1.前言
DataBinding, 又名數據綁定,是Android開發中非常重要的基礎技術,它可以將UI組件和數據模型連接起來,使得在數據模型發生變化時,UI組件自動更新,從而節省了大量的代碼和時間。
DataBinding的原理是通過編寫XML佈局文件,在其中使用特定的標籤和語法,將UI組件和數據模型連接起來。當佈局文件被加載時,DataBinding會自動生成綁定代碼,從而將UI組件和數據模型關聯起來。
通過學習DataBinding基礎知識,可以讓你的代碼速度翻倍,提高開發效率和代碼質量。因此,如果你希望在Android開發中獲得更高的成功率和更快的發展速度,那麼請務必學習DataBinding技術,掌握其基礎知識,讓自己成為一名高效率的Android開發者!
那麼話不多説,讓我們直接直奔主題。接下來我將從實用性的角度,來逐一講解DataBinding的基礎使用,文章末尾會給出示例代碼的鏈接地址,希望能給你帶來啓發。
2.準備工作
2.1 啓用
1.DataBinding啓用
android {
dataBinding {
enabled = true
}
}2.ViewBinding啓用
android {
buildFeatures {
viewBinding true
}
}2.2 快捷方式
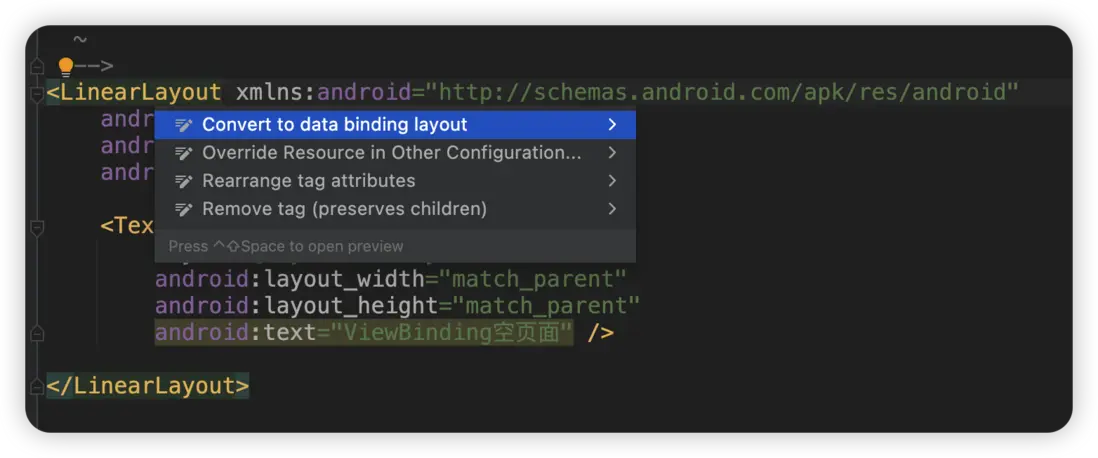
在你的佈局中找到最外層的佈局,將光標放在如圖位置。
- Windows 請按快捷鍵
Alt + 回車 - Mac 請按快捷鍵
option + 回車
3.DataBinding綁定
3.1 數據類型
通常我們在DataBinding中綁定的數據類型是ViewModel或者是AndroidViewModel,它倆都是生命週期可感知的,唯一的區別是AndroidViewModel可以獲取到應用的上下文Application。
3.2 數據創建
ViewModel的創建通常是通過ViewModelProvider進行創建和獲取。
ViewModelProvider(this).get(Xxx::class.java)而在ViewModel中,通常使用MutableLiveData作為可變UI響應數據類型。相比較LiveData而言,它開放了修改值的接口,下面是一個ViewModel的簡單例子:
class RecyclerViewRefreshState(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
val title = MutableLiveData("RecyclerView的刷新和加載更多演示")
val isLoading = MutableLiveData(false)
val sampleData = MutableLiveData<List<SimpleItem>>(arrayListOf())
val loadState = MutableLiveData(LoadState.DEFAULT)
val layoutStatus = MutableLiveData(Status.DEFAULT)
}當然了,如果你有一個LiveData會隨着一個或多個LiveData的變化而變化,這個時候你可能就需要使用MediatorLiveData,即合併LiveData。
這裏我簡單利用MediatorLiveData實現一個組合的LiveData--CombinedLiveData。
open class CombinedLiveData<T>(vararg liveData: LiveData<*>, block: () -> T) :
MediatorLiveData<T>() {
init {
value = block()
liveData.forEach {
addSource(it) {
val newValue = block()
if (value != newValue) {
value = newValue
}
}
}
}
}
fun <R, T1, T2> combineLiveData(
liveData1: LiveData<T1>,
liveData2: LiveData<T2>,
block: (T1?, T2?) -> R
) = CombinedLiveData(liveData1, liveData2) { block(liveData1.value, liveData2.value) }這個時候,我們就可以通過combineLiveData方法將兩個LiveData組合起來,形成一個新的LiveData。下面我簡單給出一個示例代碼:
class CombineLiveDataState : DataBindingState() {
val userName = MutableLiveData("小明")
val userAge = MutableLiveData(20)
val userInfo = combineLiveData(userName, userAge) { name, age ->
"${name}今年${age}歲了!"
}
fun onAgeChanged() {
userAge.value = userAge.value?.plus(1)
}
}這裏變化了userAge的值後,userInfo也會隨着一起變化。
3.3 視圖綁定
一般我們使用DataBindingUtil進行視圖綁定操作。綁定操作我們可分為:綁定Activity、綁定Fragment和綁定View。
- 綁定Activity
使用DataBindingUtil.setContentView方法進行綁定。
fun <DataBinding : ViewDataBinding> bindActivity(
activity: ComponentActivity,
layoutId: Int
): DataBinding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView<DataBinding>(activity, layoutId).apply {
lifecycleOwner = activity
}- 綁定Fragment
使用DataBindingUtil.inflate方法進行綁定。
fun <DataBinding : ViewDataBinding> bindFragment(
fragment: Fragment,
inflater: LayoutInflater,
layoutId: Int,
parent: ViewGroup? = null,
attachToParent: Boolean = false
): DataBinding = DataBindingUtil.inflate<DataBinding>(inflater, layoutId, parent, attachToParent).apply {
lifecycleOwner = fragment.viewLifecycleOwner
}- 綁定View
使用DataBindingUtil.bind方法進行綁定。
fun <DataBinding : ViewDataBinding> bindView(
view: View,
viewLifecycleOwner: LifecycleOwner,
): DataBinding = DataBindingUtil.bind<DataBinding>(view).apply {
lifecycleOwner = viewLifecycleOwner
}【⚠️特別注意事項⚠️️】
DataBinding綁定的時候,一定要給ViewDataBinding賦值LifecycleOwner, 否則ViewModel中的LiveData發生數據改變後,則不會通知UI組件進行頁面更新。
3.4 數據綁定
對ViewModel的綁定有兩種寫法。
- 直接使用
ViewDataBinding.variableId = xxx直接賦值。
val mainState = ViewModelProvider(this).get(MainState::class.java)
activityMainbinding.state = mainState- 使用
ViewDataBinding.setVariable(int variableId, @Nullable Object value)進行賦值。
val mainState = ViewModelProvider(this).get(MainState::class.java)
binding.setVariable(BR.state, mainState)這兩者的唯一區別在於,第一種需要知道ViewDataBinding的具體類型,而第二種是ViewDataBinding自身的方法,無需知道ViewDataBinding的具體類型。
一般來説在框架中使用到泛型未知ViewDataBinding具體類型的時候,都會使用第二種方式進行綁定,可以説第二種方式更通用一些。
4.基礎使用
4.1 點擊事件綁定
1.無參響應函數:
fun onIncrement() {
// 方法體
}android:onClick="@{() -> state.onIncrement()}"2.接口變量響應函數
注意,這裏變量的類型應該是View.OnClickListener接口。
val onClickDecrement = View.OnClickListener {
// 方法體
}android:onClick="@{state.onClickDecrement}"3.有參響應函數
fun onReset(view: View) {
// 方法體
}// 第一種寫法
android:onClick="@{(view) -> state.onReset(view)}"
// 第二種寫法
android:onClick="@{state::onReset}"4.2 @BindingAdapter自定義屬性
所有註解的功能都是基於XML屬性值為DataBinding表達式才生效(即@{})
使用@BindingAdapter進行控件自定義屬性綁定的時候,一定要使用 "@{}" 進行賦值,這一點非常重要!!!
- 頂級函數實現
// Kotlin拓展函數式寫法, 推薦使用
@BindingAdapter("customTitle")
fun TextView.setCustomTitle(title: String) {
text = "標題1: $title"
}
// 第一個參數必須是view的子類
@BindingAdapter("customTitle1")
fun setCustomTitle1(view: TextView, title: String) {
view.text = "標題2: $title"
}
// 多個參數進行綁定,requireAll=true,代表兩個參數都設置了才生效,默認是true.
// 如果requireAll為false, 你沒有填寫的屬性值將為null. 所以需要做非空判斷.
@BindingAdapter(value = ["customTitle", "customSize"], requireAll = true)
fun TextView.setTextContent(title: String, size: Int) {
text = "標題3: $title"
textSize = size.toFloat()
}【⚠️特別注意事項⚠️️】
很多時候,很多新手在寫DataBinding的時候,經常會漏掉"@{}",尤其是用數字和Boolean類型的值時。就比如我上面設置的customSize屬性,類型值是Int型,正確的寫法應該是下面這樣:
- 正確的寫法
<TextView
style="@style/TextStyle.Title"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
app:customSize="@{25}"
app:customTitle="@{state.title}" />- 常見錯誤的寫法
<TextView
style="@style/TextStyle.Title"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
app:customSize="25"
app:customTitle="@{state.title}" />上述錯誤的寫法,運行後編譯器會報錯AAPT: error: attribute customSize (aka com.xuexiang.databindingsample:customSize) not found.。
所以當我們寫DataBinding的時候,如果出現AAPT: error: attribute xxx (aka com.aa.bb:xxx) not found.,十有八九是你賦值漏掉了"@{}"。
- 單例類+@JvmStatic註解
object TitleAdapter {
@JvmStatic
@BindingAdapter("customTitle2")
fun setCustomTitle2(view: TextView, title: String) {
view.text = "標題4: $title"
}
}4.3 @BindingConversion自定義類型轉換
作用:在使用DataBinding的時候,對屬性值進行轉換,以匹配對應的屬性。
定義:方法必須為公共靜態(public static)方法,且有且只能有1個參數。
下面我給一個簡單的例子:
1.對於User類,age的類型是Int。
data class User(
val name: String,
val gender: String? = "男",
val age: Int = 10,
val phone: String? = "13124765438",
val address: String? = null
)2.使用@BindingAdapter定義了age的類型卻是String。
@BindingAdapter(value = ["name", "age"], requireAll = true)
fun TextView.setUserInfo(name: String, age: String) {
text = "${name}今年${age}歲"
}3.這時候使用DataBinding的時候,👇的app:age="@{state.user.age}"會編譯報錯,提示類型不匹配。
<TextView
style="@style/TextStyle.Title"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
app:name="@{state.user.name}"
app:age="@{state.user.age}"/>4.這個時候,我們就可以使用@BindingConversion自定義類型轉換: Int -> String, 這樣👆的代碼就不會編譯出錯了。
@BindingConversion
fun int2string(integer: Int) = integer.toString()4.4 @{}中表達式使用
- 常用運算符
- 算術 + - / * %
- 字符串合併 +
- 邏輯 && ||
- 二元 & | ^
- 一元 + - ! ~
- 移位 >> >>> <<
- 比較 == > < >= <=
- 三元 ?:
- Array 訪問 []
<TextView
android:text="@{@string/app_name + @string/app_name}"/><TextView
android:visibility="@{!state.user.phone.empty ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE}"/>- 常用轉義字符
- 空格: \
- <小於號: \<
- \>大於號: \>
- &與號: \&
<TextView
android:visibility="@{!state.user.phone.empty && state.user.age > 5 ? View.VISIBLE : View.GONE}"/>- 資源使用
@string @color @drawable @dimen @array
<TextView
style="@style/TextStyle.Content"
android:text="@{@string/user_format(state.user.name, state.user.gender)}"
android:textColor="@{@color/toast_error_color}"
android:textSize="@{@dimen/xui_config_size_content_text_phone}" />- 集合
集合不屬於java.lang*下, 需要導入全路徑。集合使用[]進行訪問。
<data>
<import type="java.util.List"/>
<import type="android.util.SparseArray"/>
<import type="java.util.Map"/>
<variable name="list" type="List<String>"/>
<variable name="sparse" type="SparseArray<String>"/>
<variable name="map" type="Map<String, String>"/>
</data><TextView
android:text="@{`key: key1, value:` + map[`key1`]}" />- 引用類的靜態方法
kotlin中定義靜態方法,一定要在方法上加上@JvmStatic,否則將無法成功引用。
(1) 定義方法
object AppUtils {
@JvmStatic
fun getAppInfo(context: Context?) =
context?.let {
"packageName: ${it.packageName}, \nversionName: ${
it.packageManager.getPackageInfo(
it.packageName,
0
).versionName
}"
}
}(2) 導入方法所在類路徑
<import type="com.xuexiang.databindingsample.utils.AppUtils"/>(3) 引用方法
<TextView
android:text="@{AppUtils.getAppInfo(context)}"/>- 空值合併運算符
空值合併運算符 ?? 會取第一個不為 null 的值作為返回值。
<TextView
android:text="@{`地址:` + (state.user.address ?? `默認地址`)}"/>等價於
<TextView
android:text="@{state.user.address != null ? state.user.address : `默認地址`)}"/>4.5 include 和 ViewStub
在主佈局文件中將相應的變量傳遞給 include 佈局,需使用自定義的 bind 命名空間將變量傳遞給 (include/ViewStub), 從而使兩個佈局文件之間共享同一個變量。
例如,在include中定義的變量id是:<variable name="user" type="...User"/>, 那麼就使用 app:user="@{state.user}" 來綁定數據,與variable定義的name保持一致。
- include
<include
android:id="@+id/include_layout"
layout="@layout/include_user_info"
app:user="@{state.user}" /><layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
<variable
name="user"
type="com.xuexiang.databindingsample.fragment.basic.model.User" />
</data>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginVertical="16dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_title"
style="@style/TextStyle.Content"
android:userInfo="@{user}" />
</LinearLayout>
</layout>如果你想在頁面中獲取include引用佈局的某個控件時,你需要給include設置資源id,然後通過它去訪問引用佈局中的控件,就以👆的例子為例,如果我想訪問佈局中的TextView,我們可以這樣寫:
binding?.includeLayout?.tvTitle?.text = "用户信息"【⚠️特別注意事項⚠️️】
這裏需要注意的是,include標籤,如果設置了layout_width和layout_height這兩個屬性,那麼佈局就是由include外層設置的layout屬性生效,內層屬性不生效。
如果include標籤沒有設置layout_width和layout_height這兩個屬性,那麼就是由include引用的佈局內層設置的layout屬性生效。
舉個例子,如果把👆設置的include改成下面這樣:
<include
layout="@layout/include_user_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="24dp"
app:user="@{state.user}" />那麼@layout/include_user_info加載的佈局,距離上部的距離就是24dp,而不是16dp。
- ViewStub
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/user_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:layout="@layout/viewstub_user_info"
app:info="@{state.user}" /><layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<data>
<variable
name="info"
type="com.xuexiang.databindingsample.fragment.basic.model.User" />
</data>
<TextView
style="@style/TextStyle.Content"
android:userInfo="@{info}" />
</layout>因為ViewStub功能是延遲加載引用的佈局,當我們需要讓其進行加載的時候,我們需要通過ViewStub的資源id獲取到ViewStub,然後進行inflate,示例代碼如下:
binding?.userInfo?.viewStub?.inflate()最後
以上就是本次DataBinding基礎使用的全部內容,後面我還會分享DataBinding的進階使用教程,感興趣的小夥伴可以點擊頭像關注我哦~
本文的全部源碼我都放在了github上, 感興趣的小夥伴可以下下來研究和學習。
項目地址: https://github.com/xuexiangjys/DataBindingSample
我是xuexiangjys,一枚熱愛學習,愛好編程,勤于思考,致力於Android架構研究以及開源項目經驗分享的技術up主。獲取更多資訊,歡迎微信搜索公眾號:【我的Android開源之旅】