上的間距
如圖所示,水平方向上排列了4個元素,他們之間的間距是35
實現上述效果的代碼如下:
Row({ space: 35 }) {
Text('space: 35').fontSize(15).fontColor(Color.Gray)
Row().width('10%').height(200).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
Row().width('10%').height(200).backgroundColor(0xD2B48C)
Row().width('10%').height(200).backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3)
}.width('100%')1.3 Column 主軸排列方式
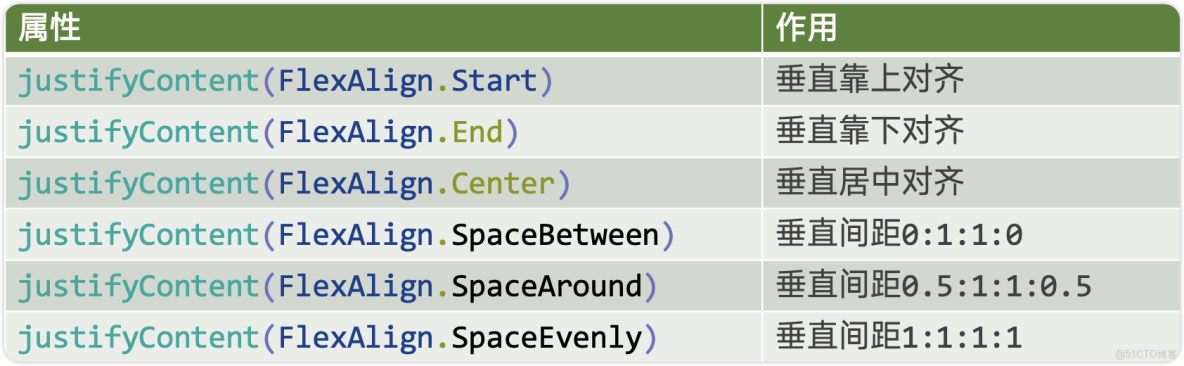
Column佈局通過調用justifyContent屬性設置佈局子元素在主軸上的排列方式。一共有6種排列方式
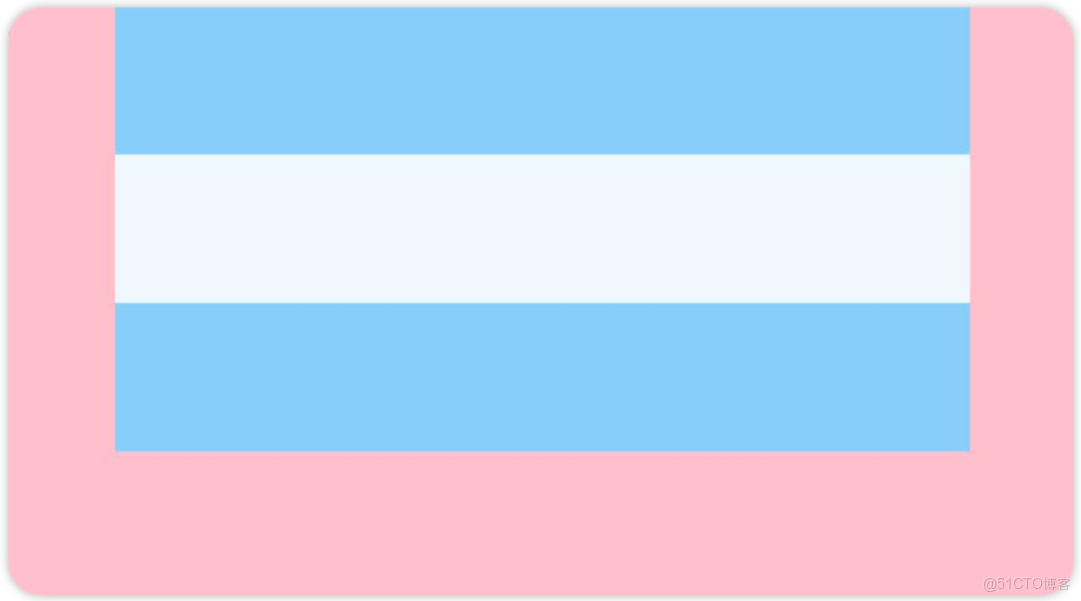
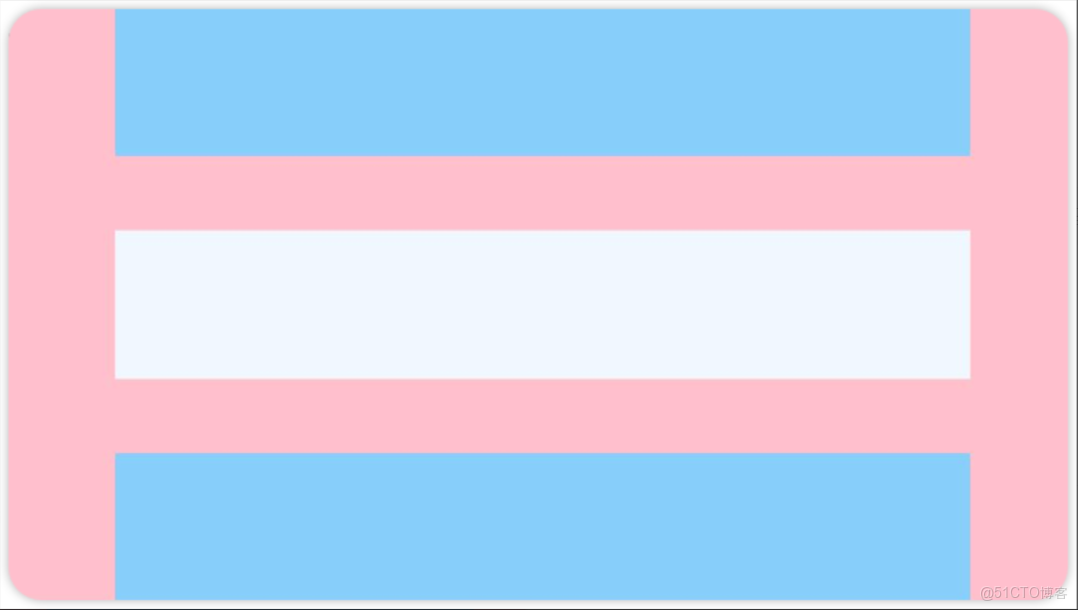
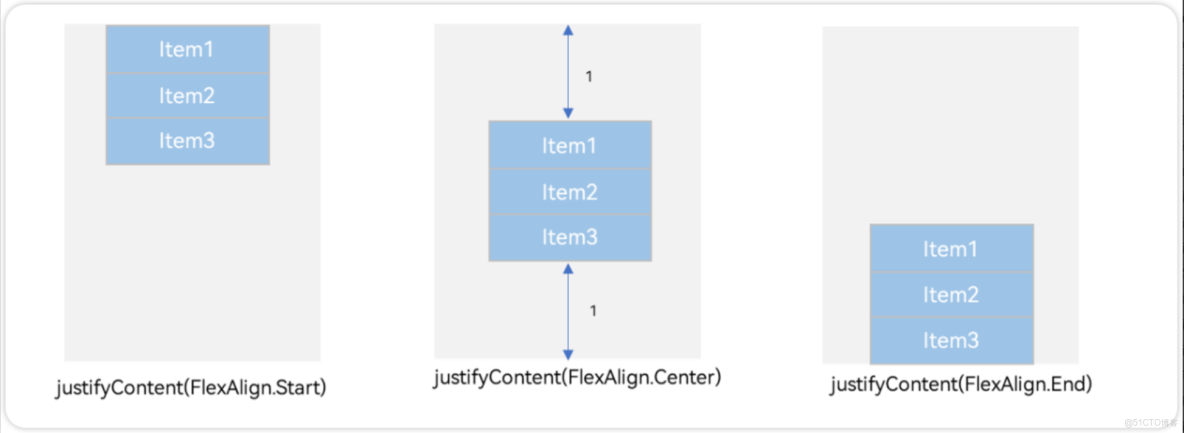
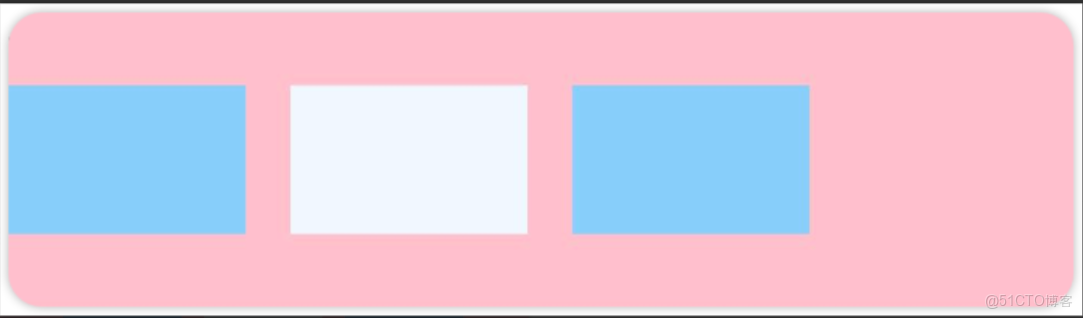
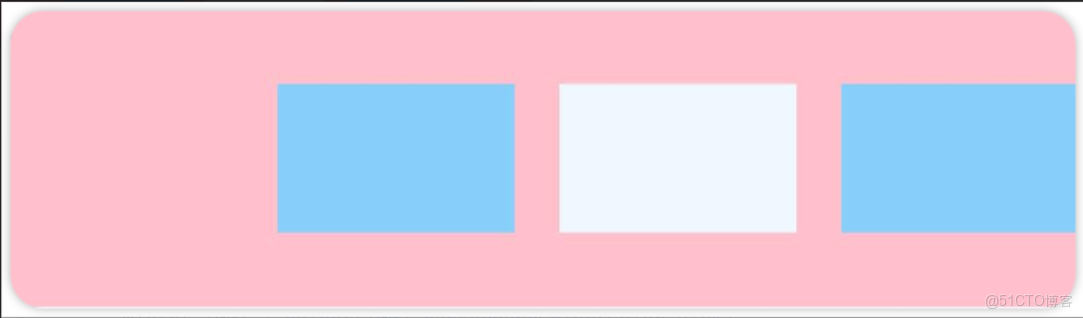
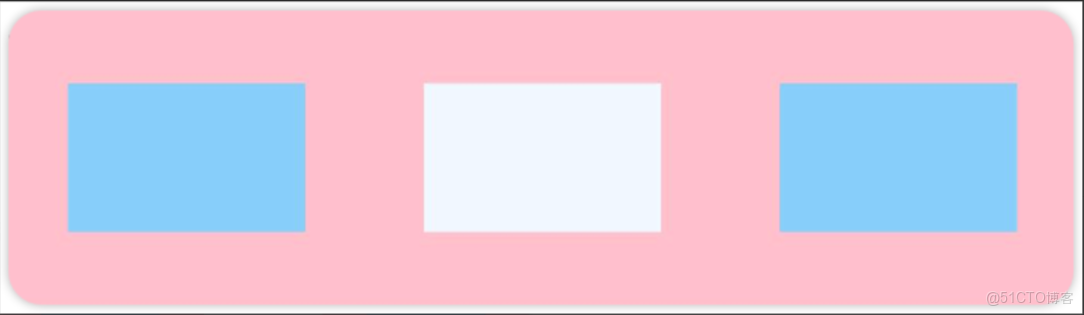
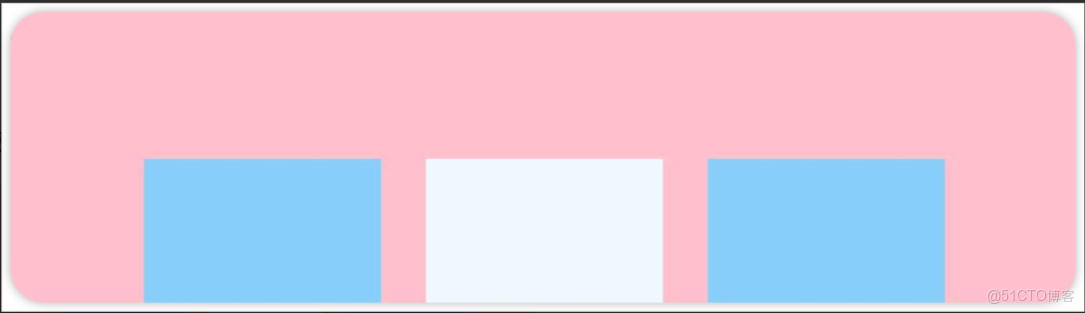
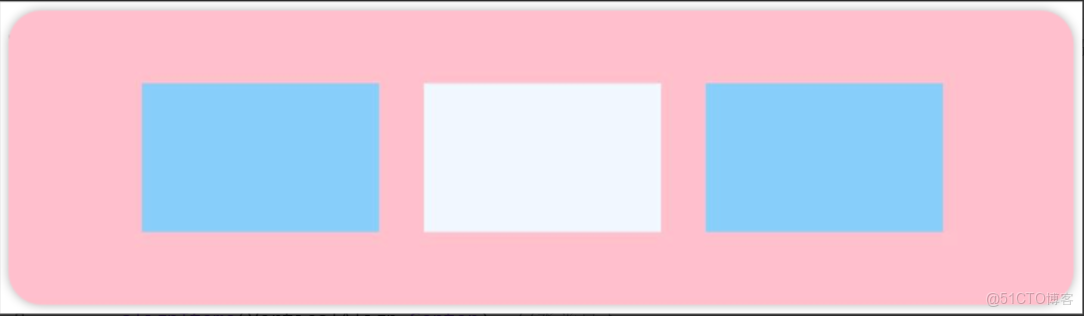
先看前三種對齊方式:如下圖所示,分別是垂直靠上對齊、垂直居中對齊、垂直考下對齊。
例1:如圖所示,垂直靠上對齊(為了演示方便,我把最外層的背景換成了品紅Color.Pink)
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(500).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
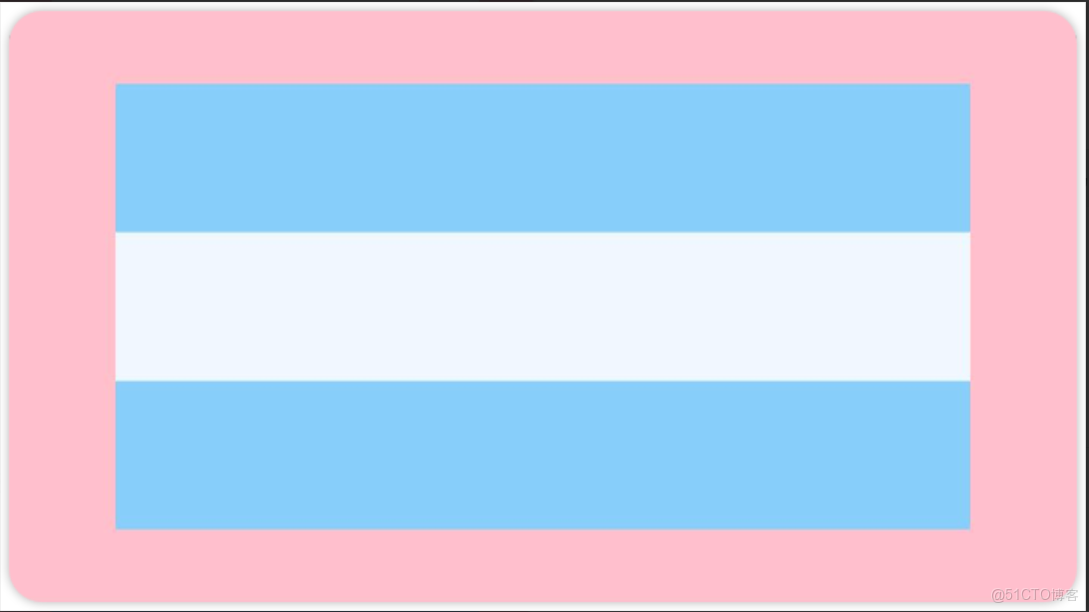
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Start)例2:如圖所示,垂直居中對齊
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(500).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
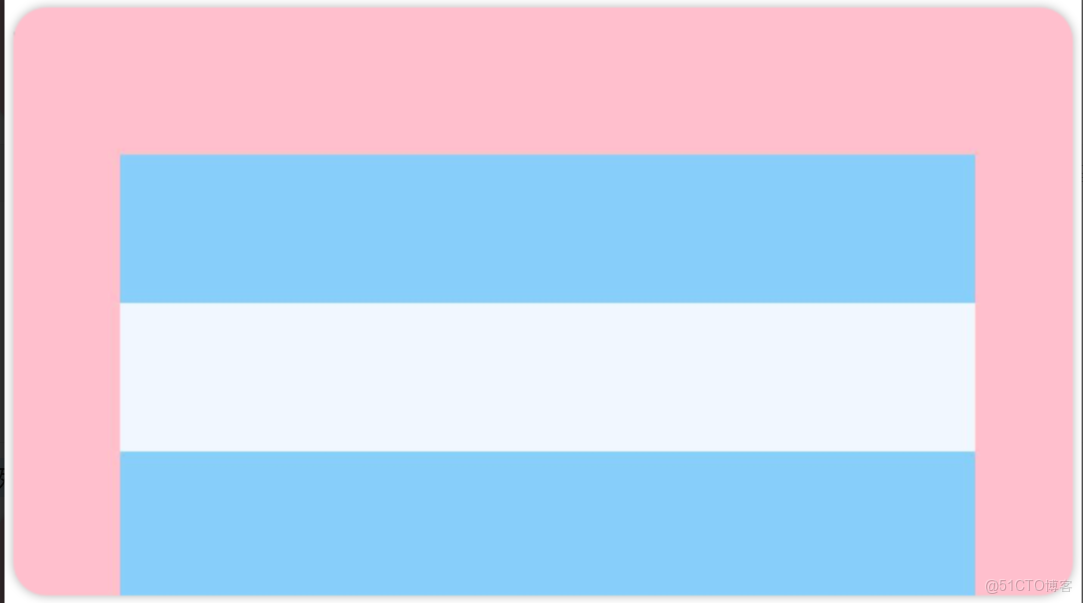
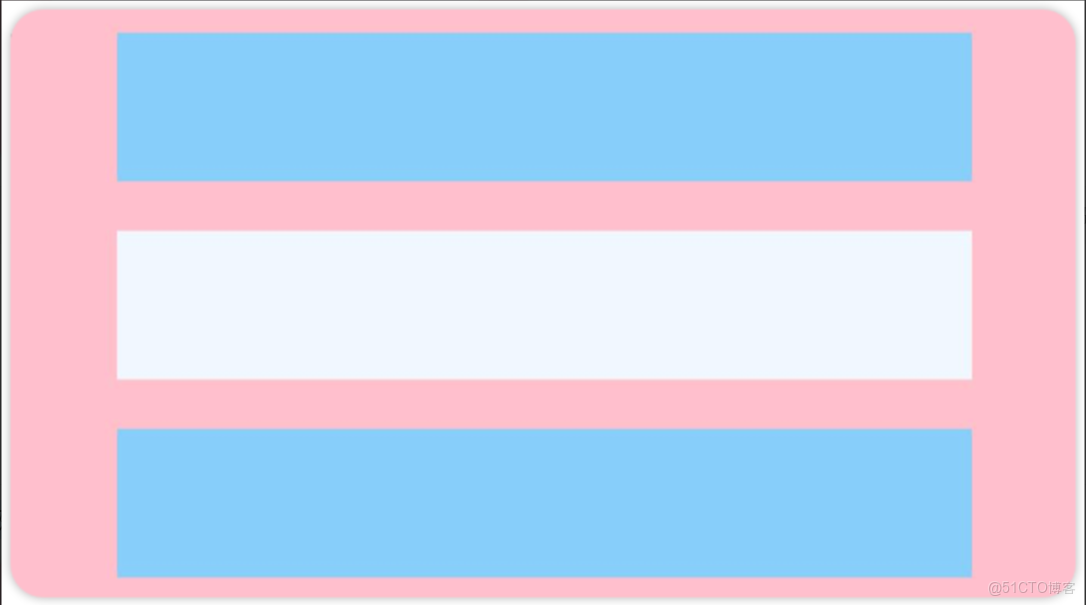
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)例3:如下圖所示,垂直靠下對齊
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(500).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
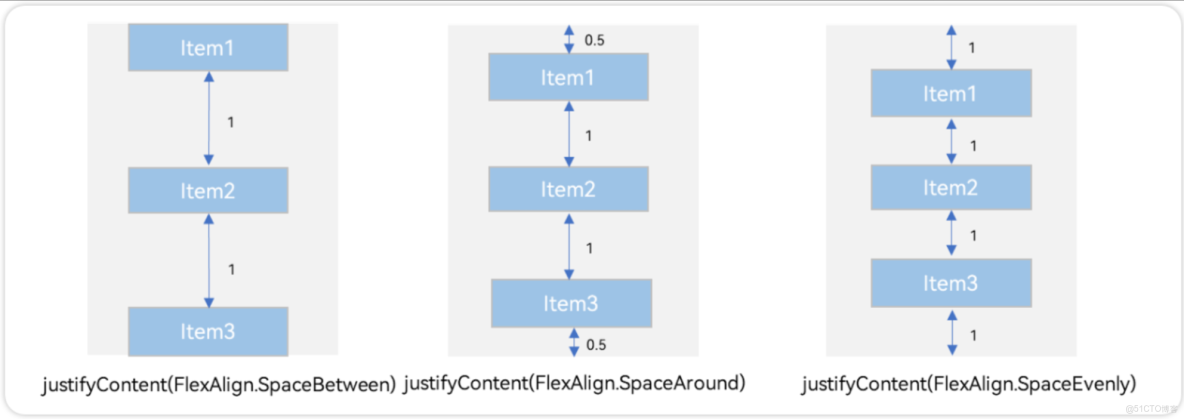
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.End)再看後三種對齊方式,可以按照比例設置佈局內子元素的間距,如圖所示
例4:按照0:1:1:0設置佈局內子元素的間距
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(500).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)例5:按照0.5:1:1:0.5設置佈局內子元素的間距
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(500).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceAround)例6:按照1:1:1:1設置佈局內子元素的間距
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(500).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly)1.4 Column 交叉軸排列方式
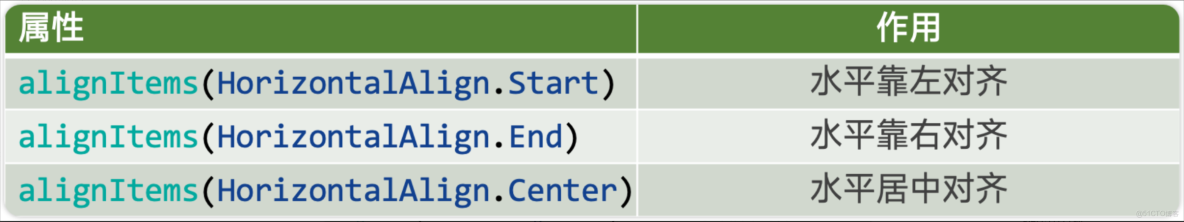
Column的主軸是垂直方向,交叉軸垂直於主軸,所以交叉軸就是水平方向;通過 alignItems屬性設置子元素在交叉軸上的對齊方式。
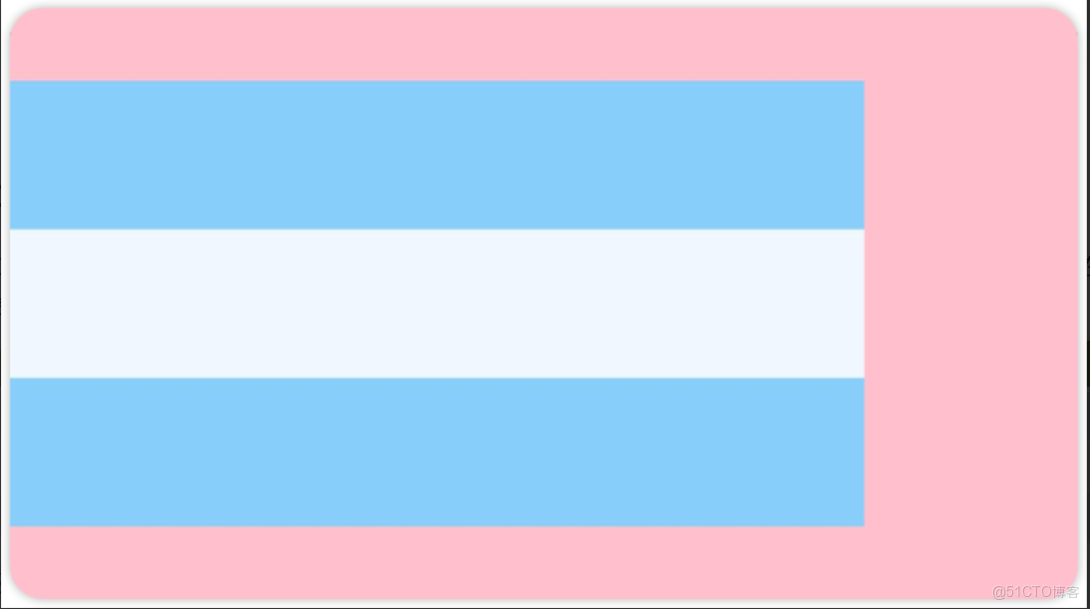
例1:Colum 子元素水平靠左對齊
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
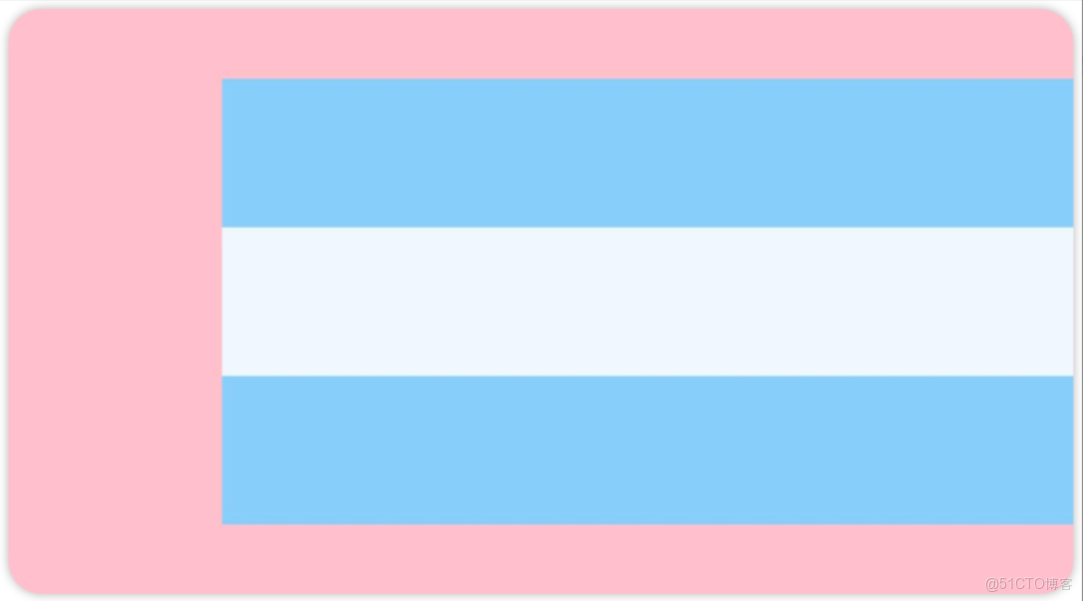
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Start) //水平靠左例2:Colum 子元素水平靠右對齊
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.End) //水平靠右例3:Colum 子元素水平居中對齊
Column() {
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Row().width('80%').height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)1.5 Row 主軸排列方式
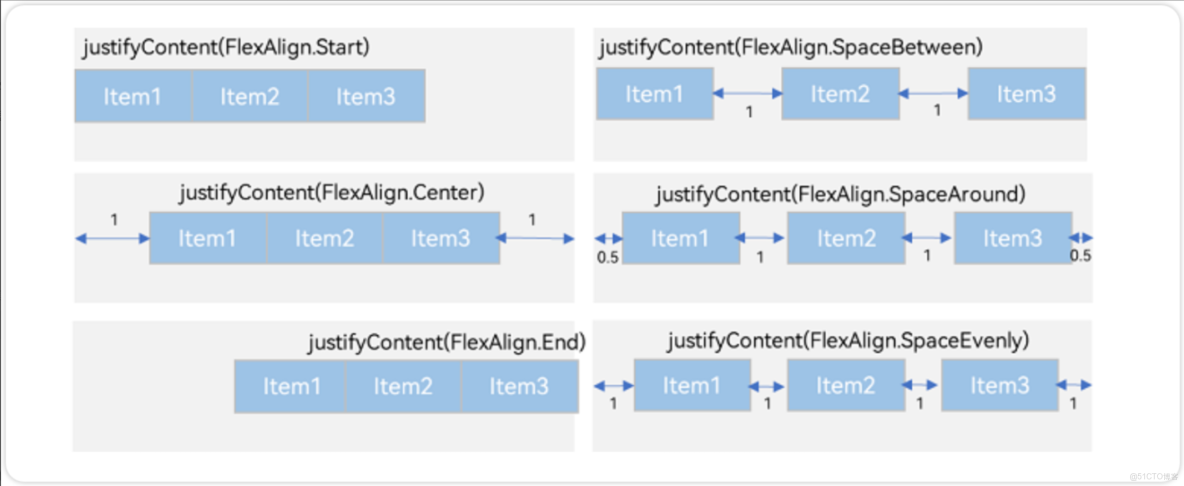
Row容器內子元素在水平方向上的排列圖
例1:水平靠左對齊
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Start)例2:水平靠居中對齊
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)例3:水平靠右對齊
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.End)例4:水平方向按照0:1:1:0設置排列間距
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)例5:水平方向按照0.5:1:1:0.5設置排列間距
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceAround)例6:水平方向按照1:1:1:1設置間距
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly)1.6 Row 交叉軸排列方式
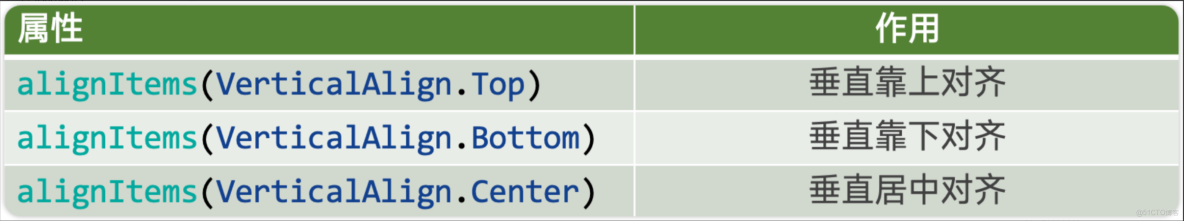
Row的主軸是水平方向,交叉軸垂直於主軸,所以交叉軸就是垂直方向;通過 alignItems屬性設置子元素在交叉軸上的對齊方式。
例1:Row 子元素垂直靠上對齊
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Top) //水平靠上例2:Row 子元素垂直靠下對齊
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Bottom) //水平靠下例3:Colum 子元素垂直居中對齊
Row({ space: 15 }) {
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#F0F8FF')
Column().width(80).height(50).backgroundColor('#87CEFA')
}
.width('100%').height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Center) //水平靠下1.7 空白填充
在線性佈局下,常用空白填充組件Blank,在容器主軸方向自動填充空白空間,達到自適應拉伸效果。Row和Column作為容器,只需要添加寬高為百分比,當屏幕寬高發生變化時,會產生自適應效果。
Column() {
Row() {
Text('Bluetooth').fontSize(18)
Blank()
Toggle({ type: ToggleType.Switch, isOn: true })
}
.backgroundColor(0xFFFFFF).borderRadius(15).width('100%')
.padding(12)
}
.width('100%').backgroundColor(0xEFEFEF).padding(20)1.8 自適應縮放
父容器尺寸確定時,使用 layoutWeight()屬性 設置子元素和兄弟元素在主軸上的權重,忽略元素本身尺寸設置,使它們在任意尺寸的設備下自適應佔滿剩餘空間。
Column() {
Row() {
Text('1').backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3).height('100%').layoutWeight(1).textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
Text('2').backgroundColor(0xD2B48C).height('100%').layoutWeight(2).textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
Text('3').backgroundColor(0xF5DEB3).height('100%').layoutWeight(3).textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}.backgroundColor(0xffd306).height('30%').width('100%')
}2.彈性佈局(Flex)
2.1 基本概念
彈性佈局和線性佈局很多基本概念都是相同的,也分為主軸和交叉軸,線性佈局能做的彈性佈局都能做。但是彈性佈局有一個特殊的效果,就是組件可以換行顯示。
● 主軸:Flex組件佈局方向的軸線,子元素默認沿着主軸排列。主軸開始的位置稱為主軸起始點,結束位置稱為主軸結束點。
● 交叉軸:垂直於主軸方向的軸線。交叉軸開始的位置稱為交叉軸起始點,結束位置稱為交叉軸結束點。
2.2 佈局方向
在Flex彈性佈局中,通過direction參數設置主軸為水平方向。默認為水平排列。
Flex({direction:FlexDirection.Row}) 水平從左往右排列
Flex({direction:FlexDirection.RowReverse}) 水平從右往左排列
Flex({direction:FlexDirection.Column}) 垂直從上到下排列
Flex({direction:FlexDirection.ColumnReverse}) 垂直從下到上排列
@Entry
@Component
struct BlankPage {
build() {
Flex({
direction: FlexDirection.Row
}) {
Text("1").width(50).height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
Text("2").width(50).height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Orange)
Text("3").width(50).height(50).backgroundColor(Color.Brown)
}
}
}2.3 對齊方式
彈性佈局的對齊方式參考線性佈局,justifyContent()用於設置主軸對齊方式、alignItems()用於設置交叉軸對齊方式。
Flex({
direction:FlexDirection.Row, //主軸方向:水平排列
justifyContent: FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly, //主軸方向對齊方式:平均分配間隙
alignItems:ItemAlign.Center //交叉軸對齊方式:居中
})2.4 佈局換行
當主軸方向上的子組件比較多時,可以讓組件換行顯示,同時還可以控制組件之間的間距、以及對其方式。需要用到下面幾個參數實現。
● 使用wrap參數實現佈局換行;
○ wrap: FlexWrap.Wrap 組件換行
○ wrap: FlexWrap.NoWrap, //換行顯示
● 通過alignContent參數設置子元素各行在交叉軸上內組件對齊方式。
○ alignContent: FlexAlign.Start 交叉軸開始對齊
○ alignContent: FlexAlign.End 交叉軸結束對齊
○ alignContent: FlexAlign.SpaceBetween 交叉軸按照0:1:1:0 分配剩餘空間
○ alignContent: FlexAlign.SpaceAround 交叉軸按照0.5:1:1:0.5 分配剩餘空間
○ alignContent: FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly 交叉軸按照1:1:1:1 分配剩餘空間
● 使用space設置子組件之間的間距;
○ main: LengthMetrics.px(20), //主軸方向組件間距
○ cross: LengthMetrics.px(20) //交叉軸方向組件簡介
Flex({
direction: FlexDirection.Row, //主軸水平排列
justifyContent: FlexAlign.Start, //主軸方向對齊方式,從左往右
wrap: FlexWrap.Wrap, //換行顯示
alignContent: FlexAlign.SpaceEvenly, //交叉軸對齊方式,在換行時才有效。
space: {
main: LengthMetrics.px(20), //主軸方向組件間距
cross: LengthMetrics.px(20) //交叉軸方向組件簡介
},
}) {
//...
}3. 層疊佈局(Stack)
3.1 基本概念
層疊佈局容器中的子元素依次入棧,後一個子元素覆蓋前一個子元素上,子元素可以疊加,也可以設置位置。
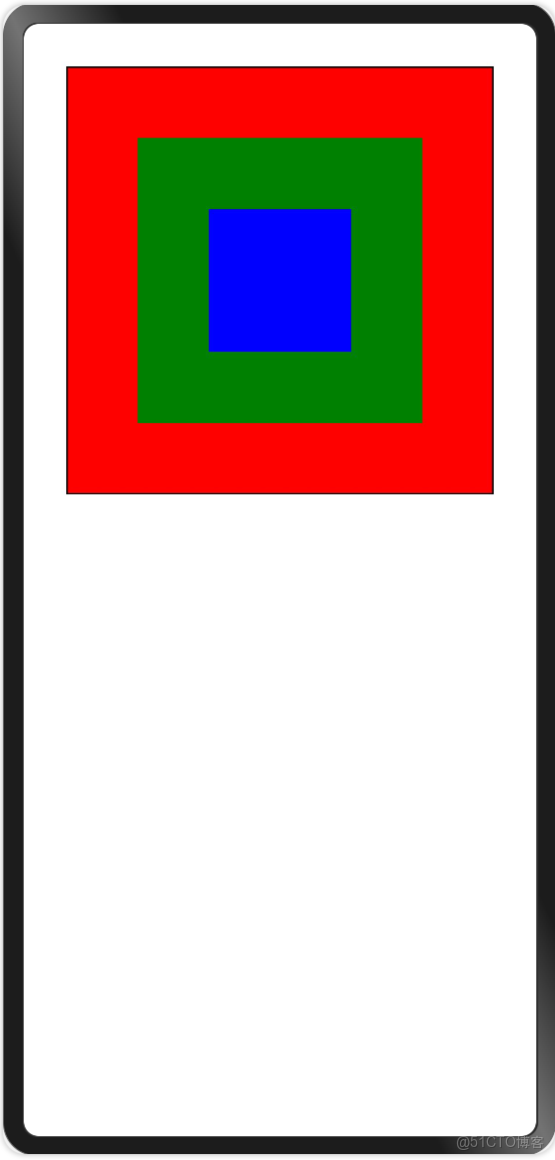
如下圖所示:第1層是紅色、第2層是綠色、第3層是藍色
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct StackExample {
build() {
Column() {
//層疊佈局內的組件的相對位置可以通過alignContent設置
Stack({ alignContent: Alignment.TopEnd }) {
//第一層
Row() {
Text('Text1').fontColor(Color.White)
}.width(300).height(300)
.backgroundColor(Color.Red)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Bottom)
//第二層
Row() {
Text('Text2').fontColor(Color.White)
}.width(200).height(200)
.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Bottom)
//第三層
Row() {
Text('Text3').fontColor(Color.White)
}.width(100).height(100)
.backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Bottom)
}.width(300).height(300).border({
width: 1,
style: BorderStyle.Solid,
color: Color.Black
})
}.width('100%').margin({ top: 30 })
}
}3.2 對齊方式
在Stack層疊佈局中子元素的對齊方式,通過alignContent參數實現。如圖下圖,支持九種對齊方式。
Stack({ alignContent: Alignment.Start }){
...
}3.3 Z序控制
Stack容器中兄弟組件顯示層級關係可以通過Z序控制的zIndex屬性改變。zIndex值越大,顯示層級越高,即zIndex值大的組件會覆蓋在zIndex值小的組件上方。
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct StackExample {
build() {
Column() {
//層疊佈局內的組件的相對位置可以通過alignContent設置
Stack({alignContent:Alignment.TopEnd}) {
//第一層
Row() {
Text('Text1')
}.width(300).height(300).backgroundColor(Color.Red)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Bottom)
.zIndex(1)
//第二層
Row() {
Text('Text2')
}.width(200).height(200).backgroundColor(Color.Green)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Bottom)
.zIndex(2)
//第三層
Row() {
}.width(100).height(100).backgroundColor(Color.Blue)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Bottom)
.zIndex(3)
}.width(300).height(300).border({
width: 1,
style: BorderStyle.Solid,
color: Color.Black
})
}.width('100%').margin({ top: 30 })
}
}